In this topic first we will see the definition of the signal. It is a physical quantity that contains some information and which is a function of one or more independent variables. The signal is classified into two types that are analog signal and digital signal.
The analog signal is defined as a signal having continuous values that have an infinite number of different values we can say it has an infinite amount of data. The digital signal is defined as a signal which has only a finite number of distinct values. These signals are not continuous signals.
Example of analog and digital clock
Analog and digital clocks are similar to an analog and digital signal. Before going to the differences we will know the difference between the analog clock and the digital clock why we call this analog and why we call this digital. Let’s first talk about the analog clock in this you can see we have three hands the first one is the hour’s hand second one is the minute hand and the small one is the second’s hand. So we can say that this analog clock or this clock can have the time as an hour then a minute and then a second. So it can take any value in 24 hours.

Fig: 2
Now let’s see what happens in the case of a digital clock in this one we have 60 seconds passed, 12 will change to and we have 13 we cannot see what is going in between this 12 and 13 because in digital we have certain levels like let’s say this is 11 minute 12 minute 13 and then 14 either you will be on 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 you cannot be in between 11 or 12 like this is 11 minutes and 30 seconds because the second is not allowed this level. This intermediate level is not allowed in the digital clock on the other hand in an analog clock we can have 11 minutes and 30 seconds definitely that’s why we call it analog because it is analogous to the time we have every value in the given limit so this is a small thing which will help you to understand the analog and digital signals.
Difference between analog and digital signals
The difference between analog and digital signals is given in the following table.
| Sl. N | Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Analog signals are continuous signals. | Digital signals are discontinuous signals. |
| 2 | It represents continuous values to represent any information | Digital signal used discrete values to represent the information |
| 3 | The effect of noise during transmission is very high to the digital signal | The effect of noise during transmission is very less or null on the digital signal |
| 4 | These signals are stored in the form of continuous waves | Digital signals are stored in the form of binary bits such as 0 and 1. |
| 5 | Analog signals consume less bandwidth | Digital signals consume more bandwidth |
| 6 | The transmission cost of the analog signal is less. | The cost of transmission is high for digit signals. |
| 7 | Analog signals are portable | Digital signals are not portable |
| 8 | It gives observation errors | Observation errors in digital signal is zero |
| 9 | Sine waves are used to represent analogue signals.
Fig: 3 |
Square waves are used to represent digital signals
Fig: 4 |
| 10 | The examples of analog signals are the human voice in the air and analog electronic devices. | The examples of digital signals are computers, CDs, DVDs, and other electronics devices |
Conversion of analog signal to digital signal
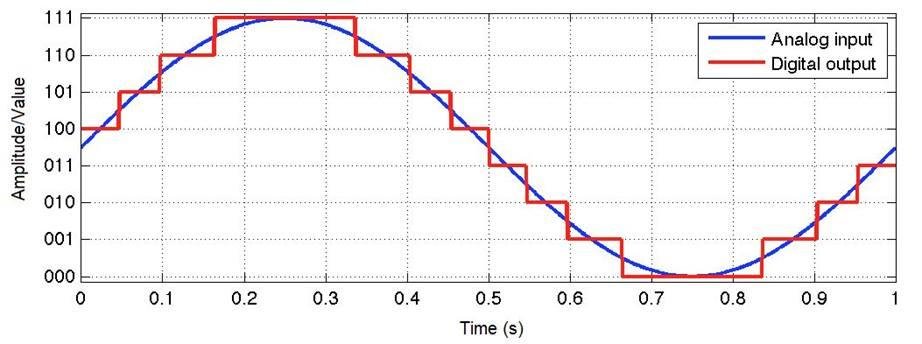
Conversion of analog signal to digital values is done using the ADC (analog to digital converter) unit. It is necessary because the values must be in digital data in order for microcontrollers to read them. This is because microcontrollers can only sense levels of voltage. ADCs follow a specific order while converting analogue signals to digital signals. To read the digital signal, they first sample the signal, quantify it to identify its resolution, set binary values on it, and send it to the system. Two essential components of the ADC are sample rate and resolution.
Recommended Articles:
Differences between Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
Difference Between Alcohol And Phenol
Difference between Alternator and Generator
Difference Between Am And Fm
Difference between Ammeter and Galvanometer
The analog signal is defined as a signal having continuous values they have an infinite number of different values we can say it has an infinite amount of data. Analog signals have the following properties Digital signal is defined as a signal which has only a finite number of distinct values. These signals are not continuous signals. Some examples of devices that used digital signals are computers, CD drives, DVDs, etc. Digit signals are transmitted as a square waveform. Difference between Analog and Digital FAQs
Explain analog signals.
Discuss some different properties of analog signals.
Analog signals are represented in the form of sine waves
Analog signals are continuous signals
Noise affects during the transmission the accuracy of analog signals
These signals are stored in the form of continuous wavesWhat is the digital signal?
Give some examples of the devices using digital signals.
What is the waveform of the transmission of digital signals?