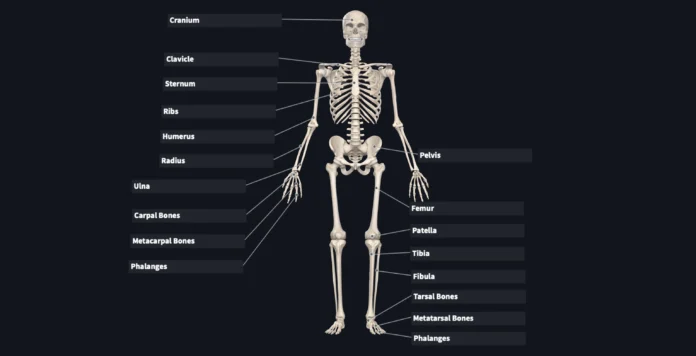
Skeletal System Introduction
The skeletal system is an incredible network of bones, cartilage, and ligaments that provide structural support and protection for the human body. It is one of the most important systems in the body, as it not only supports our body weight but also protects our vital organs, produces blood cells, and stores essential minerals such as calcium and phosphorus. In this article, we will take a closer look at the skeletal system, its components, and its functions.
Components of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, and ligaments. Bones are the hard, dense structures that form the framework of the body. They are made up of living cells that produce and break down bone tissue, as well as mineral deposits that give bones their strength and durability. There are 206 bones in the adult human body, each with its unique shape and function.
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that is found in various parts of the body, including the ears, nose, and joints. It is softer than bone but firmer than muscle and provides cushioning and support for the body. Cartilage also helps to reduce friction between bones and absorbs shock during movement.
Ligaments are strong, fibrous bands of connective tissue that attach bone to bone and help to stabilize joints. They are essential for movement and provide support and protection for the body’s internal organs.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is a complex and vital system that provides support, protection, and mobility to the human body. It is composed of bones, cartilage, and ligaments that work together to serve several functions.
Support: The skeletal system provides support to the body, allowing it to maintain its shape and structure. It serves as a framework for the attachment of muscles and other soft tissues that allow for movement. The bones in the body also provide support to the internal organs, protecting them from damage.
Protection: One of the most critical functions of the skeletal system is protection. The bones in the body protect vital organs, such as the brain, heart, lungs, and spinal cord. The ribs protect the heart and lungs, while the skull protects the brain.
Movement: The skeletal system plays a crucial role in enabling movement in the body. The muscles in the body attach to the bones via tendons and work together to create movement. The joints in the body, such as the hip, knee, and elbow joints, allow for smooth and efficient movement.
Blood Cell Production: The skeletal system is also responsible for the production of blood cells. The bone marrow, found in the centre of the bones, is responsible for the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Mineral Storage: The bones in the body act as a reservoir for minerals such as calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are essential for several bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, and maintaining healthy bones.
Common Skeletal System Disorders
Osteoporosis: It is a condition in which the bones become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures. It is caused by a loss of bone density, which can occur due to ageing, hormonal changes, or a lack of calcium and vitamin D. Women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis than men, particularly after menopause. Treatment options for osteoporosis may include medications, supplements, and lifestyle changes such as weight-bearing exercise.
Arthritis: It is a group of conditions that cause inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. There are several types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints wears down over time. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that affects the joints and can cause permanent damage if left untreated. Treatment for arthritis may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes such as weight management and exercise.
Scoliosis: It is a condition in which the spine curves to the side, leading to an abnormal posture and sometimes causing breathing difficulties. It is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence, but can also occur in adulthood. The cause of scoliosis is often unknown, but it may be related to genetics or neurological disorders. Treatment for scoliosis may include bracing or surgery, depending on the severity of the curvature.
Bone Cancer: It is a rare form of cancer that begins in the bones. It can occur at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults. The most common types of bone cancer are osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma. Symptoms of bone cancer may include pain, swelling, and a lump or mass near the affected bone. Treatment for bone cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Fractures: They are breaks in the bone, often caused by trauma or overuse. They can occur in any bone in the body but are most commonly seen in the arms, legs, and hips. Treatment for fractures may include immobilization, surgery, or a combination of both, depending on the location and severity of the fracture.
FAQs
Q1. What is the largest bone in the human body?
Ans. The largest bone in the human body is the femur or the thigh bone.
Q2. How does the skeletal system contribute to the production of blood cells?
Ans. The bone marrow, found in the centre of the bones, is responsible for the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Q3. Can a person grow new bones?
Ans. While a person cannot grow new bones, bone tissue can regenerate and repair itself to a certain extent.
Q4. How can a balanced diet contribute to a healthy skeletal system?
Ans. A balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D is crucial for maintaining healthy bones and preventing conditions such as osteoporosis.
Q5. Can poor posture affect the skeletal system?
Ans. Yes, poor posture can put extra pressure on the skeletal system, causing pain and discomfort, and potentially leading to long-term problems such as spinal curvature.