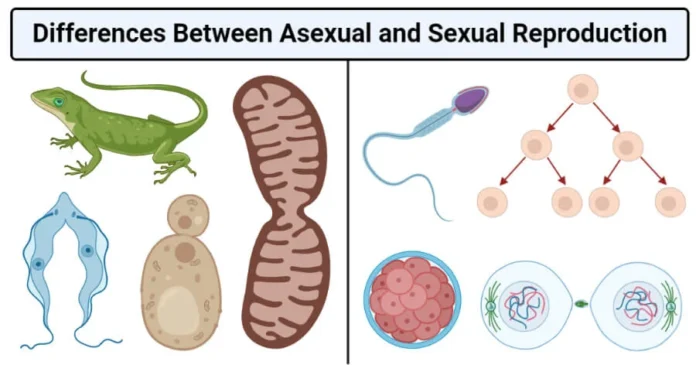
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Introduction:
Organms can reproduce through sexual or asexual means, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the mechanisms and implications of sexual and asexual reproduction is crucial for understanding the biology and ecology of various species. Keep reading to learn everything about sexual and asexual reproduction.
Reproduction and Its Types
Reproduction is the biological process by which living organisms produce new individuals of the same species. Reproduction is necessary for the continuation of a species and ensures the survival of the species over time. Reproduction can occur through different methods, including sexual and asexual reproduction.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the type of reproduction that requires the fusion of gametes (sex cells) from two different individuals. The gametes produced by males and females are usually different in size and shape, and they have different functions. In most animals, males produce small, motile gametes called sperm, while females produce larger, non-motile gametes called eggs.
Process of Sexual Reproduction
The process of sexual reproduction involves the following steps:
Gamete production
Male and female individuals produce gametes through the process of meiosis. In this process, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half, resulting in haploid gametes.
Fertilization
The gametes from the male and female individuals unite during fertilization to form a zygote. The zygote contains a complete set of chromosomes and develops into a new individual through cell division.
Embryonic development
The zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions and develops into an embryo. The embryo develops into a foetus, which grows and develops until it is ready to be born.
Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction has several advantages. Some of them are:
- It produces genetic diversity, which increases the chances of survival of a species in changing environments.
- Additionally, sexual reproduction allows for the evolution of new traits through genetic recombination.
Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction
Despite the benefits, there are some disadvantages involved with sexual reproduction including the risk of sexually transmitted diseases, dependency on a mate, energy expenditure, and cost of gene recombination.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not require the fusion of gametes. Instead, a new individual is produced from a single-parent organism.
Mechanisms Involved in Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction can occur through various mechanisms, including:
Binary fission
This is a process in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
Budding
This is a process in which a new individual develops as an outgrowth or bud from the parent organism. The bud grows until it becomes a mature individual and separates from the parent.
Fragmentation
This is a process in which a parent organism breaks into several pieces, and each piece develops into a new individual.
Parthenogenesis
This is a process in which an egg develops into a new individual without fertilization.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction has several advantages. Some of them are:
- It is a faster process.
- It requires less energy and resources than sexual reproduction.
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
Despite the advantages, asexual reproduction has some disadvantages. Asexual reproduction does not produce genetic diversity, and the offspring are genetically identical to the parent organism. This lack of genetic diversity can be disadvantageous in changing environments, as it reduces the chances of survival of a species. Asexual reproduction can limit the potential for evolution.
Difference between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction differ in the following ways:
| Sexual Reproduction
|
Asexual Reproduction |
| Involves two parents
|
Involves one parent only
|
| Gametes are produced
|
No gametes are produced |
| Fertilization occurs and a zygote is formed | No fertilization or zygote formation occurs
|
| Meiosis does not occur
|
Meiosis occurs |
| Sex organs are formed | No formation of sex organs |
| The offspring inherits characteristics of both parents | Offspring inherits characteristics of one parent |
| Progenies will be genetically different from parents | Progeny and parent will be genetically similar |
| Examples- Syngamy, external fertilization, conjugation | Examples- Bacterial fission, spore formation, etc. |
FAQs
Q1. What is the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction?
Ans. Meiosis is a type of cell division that creates gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This ensures that when gametes fuse during fertilization, the resulting offspring will have the correct number of chromosomes.
Q2. How do organisms that reproduce asexually avoid genetic defects?
Ans. Organisms that reproduce asexually can avoid genetic defects by periodically mutating their DNA, which creates new genetic variations. They can also occasionally reproduce sexually with other individuals of the same species, which introduces new genetic material into the population.
Q3. What is the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction?
Ans. Mitosis is the type of cell division used in asexual reproduction to produce genetically identical daughter cells. During mitosis, the parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each with the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process allows for rapid reproduction and can result in a large population of genetically identical offspring.
Q4. What is the major difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
Ans. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes from two different individuals to produce genetically diverse offspring, while asexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring without the involvement of gametes or another individual.
Q5. What is the ‘cost of gene recombination’ in sexual reproduction?
Ans. The cost of gene recombination in sexual reproduction is that it requires more time and energy than asexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction, individuals must find a mate and produce gametes, which requires a significant investment of resources. Additionally, gene recombination can result in the production of offspring with unfavourable traits, reducing their chances of survival. However, the benefits of genetic diversity and the potential for evolution through gene recombination can outweigh these costs in certain environments.