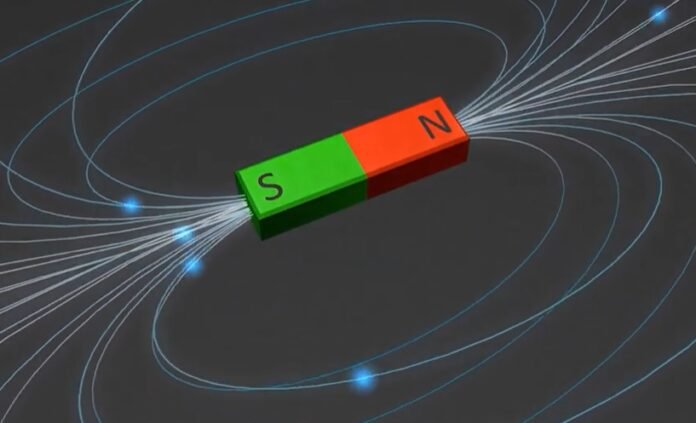
As the title suggests, in this article we will discuss two types of magnets and the differences between them. These are the two types of magnets that produce magnetic fields around their vicinity under different conditions. Due to the difference in properties of these two magnets, they found various applications in different areas of daily life.
Introduction
Before studying the difference between electromagnets and permanent Magnets, we must first understand magnets and their types. Magnets are substances that produce magnetic fields. Certain materials, including iron, nickel, cobalt, and some alloys, can be attracted to or repelled by magnets, which are objects that create a magnetic field. Permanent magnets, temporary magnets, and electromagnets are the three main categories of magnets.
Permanent magnets are substances that, when kept at room temperature, retain their ferromagnetic properties for an extended period of time. By inserting a ferromagnetic rod into a solenoid and running electricity through it, one can effectively create a permanent magnet. The rod becomes magnetised by the solenoid’s magnetic field.
High coercivity(field intensity required to demagnetize the fully magnetized substance) and high retentivity(ability to retain magnetic property) properties are necessary for a strong magnet and to prevent the magnetization from being lost due to external stray magnetic fields, temperature changes, or slight mechanical damage. The substance should also be highly permeable.
Materials that are magnetic and keep their magnetism, such as iron, nickel, cobalt, and specific alloys, are used to create permanent magnets. They create a magnetic field that doesn’t need to be sustained by an outside energy source. Permanent magnets come in a variety of sizes and forms, including rectangles, cylinders, and discs. They can also be magnetized in a variety of methods, such as by the magnetization process, which uses an external magnetic field to align the material’s internal magnetic domains. A permanent magnet’s strength is influenced by its construction material, size, form, and magnetization method. Compass needles, speaker magnets, and refrigerator magnets are a few examples of permanent magnets. From commonplace items like refrigerator magnets and magnetic toys to industrial machineries like electric motors, generators, and magnetic separators, permanent magnets are employed in a broad variety of applications. They are also utilized in scientific research for magnetic field studies as well as in medical devices like MRI machines.
Materials that become magnetized when exposed to a magnetic field lose their magnetism when the field is withdrawn, making them temporary magnets. Paperclips, nails, and screws are a few examples of transient magnets. By rubbing them against a permanent magnet or exposing them to a magnetic field, these materials can be made magnetic.
Electromagnet- An electric current is run through a wire that is wrapped around a magnetic core, which is often made of iron, to produce an electromagnet, a particular form of a magnet that works by converting electrical energy to magnetic energy. Ferromagnetic materials with high permeability and low retentivity make up the core of electromagnets. Electromagnets can be made from soft iron because of their low retentivity. A magnetic field is created around the wire’s core as a result of the current flowing through it. A magnetic field forms around a wire as an electric current passes through it. The magnetic substance in the core interacts with the magnetic field produced by the wire, amplifying it and producing a stronger magnetic field overall. The amount of current flowing through the wire, the number of turns it has, and the characteristics of the core material all affect how strong the magnetic field an electromagnet produces. There are numerous practical uses for magnets, including in MRI machines, electric motors, generators, and transformers. They are particularly adaptable since the flow of electric current can be quickly switched on and off. By adjusting the current flowing through the wire, the magnetic field’s strength can be altered. Electric motors, speakers, and MRI machines are just a few of the devices that utilize magnets.
Difference Between Electromagnet and Permanent Magnet
| Electromagnet | Permanent Magnet |
|---|---|
| Electromagnet acts as a magnet or produces a magnetic field whenever an electric current passes through a wire wrapped in a coil. | A permanent magnet is a magnet that maintains its magnetic properties without the help of an external magnetic field or an electrical current. |
| The strength of an electromagnet depends on the amount of current flowing through the wire, the number of turns around the coil, and the nature of the core material. | The strength of a permanent magnet depends upon the characteristics of a material used during its magnetization. |
| For making an electromagnet, the core should be made up of ferromagnetic materials which have high permeability, and low retentivity. | To make a permanent magnet, a ferromagnetic material of high retentivity, high coercivity, and high permeability is used. |
| The core usually consists of a soft material like soft iron. | This magnet is made up of hard materials like alnico, cobalt steel and ticonal |
| The pole of an electromagnet can be reversed by changing the direction of a current. | The pole of the permanent magnet is fixed. |
| Electromagnet requires a constant supply of electricity to retain its magnetic property. | It does not require any external source to retain its magnetic property. |
Recommended Articles:
Difference Between Discovery And Invention
Difference Between Distance And Displacement
Difference Between Earth And Neutral
Difference Between Earthing And Grounding
Difference Between Electric Field And Magnetic Field
An electromagnet is a stronger magnet because it can produce a stronger magnetic field or its intensity can be varied by increasing the current and the number of turns around the core material whereas a permanent magnet can produce a magnetic effect of fixed intensity. An Electromagnet is formed when an electric current is run through a wire that is wrapped around a magnetic core, which is often made of iron. It is a particular form of a magnet that works by converting electrical energy to magnetic energy. Permanent magnets are substances that, when kept at room temperature, retain their ferromagnetic properties for an extended period. By inserting a ferromagnetic rod into a solenoid and running electricity through it, one can effectively create a permanent magnet. The rod becomes magnetized by the solenoid's magnetic field. For making an electromagnet, the core should be made up of ferromagnetic materials which have high permeability and low retentivity whereas for making a permanent magnet, the core should be a ferromagnetic material of high retentivity, high coercivity, and high permeability. Difference between Electromagnet and Permanent Magnet FAQs
Which magnet is stronger an electromagnet or a permanent magnet?
Define Electromagnet.
What is a Permanent magnet?
What is the difference between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet based on the nature of the core material used during the process of magnetization?