Introduction
Density, a very simple but crucial concept in physics, is used in almost every branch of the subject. In simple terms, density is the value of mass (of the given substance) per unit volume (of the same substance). The density of different objects varies greatly. Even the same objects in different states (solid, liquid, and gas) have different densities.
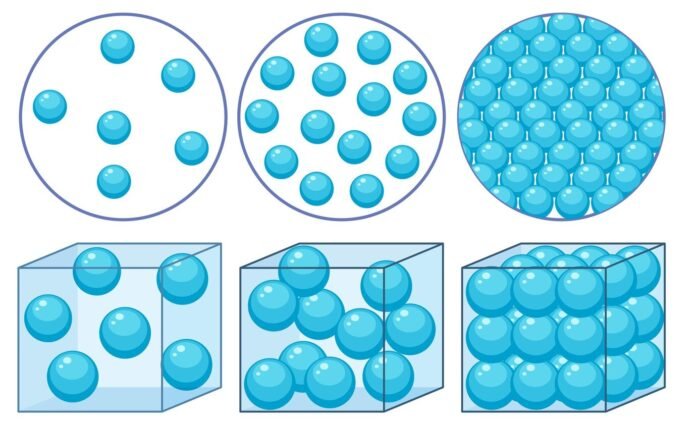
The molecules of solids are much more tightly packed than liquids; therefore, the density of solids is also higher. Similarly, gases have the least density due to very loose bonding between molecules. The SI (System International) unit of density is Kilogram per cubic metre (kg/m3). Let’s learn more about density and solve some problems involving density.
Density: Explanation
Density is a very basic term in physics that means the amount of mass (of any given substance) per unit of volume of that same substance. As described earlier, the density varies for different substances as well as the same substance in their different forms.
The density of solids is greater than liquids because the molecules of solids are tightly packed and have very less intermolecular space as compared to liquids and gases.
According to the definition of density, the derived formula is as follows:
ρ = m/V
Here, ρ = density of the given substance
m = mass of the given substance
V = volume of the substance
Relative Density
The ratio of the density of any given substance (mass per unit volume) to the density of any reference material present is termed the relative density. We usually use water as the reference material for calculating the relative density.
RD = (density of substance)/ (density of water at 4°C)
Factors Affecting Density
Several factors affect the density of a given substance such as temperature, pressure, molecular geometry of the substance, etc.
- Temperature: As we know, density depends upon the mass and volume of a given substance. However, the temperature doesn’t alter the mass but changes the volume of the substance. Therefore, temperature plays an important role in determining density.
- Pressure: When we increase the pressure on any given object, the density also increases. Thus, we can say that the density and pressure are directly proportional.
- Geometry: The geometry of molecules plays an important role in determining their density. For example, ice having wider air gaps between its molecules causes an increase in volume after freezing. Thus, the increase in volume decreases the density of the ice (solid). Therefore, water in its liquid form is denser than its solid form.
Unit of Density
The unit of density in System International or SI is kilogram per cubic metre. However, we usually use g/cm3 as the unit of density for solids. Similarly, we can use g/ml to denote the densities of liquids, and for gases, we might use g/L. The unit itself symbolizes that density is equal to the mass per volume of any given substance.
Solved Examples of Density
Q 1- What will be the density of a sugar cube weighing 14 grams? The dimensions of the cube are 4 cm.
Solution:
To calculate the density, we need mass and volume. Therefore, we will first determine the volume using the dimension of the cube.
The volume of the sugar cube
V = l3
V = 43
V = 64 cm3
Now, using the formula of density:
ρ = m/V
ρ = 14g/64cm3
ρ = 0.21875 g/cm3
Q 2- Determine the density of water given to you. It has a mass of 2000 Kg and a Volume of 2m3.
Solution:
According to the question,
Mass= 2000 Kg
Volume= 2 m3
Thus, we will use the formula of density:
Density ρ = mass/volume
ρ = 2000/2
ρ = 1000 Kg/m3
(Here the given values are in Kilogram and metres, therefore the unit of density is in Kg/m3).
Q3- You have been given an empty-density bottle of mass 21.2 grams. However, on filling the bottle with water the mass becomes 42 grams. Calculate the volume of this density bottle.
Solution:
According to the question,
Mass of empty bottle MB= 21.2 grams
Mass of bottle with water M = 42 grams
Thus, the mass of water is MW = M – MB
MW = 42 – 21.2 g
MW = 20.8 g
Recommended Articles:
Unit of Distance
Unit of Electric Field
Unit of Electric Current
Unit of Force
Unit of Heat
The relative density is the ratio between the density of the given substance with the density of the reference substance usually the water. If the value of relative density is greater than 1, then the given material is denser than the reference material (water). Similarly, if it is smaller than 1, then it will be less dense. However, if it is equal to 1, then the density of both (substance and the reference) will be the same. The water possesses maximum density at 4°C. The unit of density usually used for liquids is g/mL, whereas the unit of density for gas shall be g/L. Several factors, such as temperature, pressure, the geometry of the molecules, and the mass of the substance, affect the density of the object. The molecules of ice possess a tetrahedral geometry creating several spaces in the form of cages. On the other hand, the molecules of water are present in linear bonding, due to which their volume decreases and as a result, their density increases. Unit of Density FAQs
What do you know about the values of relative density?
State the temperature that has the maximum density of water.
State the unit of density for liquids and gases.
State the factors that determine the density of any object.
Solids have higher density, but ice is less dense than water, why?