The moon is the celestial body that makes an orbit around the planet that includes all eight major planets of the solar system, “dwarf planets”, and “minor planets”. It is referred to as the earth’s natural satellite and Galileo was the first person who observed the moon in 1609 and “Apollo 11” landing in 1969. Every time we look at the moon, it always seems the same. The moon always appears to have the same scenery, regardless of the angle at which it is viewed by us. The “dark side of the moon” is the portion of the moon’s surface that cannot be seen by us from the earth. It would be inaccurate to state here that this portion or hemisphere of the moon is dark because this site is only accessible from space and never heads towards the Earth hence not visible to us.
What is the Dark side of the Moon?
The ‘dark side’ of the Moon refers to the hemisphere or the portion of the Moon that is facing away from the Earth and hence not visible from the earth’s surface. In reality, it is no darker than any other part of the Moon’s surface as sunlight does in fact fall equally on all sides of the Moon but due to the fact that it is not visible to us from the surface of the earth, it is called the Dark side. Over time, some crescent-shaped edges of the dark side of the moon can be seen due to libration. In total, 59 percent of the Moon’s surface is visible to us from Earth at one time or another.
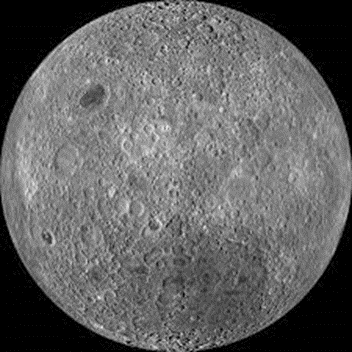
Discovery of the Dark Side of the Moon
Galileo was the first scientist who observed the moon in 1609 and “Apollo 11” landed in 1969. The Galilean moon of Jupiter was the first moon that was detected outside the earth’s surface.
Approximately 18% of the far side of the Moon is occasionally visible from Earth due to libration and the remaining 82% remained unobserved until the Soviet Lunar 3 space probe photographed it in 1959. This probe transmitted lunar photos that no one on earth had ever seen before. The Soviet Academy of Sciences published the first atlas of the far side in the year 1960. Although the photograph is blurry and hazy, it was the first time people ever viewed this side of the moon. In 1968, the far side of the Moon was seen in person by the Apollo 8 astronauts for the first time.
All spacecraft, whether manned or unmanned, used to have soft landings on the near side of the Moon, and on 3 January 2019, 4 spacecraft landed on the far side of the Moon for the first time.
Potential uses and various missions
As the far side of the Moon is shielded from radio transmissions from the Earth, it is considered a good location for placing radio telescopes for use by various astronomers.
As the near side is partly shielded from the solar wind by the Earth, the far side is expected to have the highest concentration of helium-3 on the surface of the Moon which is a relatively rare isotope on the Earth but has good potential for use as a fuel in nuclear fusion reactors.
Why is the dark side of the moon not visible?
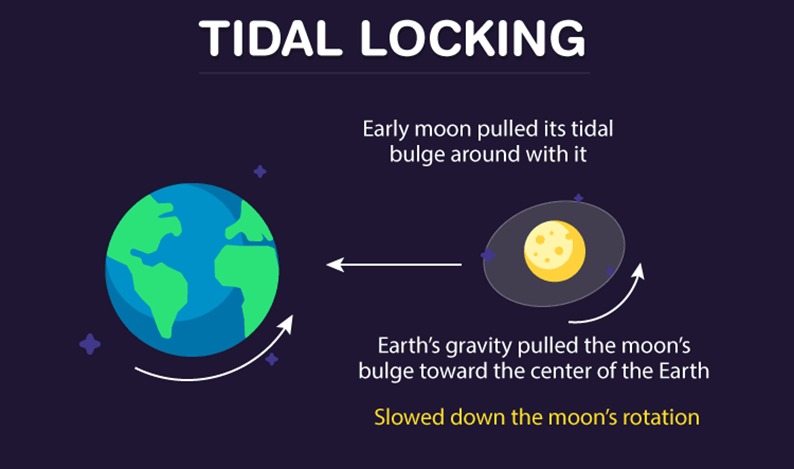
The dark side of the earth cannot be seen because the moon is tidally locked to the earth as said by the deputy project scientist for NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter project, John Keller. The earth rotates on its axis continuously and so does the moon and the time required by the Moon to rotate about its axis exactly matches the time needed for orbiting the earth i.e., 27.3 days since the earth and moon are tidally locked. In simple words, the rotational and the orbital period of the moon are the same. Therefore, we can see only one side of the moon and the other side is not visible to us. In other words, we can say that due to the sync in revolution and rotation of the earth and moon, always one side of the moon faces the earth, thereby another side which we never see is called the dark side of the moon.

