Introduction
If you’re an electronics enthusiast or working in the field, you may have come across the term “VI Characteristics.” But what exactly are VI Characteristics, and why are they important? In this article, we’ll delve into the concept of VI Characteristics and explore its various applications and uses.
What are VI Characteristics?
VI Characteristics, also known as Voltage-Current Characteristics, refer to the relationship between voltage and current in a circuit or electronic device. It tells us how the current flowing through the circuit changes in response to a change in voltage. In other words, it shows us how a circuit or device behaves under different voltage conditions.
What is the need for VI Characteristics?
VI Characteristics are essential because they help us understand the performance of a circuit or device under different voltage conditions. They can also help us design and optimize circuits and devices for specific applications. For example, if we want to design a power supply, we can use VI Characteristics to determine the voltage and current requirements of the circuit and choose the appropriate components.
Where is the concept of VI Characteristics used?
VI Characteristics are used in many applications, including power supplies, amplifiers, and other electronic devices. They are also commonly used in the analysis and design of circuits and devices, as well as in testing and debugging.
How to plot VI Characteristics?
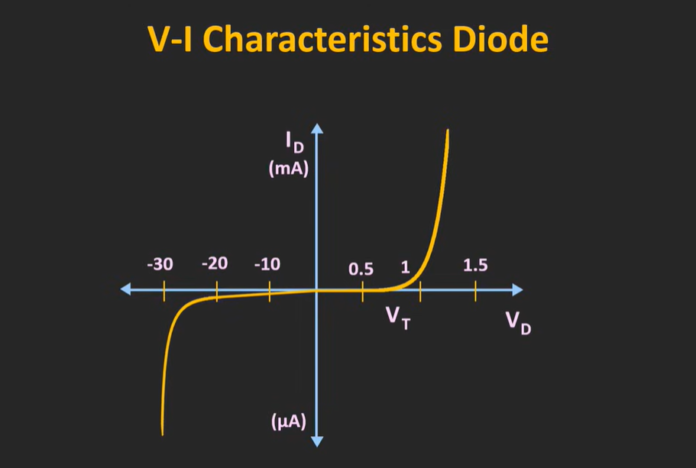
To plot VI Characteristics, we need to measure the current flowing through a circuit or device at different voltage levels. The current can be measured using an ammeter and voltage can be measured by a voltmeter. We can then plot the measured values on a graph, with the voltage on the x-axis and the current on the y-axis. This will give us a graphical representation of the VI Characteristics of the circuit or device.
Practical application of VI Characteristics
VI Characteristics have many practical applications including:
- Designing power supply circuits: The VI Characteristics of a power supply circuit can help determine the appropriate components and optimize the design for efficiency and reliability. For example, by understanding the voltage and current requirements of the load, we can choose the appropriate transformer, rectifier, and filter components to meet those requirements.
- Amplifier design: The VI Characteristics of an amplifier can help us understand its performance and choose the appropriate components for a given application. For example, by plotting the VI Characteristics of an amplifier, we can determine its gain, input impedance, and output impedance, which can in turn help us choose the appropriate load for the amplifier and optimize its performance.
- Testing and debugging: By measuring the VI Characteristics of a circuit or device, we can identify any issues or problems and troubleshoot them effectively. For example, if the VI Characteristics of a circuit are not as expected, we can use this information to diagnose the problem and fix it.
- Characterizing electronic components: The VI Characteristics of electronic components, such as transistors, diodes, and capacitors, can help us understand the quality of their performance and choose the appropriate components for a given application.
- Optimizing circuit performance: By understanding the VI Characteristics of a circuit, we can optimize its performance for a specific application. For example, we can use VI Characteristics to choose the appropriate components and design the circuit to meet specific voltage and current requirements.
- Modeling and simulation: The VI Characteristics of a circuit or device can be used to build models and perform simulations to predict its performance under different operating conditions. This can be useful for design and analysis purposes.
Read Popular Articles
Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
Different Ways of Taking Food or Indigestion in Human
To Find The Surface Tension Of Water By Capillary Rise Method
To Find Image Distance For Varying Object Distances Of A Convex Lens With Ray Diagrams
There is no specific formula for VI Characteristics, as they depend on the particular circuit or device being analyzed. To plot VI Characteristics, we need to measure the current flowing through the circuit or device at different voltage levels and plot the values on a graph. Linear VI Characteristics refer to a relationship between voltage and current that is proportional. This means that the current increases or decreases at a constant rate as the voltage changes. On the other hand, non-linear VI Characteristics refer to a relationship between voltage and current that are not linearly proportional to each other. This means the current does not change at a constant rate as the voltage changes. VI Characteristics can vary significantly depending on the type of circuit or device being analyzed. For example, a resistor has a linear VI Characteristic, while a diode has a non-linear VI Characteristic. The VI Characteristics of a transistor or amplifier may also vary depending on the specific design and operating conditions. VI Characteristics can provide helpful information about the performance of a circuit or device, but they are not always a reliable predictor. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions can all affect the VI Characteristics of a circuit or device. It is important to consider these factors when using VI Characteristics to predict performance. To measure VI Characteristics, you will need an ammeter and a voltmeter. You can use these to measure the current flowing through the circuit or device at different voltage levels. You can then plot the values on a graph to obtain a graphical representation of the VI Characteristics.VI Characteristics FAQs
What is the formula for VI Characteristics?
What is the difference between linear and non-linear VI Characteristics?
How do VI Characteristics differ for different types of circuits and devices?
Can VI Characteristics be used to predict the performance of a circuit or device?
How do I measure VI Characteristics?