The purpose of this article is to understand the concave lens. You will also find much other important information that you need to know. For a better understanding of the concave lens, we will go through some practical applications where the concave lens is very useful.
Introduction
Humans have been able to do some pretty amazing things with lenses for years. As people learned that they could do a variety of tasks using variously shaped lenses, the ways and purposes in which lenses were employed started to expand over the centuries. They might be used to make little objects appear larger and hazy objects appear clear, in addition to making distant objects seem closer (like the telescope). Two fundamental lens types are used to do these tasks: convex and concave lenses. A lens is referred to as concave if at least one of its surfaces curves inward. It is a divergent lens, which means that light rays that have been bent through it are spread out.
Terminology related to lens
Pole
For the spherical lens pole (p) is the center or middle point of the lens.
Center of curvature
Generally spherical lenses is cut from a sphere. So the center of curvature is the sphere’s center, from where the mirror is made.
Main axis
These are the lines that cross the lens’s pole and its center of curvature.
The principal focus
It is the location at which a converging or diverging narrow beam of light occurs.
Focal length
The distance between the focus and the mirror’s poles is known as the focal length (f).
Image formation by a concave lens
The image formation by a concave lens is summarized below.
The object placed at infinity
When an object is placed at infinity the image is formed at the focus of the lens. It will be virtual and a point-size image.
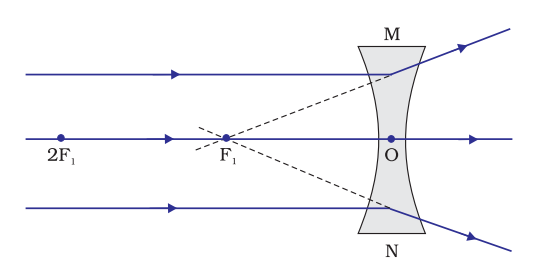
Fig- 1
The object placed between the optical center O and the infinity
When the object is placed at a finite distance between the optical center and infinity the image forms at the first focus. The size of the image is smaller than the real object and it is virtual.
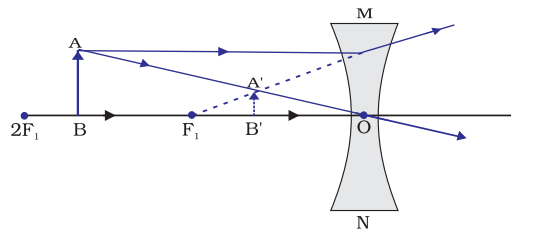
Fig- 2
Some important formulas of the concave lens
Lens formula
The type and location of the image created by the concave lens are determined using the lens formula. The lens formula looks like the following
Here, f = focal length of lens
v = distance of the image from the optical center
u = distance of the object from the optical center
Magnification formula
The magnification formula shows how big the image is formed in comparison of a real object.
Magnification, =
Application of concave lens
The concave lens has a wide area of application. Some of them are the following
- In telescopes and binoculars, concave lenses are used to magnify objects.
- Myopia, is most frequently treated with concave lenses.
- Security tools like peepholes or door viewers provide a comprehensive view of everything beyond walls or doors. To reduce the size of the items and provide a wider view of the object or region, a concave lens is utilized.
Recommended Articles:
Compressive Stress: Introduction, Unit, formula, Dimension And Strength
Compton Wavelength: Introduction, Equation, Importance, And Effect
Concave And Convex Mirrors Spherical Mirrors
Concave Convex Lenses: Introduction, Difference, And Applications
Concave Mirror And Convex Mirror: Introduction, Types, Difference, And Applications
The magnification of the lens is the comparison of the size of the image and the size of the object. In a telescope, there is concave lens is used. The radius of the sphere from which the lens is produced is known as the radius of curvature. Concave lens is formed a virtual image that is smaller than a real object. Concave lens FAQs
What is the magnification of the lens?
Which type of lens is used in the telescope?
What is the radius of curvature?
What type of images are formed with the concave lens?