Tidal locking
The moon has orbited the earth for millions of years, and over that time, gravitational perturbations between the moon and the earth have somewhat changed both their orbits and rotational velocities. Also, the mass distribution of the Moon is uneven. It appears spherical, but its geometric center differs from its centre of mass. This offset is also responsible for creating a gravitational gradient between the two entities. Because the earth is significantly bigger than the moon, its rotation is slowed until it achieves a balance point and At this point, the moon becomes “tidally locked” i.e., it’s time for full rotation around its axis coinciding with its time for a complete orbit around the earth.
The surface temperature of the Moon
Temperatures on the Moon are extreme and depend on the warmth of the sun. Temperature ranges from scorching hot to freezing cold.
As there is no atmosphere on the Moon, so heat cannot be trapped by the moon to insulate its surface.
The rotation of the Moon about its axis occurs in 27.3 days. Daytime one side of the Moon is of about 13.5 Earth days, while its other side experiences equal night time.
The temperature of the surface of the moon can reach about 127° C during the daytime, in the presence of sunlight while in the absence of sunlight i.e., during night time, the temperature of the surface of the Moon can reach about -173°C. Temperature changes occur rapidly across the moon.
Different Phases of the moon
Following are the eight phases of the moon:
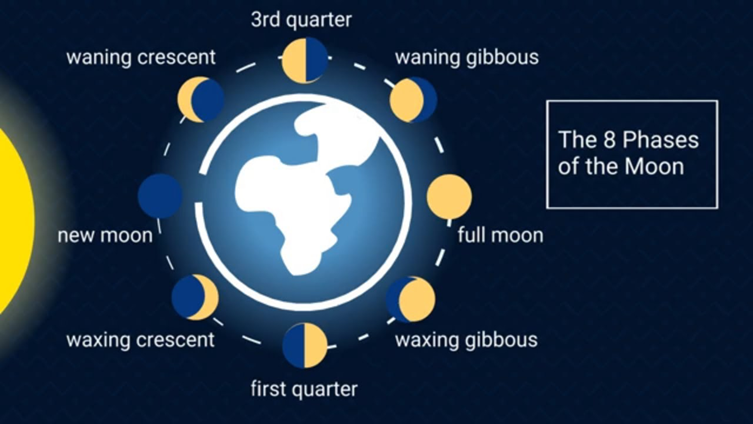
New Moon: When the moon is situated between the earth and the sun, it is said to be in its new phase and as the moon’s dark side is toward the earth, it cannot be seen during this phase.
Waxing Crescent: A few days after the new moon, the moon enters its second phase i.e., the waxing crescent and the moon moves toward the east during this phase.
First-Quarter: Depending on the location, the third phase i.e., the First quarter phase allows us to see either the lighted right or lighted left halves of the moon. The first quarter of the lunar phase has been accomplished by the moon.
Waxing Gibbous Moon: The fourth phase i.e., Waxing Gibbous Moon is where “growing shape” refers to the moon’s shape and “getting large” refers to its size.
Full Moon: The moon’s fifth phase is the Full moon phase when the sun and moon are on opposite sides of the earth.
Waning Gibbous Moon: The sixth phase of the moon i.e., the Waning Gibbous Moon is characterized by a decline in shape that lasts till the moon is halfway lighted.
Third-Quarter Moon: The moon has finished 3/4 of its current lunar phase and is in its seventh phase i.e., Third-Quarter Moon.
Waning Crescent Moon: This is the moon’s eighth or final phase.
Recommended Articles:
Current Density: Introduction, Types, And FAQ
Cyclic Process: Introduction, Types, And FAQ
D’alembert’s Principle: Introduction, Derivation, Examples, And Applications
Darcy Weisbach Equation Derivation
DARCY’S LAW: Introduction, Equation, Application, Properties, And Limitation
The 'dark side' of the Moon refers to the hemisphere or the portion of the Moon that is facing away from the Earth and hence not visible from the earth’s surface. Galileo was the first scientist who observed the moon in 1609 and “Apollo 11” landing in 1969. It’s time for full rotation around its axis coinciding with its time for a complete orbit around the earth. Galilean moon of Jupiter was the first moon detected outside the surface of the earth. The Dark side of the moon FAQs
Define the dark side of the Moon.
Who observed the moon first?
Explain tidal locking.
Name the moon which was detected outside the surface of the earth.