Diodes:
Diodes have a wide range of applications in electronic circuits. One of the most common uses of diodes is to rectify AC voltage, similar to rectifiers. However, diodes are also used in a variety of other circuits, such as voltage regulators, oscillators, and signal modulators.
One important characteristic of diodes is their voltage drop, which is the voltage across the device when conducting current. This voltage drop is typically around 0.7 volts for silicon diodes but can vary depending on the material and construction of the diode.
Diodes can also be used in a variety of other applications, such as protecting circuits from voltage spikes or as a switch in digital circuits. In these applications, the diode is used to prevent current from flowing in a certain direction or to limit the voltage to a safe level.
Rectifiers:
Rectifiers are a type of diode that is designed specifically for the rectification of AC voltage. They have a larger junction and are capable of handling higher voltages and currents than standard diodes.
One of the main applications of rectifiers is in power supplies. In a power supply, the rectifier converts the AC voltage from a wall outlet to a DC voltage that can be used to power electronic devices. There are several different types of rectifiers, including half-wave, full-wave, and bridge rectifiers.
In addition to power supplies, rectifiers are also used in a variety of other applications, such as in welding machines, battery chargers, and inverters.
How diode and rectifier it works?
Sure, here’s an explanation of how diodes and rectifiers work:
- How a Diode Works:
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. It consists of a P-type semiconductor material and an N-type semiconductor material that are sandwiched together to form a PN junction.
When a voltage is applied to the diode in the forward direction, electrons flow from the N-type material to the P-type material, and current flows through the diode. However, when a voltage is applied in the reverse direction, the diode acts as an insulator and blocks current from flowing.
- How a Rectifier Works:
A rectifier is a specific type of diode that is designed to convert AC voltage to DC voltage. In a half-wave rectifier, only one-half of the AC voltage is converted to DC voltage, while in a full-wave rectifier, both halves of the AC voltage are converted. A bridge rectifier is a type of full-wave rectifier that uses four diodes to convert the AC voltage.
In a rectifier circuit, the AC voltage is applied to the input of the rectifier, and the output is a DC voltage. The rectifier works by allowing current to flow in only one direction through the circuit. The AC voltage is first converted to a pulsating DC voltage, where the voltage alternates between positive and negative but do not drop to zero. The pulsating DC voltage is then smoothed out using a capacitor or other circuit components to create a steady DC voltage output.
Characterises of Diode And Rectifier
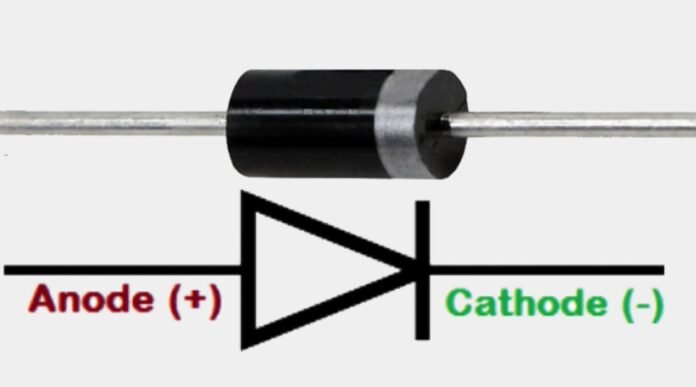
A diode is an electronic component that allows current to flow in only one direction. It has two terminals: an anode, which is connected to the positive voltage source, and a cathode, which is connected to the negative voltage source. When the voltage applied to the diode is in the forward direction, it conducts current easily; when the voltage is in the reverse direction, the diode blocks current flow.
Some characteristics of diodes include:
- Forward voltage drop: Diodes have a voltage drop when conducting in the forward direction. This voltage drop is typically around 0.7 volts for silicon diodes and 0.3 volts for germanium diodes.
- Reverse breakdown voltage: When the voltage applied to a diode in the reverse direction exceeds a certain value, called the reverse breakdown voltage, the diode breaks down and conducts current in the reverse direction.
- Current flow: Diodes have a current flow that depends on the voltage applied to them in the forward direction. The current flow through the diode increases exponentially with increasing voltage.
A rectifier is a device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). It uses diodes to allow current to flow in only one direction. There are two types of rectifiers: half-wave rectifiers and full-wave rectifiers.
Some characteristics of rectifiers include:
- Output voltage: The output voltage of a rectifier is the same as the peak voltage of the input AC voltage.
