Introduction
Seeds and fruits are essential parts of a plant’s life cycle. They play a crucial role in plant reproduction and are responsible for the continuation of plant species. The formation of seeds and fruits involves complex biological processes that result in the production of structures with unique characteristics.
Seed Formation
1. Introduction to Seed Formation
Seed formation is an essential process in plant reproduction. It is the process by which a fertilized ovule develops into a mature seed. The seed contains an embryo, which can grow into a new plant. Seed formation is a complex process that involves the development of various structures and tissues.
2. Process of Seed Formation
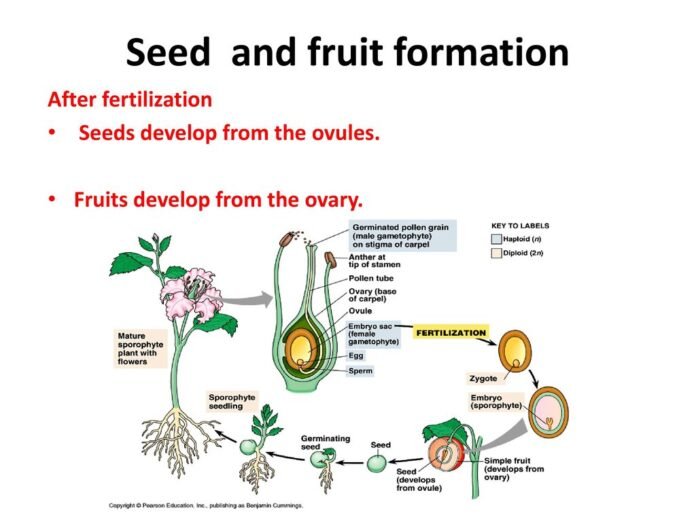
Seed formation begins with the fusion of the male and female gametes during fertilization. After fertilization, the zygote divides and differentiates into an embryo and endosperm. The embryo contains the future plant while the endosperm serves as a food source for the developing embryo. The outer layer of the ovule develops into a seed coat, which protects the embryo and endosperm. The ovary also undergoes changes, becoming the fruit.
3. Structure of a Seed
A seed has three main parts: the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The embryo is the future plant and consists of the radicle, hypocotyl, and cotyledons. The radicle is the embryonic root, while the hypocotyl is the embryonic shoot. The cotyledons are the embryonic leaves and serve as a source of nutrients for the developing embryo. The endosperm is a food source for the developing embryo and is located between the embryo and the seed coat. The seed coat protects the embryo and endosperm.
Fruit Formation
1. Introduction to Fruit Formation
Fruit formation is the process by which the ovary of a flower develops into a fruit. The fruit is a mature ovary that contains seeds. The fruit protects the seeds and facilitates their dispersal. Fruits come in various shapes and sizes and can be classified into different types based on their structure.
2. Process of Fruit Formation
Fruit formation begins with pollination, where the pollen grains from the male part of the flower (the anther) are transferred to the female part (the stigma). After pollination, the ovules in the ovary are fertilized, leading to the development of seeds. The ovary also undergoes changes, becoming the fruit. The fruit can develop from a single ovary (simple fruit) or from multiple ovaries (aggregate fruit or multiple fruits).
3. Structure of a Fruit
A fruit has three main layers: the exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp. The exocarp is the outer layer of the fruit, while the mesocarp is the fleshy middle layer. The endocarp is the innermost layer and surrounds the seeds.
Significance of Seeds and Fruits
1. Role of Seeds in Plant Life
Following are some of the roles played by seeds in the life cycle of plants:
- Survival:Seeds contain all the necessary components for the development of a new plant. They have stored nutrients, genetic material, and a protective outer covering that can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
- Dispersal: Seeds provide a means of dispersal of plant species. Plants have evolved various mechanisms to disperse their seeds such as wind, water, animals, and humans.
- Dormancy: Seeds have the ability to remain dormant for extended periods until favourable environmental conditions are met for germination.
2. Role of Fruits in Plant Life
Following are some of the roles played by fruits in the life cycle of plants:
- Seed dispersal: Fruits provide an effective means of seed dispersal. They can be dispersed through wind, water, animals, and humans.
- Protection:Fruits protect the developing seeds from external factors like predators, harsh weather conditions, and microbial attacks.
- Attraction:Fruits attract animals to consume them, aiding in the dispersal of seeds. Fruits are often colourful and sweet-smelling, attracting animals that consume them, and later dispersing the seeds through their faeces.
3. Importance of Seeds and Fruits in Human Life
Following are some of the importance of seeds and fruits in human life:
- Nutritional value:Seeds and fruits are rich sources of essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. They help in maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
- Culinary use: Seeds and fruits are used extensively in the culinary world. They are used in cooking, baking, and as a snack.
- Economic importance: Seeds and fruits have significant economic value. They are an essential component of the agricultural industry, and many countries rely on them for their economic growth.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between a seed and a fruit?
Ans. A seed is the matured ovule of a plant that contains the embryonic plant and its food source. A fruit, on the other hand, is the matured ovary of a flower that contains seeds. A fruit is a structure that contains seeds, whereas a seed is a structure that can grow into a new plant.
Q2. Can all fruits be eaten?
Ans. No, not all fruits can be eaten as some are poisonous or have inedible parts. For example, the seeds of an apple contain a small amount of cyanide, while the pits of cherries and peaches are toxic if consumed in large amounts.
Q3. Can all fruits produce seeds?
Ans: No, not all fruits produce seeds. Some fruits like bananas and seedless grapes are produced through asexual reproduction and do not have seeds.
Q4. How are seeds and fruits dispersed in nature?
Ans. Seeds and fruits can be dispersed in various ways, including wind, water, animals, and gravity. For example, the seeds of dandelions and maple trees are dispersed by the wind, while coconut palms rely on water for seed dispersal.
Q5. Can seeds survive in extreme temperatures?
Ans. Some seeds can survive in extreme temperatures, such as freezing or scorching temperatures, through a process called cryopreservation or desiccation tolerance. However, not all seeds have the ability to survive in extreme temperatures.