Introduction
Conductivity is a physical property of any material. It shows the ability to transfer the electric charge of heat in any object. The conductivity of water is the measure of passing heat and electricity from it. If it is studied in terms of heat transfer then it will be the thermal conductivity of water. But if we focus on the transfer of electric charge then it says electric conductivity. Water has positive behavior towards both heat and electricity transfer. So we can say it has positive conductance as well as a positive heat transfer coefficient.
Electric conductivity
Electric conductivity is termed as the ability of the material to pass electric current from one point to another. The transfer of electricity occurs due to the presence of free electrons. In the case of water, the current carrying capacity depends on the ions present in the water. These ions come from the electrolytes present in the water. Electrolytes are present in form of different minerals in pure water. More electrolytes mean more ions generation which results in high conductivity. So it can be said that pure water which has no minerals present is a bad conductor of electricity. But if we add some amount of salt in pure water then it will become conductive to electricity because it can produce ions and transfer electrons. SI unit of the conductivity of water is Siemens per meter. Figure-1 shows the current flow between the anode and cathode after mixing the NaCl (electrolyte) in pure water. NaCl breaks into Na+ and Cl- ions and current will flow because of the movement of these ions.
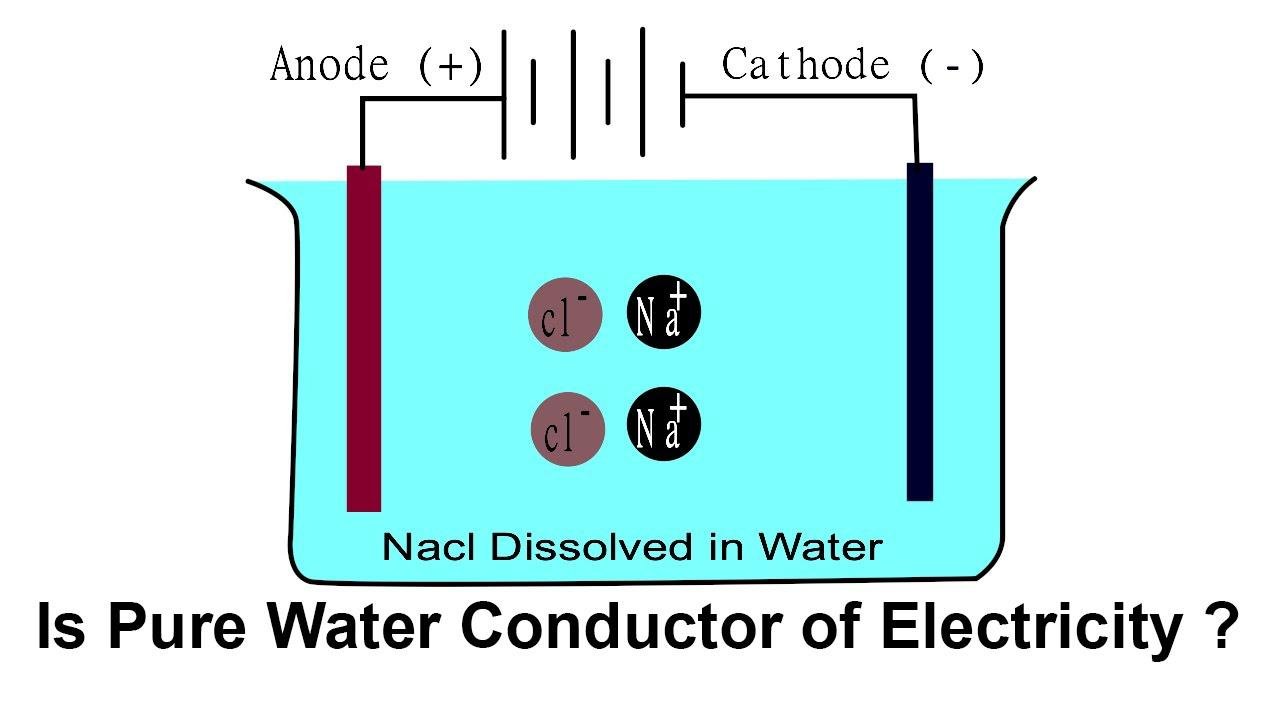
Fig-1
Thermal conductivity
Heat conductivity or thermal conductivity of any material is the ability of a material to transfer heat from one point to another. High heat conductivity means high heat transfer occurs in the material. SI unit of thermal conductivity is W/m-K. The value of thermal conductivity is different for every material so it is a property of the material. The materials having high thermal conductivity are used as heat transfer agents and heat sink whereas; the materials having low thermal conductivity are used as insulators. For example on motorbike engines aluminum (Having high thermal conductivity) fins are used on the outer surface to increase the rate of heat transfer from the engine to the atmosphere. Warm cloths having wool which has low thermal conductivity are used as an insulator and reduce the rate of heat transfer from our body to the atmosphere. Thus we feel warm in the winter. The heat conductivity of water is 0.598 W/m-K. So water is a bad conductor of heat.
Variation of the conductivity of water with temperature
Conductivity of water increased with increasing temperature. This is because of the increasing kinetic energy of the ions due to the heating of water. This results in ions moving faster and conducting their bearing charge faster which leads to an increase in conductivity.
Specific Conductance
At 25 °C, conductivity is determined using specific conductance. Since the conductivity value is influenced by the water’s temperature, stating the conductivity at a temperature of roughly 25° C makes it simple to compare the results. Basically, the Specific conductance is expressed in µS/cm at a temperature of 25 °C. When measuring electrical conductivity at a temperature of 25 °C, the result is referred to as the specific conductance. Additionally, the measurement is known as the temperature coefficient if it is made at various temperatures and then corrected to 25 °C.
Recommended Articles:
Concave Mirror And Convex Mirror: Introduction, Types, Difference, And Applications
Concave lens: Introduction, Terminology, Image, And Application
Concentration of Ore: Introduction, Types and Properties of Ore
Conduction of Electricity in liquids
Conduction Of Electricity: Introduction, Liquids, Substances, And Compounds
Electric conductivity is termed as the ability of the material to pass electric current from one point to another. SI unit of the conductivity of water is Siemens per meter. Electric and thermal conductivity both are increased with increasing temperature. This is due to an increase in the kinetic energy of water because of the temperature increase. Which leads to faster molecular movement? That’s why the movement of in becomes faster which leads to an increase in the electric conductivity. Similarly increasing molecular movement also leads to an increase in the thermal conductivity of water. thermal conductivity of water is 0.598 W/m-K approx. Conductivity of Water FAQs
Explain electric conductivity in brief.
What is the SI unit of electric conductivity?
Discuss the effect of temperature on the thermal and electric conductivity of water.
what is the thermal conductivity of water?