- Ripple voltage: The DC output of a rectifier is not perfectly smooth; it has a small amount of ripple voltage due to AC voltage fluctuations.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a rectifier is the ratio of the DC output power to the AC input power. It is typically around 70-80% for most rectifiers.
Differences Between Diodes and Rectifiers:
Diodes and rectifiers are both important components in electronics, but they have some key differences. Here are some of the main differences between diodes and rectifiers:
- Function: The main function of a diode is to allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. This property is used in a variety of applications, such as voltage regulators and signal modulators. On the other hand, rectifiers are specifically designed to convert AC voltage to DC voltage. They are used in power supplies and other applications where a steady DC voltage is needed.
- Construction: Diodes and rectifiers are both made from semiconductor materials, but rectifiers are typically larger and more robust than standard diodes. This is because rectifiers are designed to handle higher voltages and currents than diodes.
- Types: There are several different types of diodes, including zen diodes, Schottky diodes, and varactor diodes. Each type of diode has its specific properties and is used in different applications. Rectifiers, on the other hand, are typically categorized into three main types: half-wave rectifiers, full-wave rectifiers, and bridge rectifiers.
- Voltage Drop: When current flows through a diode, there is a voltage drop across the device. This voltage drop is typically around 0.7 volts for silicon diodes. In contrast, rectifiers have a higher voltage drop, typically between 1.4 and 2 volts. This means that rectifiers are less efficient than diodes, but they are necessary for converting AC voltage to DC voltage.
- Applications: Diodes are used in a variety of applications, such as voltage regulators, oscillators, and signal modulators. They are also used to protect circuits from voltage spikes or as a switch in digital circuits. Rectifiers, on the other hand, are primarily used in power supplies and other applications where a steady DC voltage is needed.
In summary, diodes and rectifiers are both important components in electronics, but they have different properties and are used in different applications. Diodes are used to control the flow of current in a circuit, while rectifiers are specifically designed to convert AC voltage to DC voltage.
Understanding the differences between diodes and rectifiers is important for designing and building electronic circuits.
Benefits of diode and a rectifier?
Sure, here are some benefits of diodes and rectifiers:
Benefits of Diodes:
- Protection: Diodes are commonly used to protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes and surges. They can conduct high currents for short periods, which can help to prevent damage to other components in the circuit.
- Voltage Regulation: Diodes can be used to regulate voltage by limiting the amount of voltage that is allowed to pass through the circuit.
- Low Cost: Diodes are relatively inexpensive to produce and are commonly used in a variety of electronic devices.
- Easy to Use: Diodes are simple to use and do not require any external components or complex circuitry to operate.
Benefits of Rectifiers:
- Conversion of AC to DC: Rectifiers are specifically designed to convert AC voltage to DC voltage. This is an essential function in many electronic devices and power supplies.
- High Power Handling: Rectifiers are designed to handle high voltages and currents, which makes them suitable for use in high-power applications.
- Efficiency: While rectifiers have a higher voltage drop than diodes, they are still highly efficient at converting AC voltage to DC voltage.
- Reliability: Rectifiers are typically built to be durable and reliable, with long operating lifetimes.
In summary, both diodes and rectifiers have important benefits in terms of protecting electronic circuits, regulating voltage, converting AC to DC, and handling high power. Understanding these benefits is important for choosing the right component for a particular electronic application.
Recommended Articles:
Difference Between Conduction, Convection and Radiation
Difference Between Cyclone And Hurricane
Difference Between Density and Specific Gravity
Difference Between Density And Volume
Difference Between Diffraction And Interference
A diode is a two-terminal device that allows current to flow in only one direction, while a rectifier is a type of diode that is used to convert AC to DC. Diodes are used in a wide variety of circuits, including amplifiers, oscillators, and voltage regulators. Rectifiers work by allowing current to flow in only one direction through the device, effectively removing the negative portion of the AC waveform. Yes, a diode can be used as a rectifier, but it may not be as efficient as a specialized rectifier. Diodes and rectifiers are polarized, which means they have a specific orientation for correct connection. The anode (positive terminal) should be connected to the higher voltage source in the circuit, while the cathode (negative terminal) should be connected to the lower voltage source. Diode And Rectifier FAQs
What is the difference between a diode and a rectifier?
What are diodes used for?
How do rectifiers work?
Can a diode be used as a rectifier?
How do you connect a diode or rectifier in a circuit?