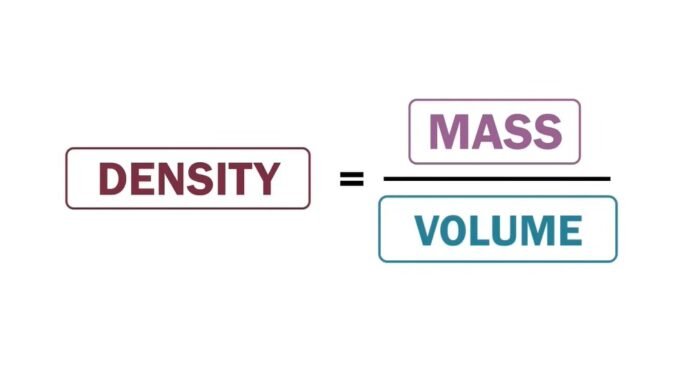
Density is the amount of mass per unit volume of a substance, while volume is the amount of space occupied by an object or substance. They are related but distinct concepts that are used in a wide range of applications, including buoyancy, materials science, and fluid mechanics.
Introduction:
In physics, density, and volume are fundamental concepts that are used to describe the properties of matter. They are closely related, yet distinct, concepts that are used in a variety of applications, from determining the mass of an object to calculating the buoyancy force on a submerged object.
Definition:
Density is defined as the amount of mass per unit volume of a substance. It is the measure of how tightly packed the particles in a substance is. It is usually represented by the Greek letter . Mathematically, it is expressed as:
Volume, on the other hand, is the amount of space occupied by an object or substance. It is the measure of the three-dimensional space enclosed by an object or substance. It is usually represented by the symbol . Mathematically, it is expressed as:
Units of Measurement:
The units of measurement for density are usually given in , , or . These units represent the mass per unit volume of a substance. For example, the density of water at room temperature is approximately .
The units of measurement for volume are usually given in cubic meters , cubic centimeters , or liters . These units represent the amount of space occupied by an object or substance. For example, the volume of a cube with sides of length is .
Key Differences Between Density And Volume
Here are ten key differences between density and volume:
- Definition: Density is the amount of mass per unit volume of a substance, while volume is the amount of space occupied by an object or substance.
- Formula: The formula for density is mass divided by volume, while the formula for volume is length times width times height.
- Units of measurement: The units of measurement for density are typically kilograms per cubic meter or grams per milliliter, while the units of measurement for volume are typically cubic meters, cubic centimeters, or liters.
- Physical properties: Density is a physical property of a substance that describes how tightly packed the particles are, while volume is a physical property that describes the amount of space an object or substance occupies.
- Relationship: Density and volume are related, but distinct, concepts. An object’s volume determines the amount of space it occupies, while its density determines how much mass is contained within that space.
- Effects of temperature: Temperature can affect both density and volume. In general, as the temperature of a substance increases, its density decreases, while the volume of a substance may expand or contract with changes in temperature.
- Role in buoyancy: Density plays a crucial role in determining whether an object will float or sink in a fluid. Objects with densities greater than the fluid will sink, while those with densities less than the fluid will float.
- Importance in materials science: Density is an important property in materials science, as it can indicate a substance’s strength, durability, and resistance to deformation. Volume is also important in materials science, as it can determine the amount of material needed for a particular application.
- Role in fluid mechanics: Both density and volume are important in fluid mechanics, as they can affect a fluid’s viscosity, thermal conductivity, and other properties.
- Measurement: Density and volume can be measured using different methods. Density can be measured using a balance and a volumetric apparatus, while volume can be measured using a graduated cylinder or other volumetric apparatus.
Relationship between Density and Volume:
The relationship between density and volume can be understood by considering the example of a block of iron. The density of iron is approximately . This means that for every cubic centimeter of iron, there are of mass. If we have a block of iron with a volume of , its mass would be . Similarly, if we have a block of iron with a mass of grams, its volume would be (calculated by dividing the mass by the density).
Applications of Density and Volume:
Density and volume are important concepts in a wide range of applications in physics, engineering, and everyday life. Here are some common applications:
- Buoyancy: Density is used to determine the buoyancy force on a submerged object. According to Archimedes’ principle, the buoyancy force on an object is equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. The weight of the displaced fluid depends on its volume and density, while the weight of the object depends on its mass. By comparing the densities of the object and the fluid, we can determine whether the object will float or sink.
- Mass and Weight: Density and volume are used to calculate the mass and weight of an object. The mass of an object is equal to its density multiplied by its volume. The weight of an object is equal to its mass multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity.
- Materials Science: Density and volume are important parameters in materials science. The density of a material is an indication of its strength, durability, and resistance to deformation. For example, high-density materials such as tungsten are used in applications that require high strength and hardness, such as cutting tools and armor.
- Fluid Mechanics: Density and volume are used to describe the properties of fluids in fluid mechanics. The density of a fluid affects its viscosity, thermal conductivity, and other properties. For example, the density of air decreases with increasing altitude, which affects the performance of aircraft engines.
Properties of Materials Based on Density and Volume
Sure, here are some potential properties of materials based on density and volume:
- Strength: Materials with higher density and volume tend to be stronger and more durable. For example, metals like steel and titanium have high densities and volumes, which make them ideal for building structures and machines that need to withstand large forces.
- Thermal Conductivity: The thermal conductivity of a material is related to its density and volume. Materials with higher densities and volumes tend to have higher thermal conductivities, which means they can transfer heat more efficiently. Examples of high thermal conductivity materials include metals like copper and aluminum.
- Sound Transmission: The density and volume of a material also affect its ability to transmit sound. Materials with higher densities and volumes tend to be better at transmitting sound waves, while materials with lower densities and volumes tend to be more resistant to sound transmission. This is why materials like glass and metal are often used in concert halls and recording studios.
- Electrical Conductivity: The electrical conductivity of a material is also related to its density and volume. Metals with high densities and volumes tend to be good conductors of electricity, which makes them ideal for use in electrical wiring and circuitry.
- Corrosion Resistance: The density and volume of a material can also affect its corrosion resistance. Materials with high densities and volumes tend to be more resistant to corrosion, which is why they are often used in applications where corrosion resistance is important, such as in the construction of boats and bridges.
Understanding these properties of materials based on density and volume is important in many scientific and engineering applications, including material science, manufacturing, and product design.
Recommended Articles:
Difference Between Concave and Convex Mirror
Difference Between Concave Convex Lens
Difference Between Conduction, Convection and Radiation
Difference Between Cyclone And Hurricane
Difference Between Density and Specific Gravity
Density and specific gravity are related concepts but not the same. Density is the amount of mass per unit volume of a substance, while specific gravity is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance (usually water). Specific gravity is a dimensionless quantity and is often used to compare the densities of liquids or solids. The density of a substance can be measured by dividing its mass by its volume. The mass of a substance can be measured using a balance, while the volume can be measured using a graduated cylinder or other volumetric apparatus. The density of most substances changes with temperature. In general, as the temperature of a substance increases, its density decreases. This is because the particles in the substance move faster at higher temperatures, leading to a decrease in their average distance from each other. The density of a gas is directly proportional to its pressure, assuming constant temperature. This is known as the ideal gas law, which states that, where is pressure, is volume, is the number of moles of gas, is the gas constant, and is temperature. Difference Between Density And Volume FAQs
What is the difference between density and specific gravity?
How do you measure the density of a substance?
How does temperature affect the density of a substance?
What is the relationship between density and pressure?