The electric field is a vector field that can be associated with each point in space and exerts a force on a positive test charge at rest at that point. The electric field is generated by time-varying magnetic fields and the electric charge. Electric field intensity depends only on the source charge and not on other charges that are present in the surrounding.
Electric Field and Electric Field Intensity
Mathematically, the electric field is a vector field that can be associated with each point in space and exerts a force on a positive test charge at rest at that point while the electric field intensity at a point can be defined as the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point.
The electric field is a vector quantity which means it has both a magnitude and a direction. The electric field intensity is just the magnitude of the vector.
For example, if we had an electric field vector that extended 2 units in the x direction and 2 units in the y direction, then its magnitude would be +2√2 units.
The strength of the electric field at any point is the force per unit positive charge, i.e.,
E = F/Q
This is known as electric field intensity, and its SI unit is volts/meter i.e., V/m.
Gauss’s Law
Gauss’s law states that the net flux of an electric field in a closed surface-like sphere is directly proportional to the enclosed electric charge and it is one of the four equations of Maxwell’s laws of electromagnetism. Carl Friedrich Gauss formulated this in the year 1835 and relates the electric fields at the points on a closed surface and the net charge enclosed by that surface.
Electric flux is the electric field passing through a given area multiplied by the area of the surface in a plane perpendicular to the field. Therefore, another statement of Gauss’s law states that the net flux of a given electric field through a given surface, divided by the enclosed charge by it should be equal to a constant.
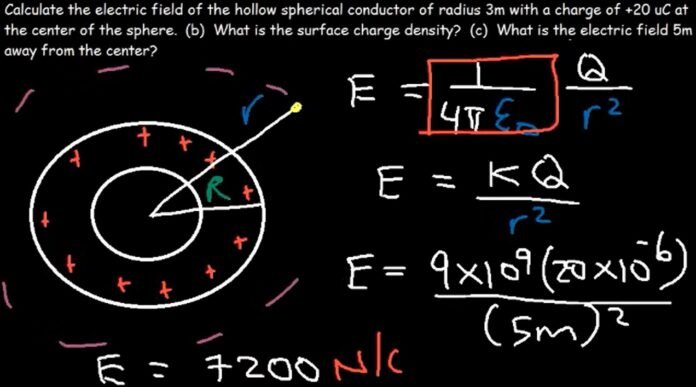
The electric field of a sphere
Gauss’ law tells that the electric field outside the sphere is the same as the field from a point charge with a net charge of Q and the electric field inside the plane sphere is zero. This result is true for a solid and a hollow sphere. So, we can say that
The electric field is zero inside a conducting sphere and the electric field outside the sphere is given by: E = kQ/r2, like a point charge while the excess charge is located on the outside of the sphere in the case of a plane sphere.
Consider a charged spherical shell with radius r and a surface charge density σ. Consider a spherical Gaussian surface centered with the spherical shell with any arbitrary radius r. By symmetry, the electric field must point radially, and thus, for a Gaussian surface outside the sphere, the angle between the electric field and area vector is 0 degrees i.e., cosθ = 1. For a Gaussian surface outside the sphere, the angle between the electric field and area vector is 180 degrees i.e., cosθ = -1. We shall consider two cases:
Case I- Inside the sphere i.e., r<R
The charge distribution is uniform. Volume density will be the same. Let the charge enclosed by a circle of radius r be q′. Since volume density is the same then-
q′/ 43πr3=q/43πR3
q′=q r3/ R3
Applying Gauss Theorem here, we get
ϕ=E4πr2
Qenclosed/ε0=E4πr2
q′/ε0=E4πr2
q/ε0×r3/R3=E4πr2
E=1/4πε0 ×qr/R3 = electric field inside the charged sphere
Case 2- On the surface i.e., r= R
E=1/4πε0 ×q/R3
Case 3- When r> R i.e., the electric field outside the sphere
ϕ=EA
q/ε0=E4πr2
E=1/4πε0× q/r2
A variation on the graph is as follows:
Recommended Articles:
Changing the Period Of A Pendulum
Configuration and Characteristics of a Transistor
Characteristics of EM Waves
Characteristics of Sound Waves
Charge Transfer: Mechanism, Types, and Applications
The electric field is a vector field that can be associated with each point in space and exerts a force on a positive test charge at rest at that point. Yes, the electric field inside the sphere is zero. The electric field intensity at a point can be defined as the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point. Electric flux is the electric field passing through a given area multiplied by the area of the surface in a plane perpendicular to the field. The strength of the electric field at any point is the force per unit positive charge is known as the electric field intensity and has the formula E= F/Q. Charged Plane Sphere FAQs
Define electric field.
Is the Electric field inside a sphere zero?
Define electric field intensity.
Define electric flux.
The strength of the electric field at any point is the force per unit positive charge known as.