Introduction
Force acting on an object on a plane surface or horizontal surface is different from forces acting on an inclined surface. In order to Find Downward Force Along the Inclined Plane On A Roller Due To the Gravitational Pull Of The Earth And Its Relationship With The Angle Of Inclination, first we have to understand the inclined surface and the forces acting on it.
Inclined Surface
On a surface that is inclined, an object will frequently slip downward. The amount of tilt on the surface affects how quickly the object slides down; the more tilted the surface, the faster the object will tend to slide down. A slanted surface is referred to as an inclined plane in physics.
Forces Operating on Inclined Surface
A known imbalanced force causes objects to accelerate down inclined planes. It is crucial to examine the forces acting against an item on an inclined plane in order to comprehend this form of motion. The gravitational force and the normal force are the two forces operating on an item that is placed on an inclined plane. While the normal force acts perpendicular to the surface, the force of gravity, often known as weight, works downward.
Steps to Find Downward Force along Inclined Plane On A Roller Due To Gravitational Pull Of The Earth And Its Relationship With The Angle Of Inclination
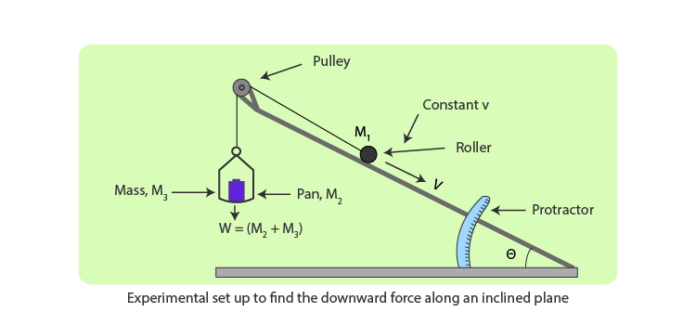
Objective
To Find Downward Force Along Inclined Plane On A Roller Due To Gravitational Pull Of The Earth And Its Relationship With The Angle Of Inclination
Devices
A sloping plane, a pan, weight box, roller or trolley, spring balance, spirit level, strong thread, and a scale measuring half a metre.
Theory
If the body is moved up by total weight W1 = M1 g and down by total weight W2 = M2 g, then the body will experience downward force along the inclined plane,
W = (W1 + W2 )/2 = (M1 + M2 ) g/2
This force must equal Mg sin θ
For the same body, m = constant
Hence, W sin θ
Procedure
- Verify that the inclined plane’s pulley is friction-free by testing it. If required, oil it.
- Keep the device on the table with the slotted piece of the base extending past the edge.
- Make the slanted plane’s base horizontal (check with a spirit level) and stable (by putting paper pieces if necessary).
- Position the inclined plane horizontally (touching the base). The inclination angle is now zero.
- Using a spring balance, determine the roller’s weight before setting it on the inclined plane in the centre.
- Pass a thread over the pulley by tying one end to the roller that is mounted on the inclined plane.
- The thread should be threaded through the base’s slot.
- By using a spring balance, determine the weight of the pan, and then attach it to the free end of the thread to keep it away from the board.
- Lift the inclined plane and position it at a 30° angle. The roller may begin to descend more quickly.
- Place weights on the pan and raise them until the roller barely begins to rise with a constant velocity only upon tapping. Take note of the pan’s overall weight.
- Remove a few small weights from the pan’s weights until the roller only begins to descend at a consistent speed upon tapping. Take note of the pan’s overall weights.
- Repeat steps 10 and 11 as you increase the angle of inclination in steps of 5° each, making it 35°, 40°, 45°, 50°, 55°, and 60°.
- Keep recording your findings.
Observation
The least count of spring balance = ………..g wt.
Zero error of spring balance (e) = …………g wt.
Zero correction of spring balance (c) = (- e) = ……….g wt.
Observed weight of the roller (w0) = …………g wt.
Corrected weight of the roller (w = Mg) = (w0 + c)
= ………..g wt.
Observed weight of the pan (p0) = ………..g wt.
Corrected weight of the pan (p) = (p0 + c) = ………..g wt.
| Serial No of Observation | Angle of inclination θ | sin θ | Mg sinθ | Weight in pan when roller moves | Total weight when roller moves | Force acting on roller downward | Error | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upward | Downward | Upward | Downward | (W1+ W2)/2 | |||||
| 1 | 5° | 0.50000 | |||||||
| 2 | 35° | 0.57358 | |||||||
| 3 | 40° | 0.64279 | |||||||
| 4 | 45° | 0.70711 | |||||||
| 5 | 50° | 0.76604 | |||||||
| 6 | 55° | 0.81915 | |||||||
| 7 | 60° | 0.86603 | |||||||
FAQs
Q1. What is Inclination?
Ans. A slanted surface is referred to as an inclined plane.
Q2. What are the two forces that work on an inclined plane?
Ans. The two forces that work on an inclined plane are gravitational force and Normal force.
Q3. What is the objective of this study?
Ans. Finding Downward Force along Inclined Plane on a Roller Due To Gravitational Pull Of the Earth and Its Relationship with the Angle Of Inclination.
Q4. What are the devices used in this study?
Ans. A sloping plane, a pan, weight box, roller or trolley, spring balance, spirit level, strong thread, and a scale measuring half a metre.