Introduction
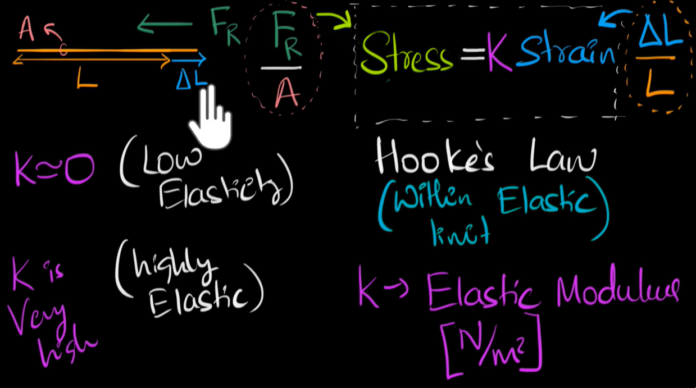
Young’s Modulus is defined as the stress along the longitudinal axis of the specimen tested, the ratio of the stress applied to the material along the material, and the strain that is measured on the same axis of stress.
Another name for Young’s modulus is the tensile modulus or modulus of elasticity or elastic modulus.
The SI unit is Pascal (Pa)
Hooke’s law: When a tensile or stretching force is applied to any object to such an extent that its behaviour can be obtained by the curve of stress-strain in the region of elastic deformation.
Factors on which it is dependent
- Material
- Dimensions of the object i.e. length and thickness.
What Is Stress?
It is defined as the force per unit area of plastic.
Its unit is Nm-2 or Pa.
Its symbol is sigma.
Stress = F/A
Stress in Newtons per square metre or Pascals
F is a force in Newton
A is a cross-sectional area.
What Is a Strain?
Strain is an extension per unit length. Since it is a ratio of lengths.
It has no units.
Strain= ∆L/L0 [ ∆L = L – L0 ]
L0 = original length of a bar that is being stretched.
L = Length after it has been stretched.
∆L = Extension of the bar
L-L0 = difference between two different lengths.
How does the stiffness of different materials compare to young’s modulus?
By using measurements of tensile stress and tensile strain. The stiffness of different materials is compared by Young’s modulus (E).
E is constant and it does not change for a given material.
E= stress/ strain
Application of Young’s Modulus Elastic Modulus
- The mechanical property of materials is important because it helps one to understand the behaviour of the materials which helps in the development of new products and by which existing ones can be improved.
- On a minute scale, some products contain biological and nonbiological microparticles. Through understanding the mechanical behaviour in manufacturing and maximising performance capabilities.
- From bridges and buildings to vehicles, Young’s modulus is useful.
Unit of Young’s Modulus Elastic Modulus
The unit of Young’s modulus is pressure units.
The most commonly used is Pascal’s SI unit.
Pounds per square inch:- depending on industry and sometimes the geographical location.
Some material’s values of the modulus of elasticity (Young’s modulus)
- Diamond:- 1050 – 1200 GPa it is highly rigid
- Carbine:- highest known young modulus 32100 GPa is the least elastic or most rigid known at the moment.
- Rubber:- low Young’s modulus that is 0.01 to 0.1 GPa it has high elasticity.
Factors That Affect Young’s Modulus
Young’s modulus is closely related to the binding energies of the atoms. Binding forces are higher for melting point materials.
Temperature:- as the material increases its atomic vibration it decreases its energy to further transfer it to other atoms.
Presence of impure atoms:– Non-metallic inclusions, dislocations, and defects. All of these can result in the weakening or strengthening of a material.
How to Measure Young’s Modulus?
For measuring Young’s modulus of different materials.
- Brittle material:- They can withstand a lot of stress so they are very strong, they don’t stretch and break easily.
- Ductile materials:- The stress-strain relationship is linear; they have larger elastic regions, and at first, linearity breaks down; later material can not return to its original position or form.
- Plastic materials:- They are not very strong but have a quality that can withstand a lot of strain.
Calculating Young’s Modulus i.e. Force Exerted by Stretched Material
Under specific strain:-
F= EA∆L/L0
F= Force exerted
∆L= material contracted or stretched.
Applying Hooke’s Law
F= ( EA/ L0) ∆L = kx
When it comes to saturation:-
k= EA/ L0
x= ∆L
The elasticity of coiled springs comes from the shear modulus and not Young’s modulus.
Recommended Articles:
Brief Introduction of Zener Diode
Important notes on Derivation of Bulk modulus
Thin Lens Formula for Concave and Convex Lens
The Gold Mine of Physics: Deriving Important Physics Formulas
The Working of a Boiler: How Does It Work?
Young's modulus depends upon temperature and pressure and in the essence of stiffness. Diamond has the highest Young's modulus. Yes, Young's modulus is positive under static forcing conditions. Yes, Young's modulus is only for solids, not for liquids and gases. For this reason, steel is more elastic than rubber. Fluids do not have Young's modulus because Young's modulus is only of the material which has fixed shapes and sizes.Young's Modulus Elastic Modulus FAQs
What are the factors that Young's modulus depends on?
Which material has the highest Young's modulus?
Is Young's modulus positive?
Is Young's modulus only for solids?
Why do fluids not have Young's modulus?