If you’re looking for information about the details and differences between thorns and spines, you’ve come to the right place.
This article will explore the key differences between thorns and spines, including their function, structure, and role in plant protection.
First, we will briefly define what thorns and spines are and how they work. Then, we’ll compare their structure and the type of plants they are found in. Following that, we will examine their role in plant protection and the effect of their presence on herbivores and the surrounding ecosystem. Finally, we’ll discuss the significance and importance of thorns and spines in the growth and survival of plants.
This article aims to understand the difference between thorns and spines comprehensively. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply interested in the topic, this article is a great starting point for learning about the functions of these important plant structures.
Introduction
Plants have evolved various forms of defence mechanisms to protect themselves from herbivores and other predators. One such mechanism is the presence of thorns and spines on their stems, leaves, and branches. These structures can be sharp and prickly, making it difficult for animals to eat or damage the plant. However, thorns and spines are different despite their similar appearance and function.
Structure
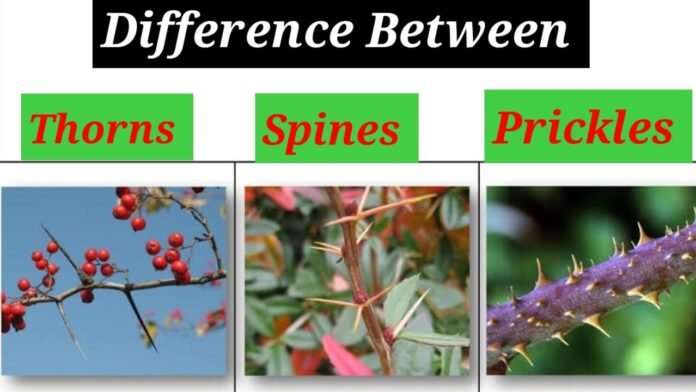
Thorns and spines both have a similar appearance, but they are different structures. Thorns are modified stems that grow from the base of the plant and are a permanent part of the plant’s structure. They are thicker, more robust than spines, and several centimetres long. Plants often use thorns as a physical barrier to protect themselves from predators and herbivores.
On the other hand, spines are modified leaves or leaflets that grow from the base of the plant and are much shorter than thorns. They are thin and sharp and can deter predators or protect the plant from damage. Unlike thorns, spines are not a permanent part of the plant’s structure and can fall off or be shed over time.
Function
The main function of both thorns and spines is to protect the plant from herbivores and other predators. Thorns provide a physical barrier that makes it difficult for animals to eat or damage the plant, while spines can be sharp and prickly, deterring predators from approaching the plant.
In addition to their defensive function, thorns and spines can serve other purposes. Thorns can support the plant, helping it maintain its upright position and resist the effects of wind and rain. They can also provide a place for climbing vines to attach to, allowing the plant to climb higher and reach more light.
Spines can also serve other purposes, such as providing shade for the plant’s leaves or protecting delicate flowers and fruit from damage. In some cases, spines can also help to collect dew or rainwater, providing the plant with additional moisture.
Diversity
There is a great deal of diversity in the forms and functions of thorns and spines in the plant kingdom. Thorns can vary in size, shape, and thickness and can be straight, curved, or hooked. They can also be covered in a hard, protective layer or have a smooth surface, making them difficult for animals to grip.
Spines can also vary in size, shape, and thickness and can be straight, curved, or hooked. They can also be covered in a hard, protective layer or have a smooth surface, making them difficult for predators to grip. Some plants have multiple spines on a single leaf or stem, while others may have only one or two.
Evolution
The evolution of thorns and spines in the plant kingdom is thought to be an adaptive response to the pressures of predation. Plants that could protect themselves from herbivores and other predators were more likely to survive and reproduce, passing their defensive adaptations to future generations.
Over time, the structures of thorns and spines evolved to become more effective at deterring predators. Thorns became thicker and more robust, while spines became sharper and more numerous. These adaptations allowed plants to protect themselves from predators better and increase their chances of survival.
Significance
The presence of thorns and spines on plants significantly impacts the ecosystems they inhabit. By deterring predators, plant populations remain stable, providing a crucial food source and habitat for other organisms. Thorns and spines also help to maintain the balance of ecosystems by controlling herbivore populations and preventing overgrazing.
In addition, the presence of thorns and spines has important implications for humans. These structures can make it difficult for people to access plants for food, medicine, or other uses. They can also be a hazard people and livestock, causing injury or damage. However, despite these challenges, the presence of thorns and spines on plants is a crucial component of the world’s ecosystems and plays an important role in maintaining the balance of life on earth.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between a thorn and a spine?
Ans- Thorns and spines are similar in appearance but have different structures. Thorns are modified stems that grow from the base of the plant and are a permanent part of the plant’s structure. Spines are modified leaves or leaflets that grow from the base of the plant and are much shorter than thorns.
Q2. What is the main function of thorns and spines in plants?
Ans- The main function of both thorns and spines is to protect the plant from herbivores and other predators.
Q3. How do thorns and spines vary among different plants?
Ans- There is a great deal of diversity in the forms and functions of thorns and spines in the plant kingdom. Thorns can vary in size, shape, and thickness and can be straight, curved, or hooked. Spines can also vary in size, shape, and thickness and can be straight, curved, or hooked.
Q4. Why do some plants have thorns and spines?
Ans- The evolution of thorns and spines in the plant kingdom is thought to be an adaptive response to the pressures of predation.
Q5. Are thorns and spines the same thing as prickles?
Though they are often used interchangeably, thorns and spines are not the same as prickles. Prickles are sharp outgrowths from the epidermis or outer layer of the plant’s stem, and they do not have the same underlying structure as thorns and spines
Q6. Can thorns and spines be harmful to humans?
Ans- Yes, thorns and spines can be harmful to humans. They can cause injuries, punctures, and scratches, leading to infections if not treated properly.
Q7. Are all plants with thorns and spines dangerous?
Ans- No, not all plants with thorns and spines are dangerous. Many plants, such as roses and cacti, have thorns and spines that are not harmful to humans. However, some plants, such as poison ivy and oak, have thorns and spines that can cause serious health problems if touched or ingested.