Introduction
Volcanic eruptions are one of the most powerful and destructive natural events on earth. They have been studied for centuries to understand the physical and chemical processes behind them. Through an analysis of the physics involved, scientists have been able to gain insight into the mechanisms behind the eruptions and the potential for their mitigation. By understanding the physics of a volcanic eruption, we can prepare for potential disasters and mitigate the damage they can cause. In this article, we will explore the physics behind a volcanic eruption and how it can be studied and understood.
What is a volcanic eruption?
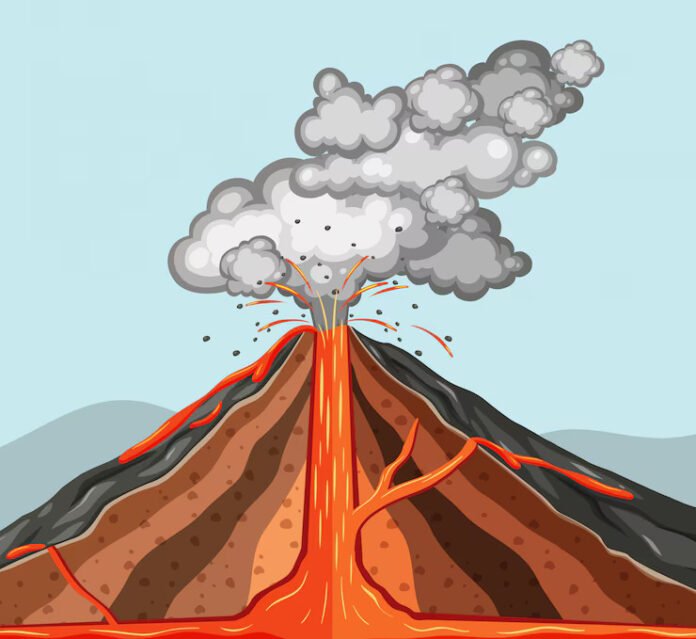
A volcanic eruption is a natural event that occurs when molten rock, ash, and other materials are released from a volcano. During an eruption, the magma, which is the molten rock beneath the surface of the Earth, is forced up through the volcano’s vent. This process is accompanied by the release of gases, such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide, and steam.
The eruption can be explosive, with lava and other materials being ejected into the air, or it can be effusive, with lava slowly flowing out of the volcano. Volcanic eruptions can be very destructive, as they can cause landslides, flash flooding, and severe air pollution. Moreover, they can also cause significant damage to infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings.
Types of volcanic eruptions
The type of eruption that accompanies a volcanic event is determined by several factors, such as the amount of pressure and the type of magma involved. There are four main types of volcanic eruptions: Hawaiian, Strombolian, Vulcanian, and Plinian.
- The Hawaiian type of volcanic eruption is characterized by a low-level, steady flow of lava. This type of eruption is usually not very explosive, and the lava flows from the volcano at a slow pace.
- The Strombolian type of volcanic eruption is characterized by a series of short and explosive eruptions. The eruption is usually accompanied by lava fountains and bombs, which are large chunks of solidified lava.
- The Vulcanian type of volcanic eruption is characterized by a series of strong explosive eruptions. The eruption can be accompanied by a large amount of lava, but it is usually not as voluminous as the lava emitted during the Hawaiian type of eruption.
- The Plinian type of volcanic eruption is characterized by a series of very powerful and explosive eruptions. The Plinian type of volcanic eruption is usually very destructive and can cause hazardous conditions.
The causes of volcanic eruptions
What causes volcanic eruptions? There are a variety of factors that can contribute to volcanic activity, but here are some of the most common causes of volcanic eruptions.
- Volcanic eruptions happen due to the movement of tectonic plates. The Earth’s crust is made up of several large pieces of rock, known as tectonic plates, that move and interact with one another. When two plates collide, one of them can be forced underneath the other, forming a subduction zone. This process often causes the molten rock to be forced upward and ejected out of the volcano, resulting in an eruption.
- When rocks and sediments are heated by the Earth’s mantle, they can become hot enough to melt and form magma. This magma is then forced through cracks and fissures in the Earth’s surface, resulting in an eruption.
- When a volcano is overfilled with magma, it can cause an eruption. As magma builds up pressure beneath the surface of the volcano, it can eventually force its way out, resulting in an eruption.
- When a volcano is located near a lake or other large body of water, the pressure of the water can cause an eruption. The water can cause the pressure of the magma to build up, resulting in an explosive eruption.
- When a volcano is located in a region of intense seismic activity, it can cause an eruption. Earthquakes and other seismic events can cause cracks in the Earth’s surface, allowing magma to escape and resulting in an eruption.
- When a volcanic region has been dormant for a long period, a sudden increase in earthquakes or other seismic activity can cause an eruption. This is because seismic activity can cause magma to move and become more pressurized, resulting in an eruption.
- When a large amount of volcanic ash is released into the atmosphere, it can cause an eruption. The ash can block the flow of magma, resulting in a buildup of pressure and an explosive eruption.
The impact of a volcanic eruption
Volcanic eruptions can cause a variety of impacts that can range from minor to disastrous. Here are a few impacts of volcanic eruptions:
- The first impact of a volcanic eruption is the release of ash and gas into the atmosphere. These materials can cause significant air pollution and can even disrupt air travel.
- The release of lava can be incredibly destructive. Large lava flows can destroy homes and businesses, bury entire cities, and have devastating effects on the landscape.
- A volcanic eruption is the release of hot gases and ash. These gases can cause significant respiratory problems for anyone in the vicinity and can be especially dangerous for those with pre-existing conditions.
- Volcanic eruption is the release of seismic waves. These waves can cause significant ground shaking and can cause buildings and other structures to collapse.
- Volcanic eruption is the release of toxic gases such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide. These gases can be deadly to anyone in the vicinity and can cause significant long-term health problems.
Recommended Articles:
What is Vt Graphs? Definition, Case and Formula
Wave Function – Definition, Equation, Function and Mechanics
Wave Theory Of Light – History, Theory, Principle & Types
Waves I Definition, Types, Characteristics and Properties
Weathering Types I Physical, Chemical & Biological
Volcano Eruption FAQs
Which is the largest volcano in India?
Barren Island Volcano, is located off the coast of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
How can people prepare for a volcanic eruption?
People can prepare for a volcanic eruption in the following ways:
Stay informed about volcanic activity in the area
Follow the instructions of local authorities
Prepare an emergency kit
Familiarize yourself with evacuation routes
Know where the safe areas are
Which is the silent volcano in India?
Dhinodhar Hill
How does a volcano eruption affect the environment?
Volcano eruptions affect the environment in the following ways:
Increased air pollution from ash and volcanic gases
Contamination of water source
Release of toxic metals and minerals into the air and water
Increased risk of flooding and landslides
What are the 3 main effects of volcanic eruptions?
The 3 main effects of volcanic eruptions are:
Production of ash and other airborne particles
Release of gases and volatiles
Generation of seismic waves and tremors