Introduction
Nuclear power plants generate electricity by harnessing the energy released from nuclear reactions. These power plants use uranium as fuel to produce heat, which creates steam to spin turbines that generate electricity. Nuclear power is a clean and efficient source of energy, but it also comes with risks and concerns. In this article, we discuss the nuclear power plant working in detail.
Basic Structure of a Nuclear Power Plant
A nuclear power plant has several components that work together to generate electricity. The primary components of a nuclear power plant are the reactor, steam generator, turbine, and generator. Let us have a closer look at each one of them:
Reactor
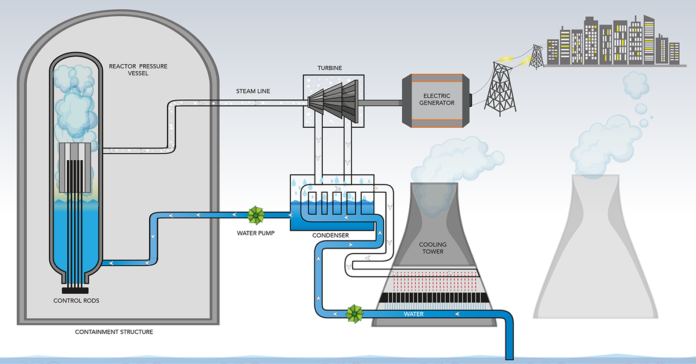
The reactor is the heart of a nuclear power plant. It contains fuel rods made of uranium that undergo fission to release energy. The heat produced by the fission of uranium generates steam, which drives the turbines. The reactor is usually housed in a large steel vessel, designed to contain any radioactive material in case of an accident.
Steam Generator
The steam generator is responsible for producing steam from the heat generated by the reactor. It is a large, cylindrical vessel that contains thousands of thin tubes. The hot water from the reactor flows through the tubes, which heats the water in the steam generator, producing steam. The steam then moves on to the turbine.
Turbine
The turbine is a large, cylindrical device connected to a generator. It spins at high speeds, generating electricity as it turns. The steam produced by the steam generator flows through the turbine blades, causing them to spin.
Generator
The generator is the final component of a nuclear power plant. It converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy. The generator is connected to the turbine by a shaft, which spins the generator’s rotor. As the rotor spins, it generates electrical energy, which is sent to the electrical grid.
Nuclear Power Plant Working
Now that we have a basic understanding of the components of a nuclear power plant, let us discuss the nuclear power plant working steps:
- Fuel Production: The first step in generating nuclear power is to produce fuel. Uranium is mined from the earth and enriched to increase the concentration of uranium-235, the isotope used to fuel nuclear reactors. The enriched uranium formed into pellets loaded into fuel rods.
- Fission: In the second step of the nuclear power plant working, the fuel rods are loaded into the reactor, where they undergo fission. Fission occurs when a uranium nucleus is split into two smaller nuclei, releasing energy in the form of heat. The heat produced by fission generates steam.
- Steam Generation: The hot water from the reactor flows through the steam generator, where it heats the water in the tubes, producing steam. The steam is sent to the turbine.
- Electricity Generation: The steam produced by the steam generator flows through the turbine blades, causing them to spin. The spinning turbine is connected to a generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The electrical energy is then sent to the electrical grid.
- Cooling: The steam produced by the reactor is cooled back into the water, which is then pumped back into the reactor to repeat the cycle. The cooling process is critical to the safe operation of a nuclear power plant.
Safety Measures in Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power plants working are highly regulated and are subject to strict safety measures to prevent accidents and protect workers and the surrounding community. Some of the vital safety measures in place include:
- Containment Buildings: All nuclear power plants are equipped with containment buildings, designed to prevent the release of radiation in the event of an accident. These buildings are made of reinforced concrete and are designed to withstand extreme weather events, explosions, and other types of damage.
- Emergency Cooling Systems: If the coolant system in the reactor fails, the reactor can overheat and potentially release radiation. To prevent this from happening, nuclear power plants are equipped with emergency cooling systems that can quickly bring the reactor back to a safe temperature.
- Radiation Monitoring: Nuclear power plants workinghave extensive radiation monitoring systems in place to detect any potential releases of radiation. These systems include sensors located throughout the plant and in the surrounding community, as well as air and water sampling systems.
- Emergency Response Plans: In the event of an accident, nuclear power plants have detailed emergency response plans to quickly and effectively respond to the situation. These plans include evacuation procedures, communication protocols, and managing the release of radiation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1- Is it safe to live near a nuclear power plant?
Ans- Living near a nuclear power plant working space is generally considered safe. Nuclear power plants are designed with multiple layers of safety features, including containment buildings, emergency cooling systems, and radiation monitoring systems, to prevent accidents and protect workers and the surrounding community.
Q2- What is nuclear fission?
Ans– Nuclear fission is a process where the nucleus of an atom is split into two smaller nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of heat and radiation. In a nuclear power plant working, this process is used to generate heat, which is then used to produce steam to generate electricity.
Q3- How is nuclear waste managed?
Ans- Nuclear waste is managed using a combination of techniques, including reprocessing, storage, and disposal. Reprocessing involves separating and recycling usable nuclear materials from waste. Storage involves keeping the waste in specially designed containers until it is safe to dispose of.
Q4- Can a nuclear power plant explode like a nuclear bomb?
Ans- No, a nuclear power plant cannot explode like a nuclear bomb. Nuclear bombs rely on a rapid and uncontrolled chain reaction, while nuclear power plants are designed to control the chain reaction through the use of control rods and cooling systems.
Q5- How does a nuclear power plant compare to other forms of energy generation in terms of environmental impact?
Ans- Nuclear power plants are considered to have a relatively low environmental impact compared to other forms of energy generation, such as coal-fired power plants. Nuclear power plants do not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants during operation, and they require a relatively small amount of land compared to other forms of energy generation.