Radio communication is a crucial aspect of modern life. It enables us to listen to music, stay updated on news, communicate with emergency services, and engage in many other activities. Radio communication relies on electromagnetic waves to transmit information over long distances.
Introduction
These waves can take various forms, such as amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM). This article aims to explain the difference between AM and FM in physics.
What is Amplitude Modulation (AM)?
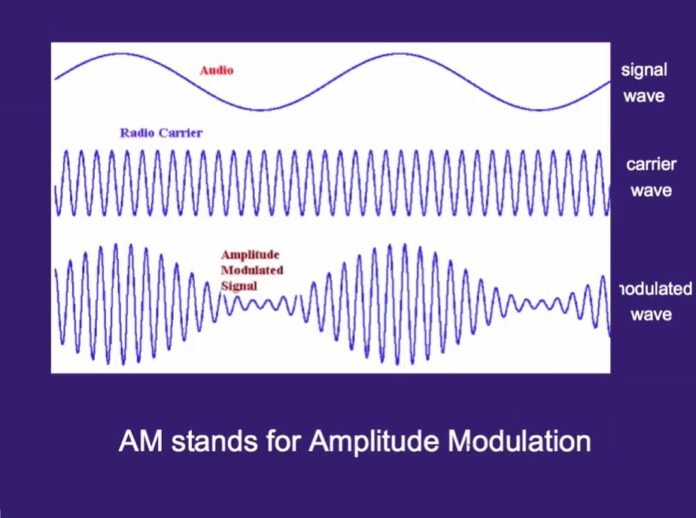
Amplitude modulation is a technique used to transmit information over radio waves. It involves varying the amplitude of a carrier wave in proportion to the signal that needs to be transmitted. In AM, the amplitude of the carrier wave varies while its frequency remains constant.
How does AM work?
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a technique used to transmit information over radio waves. It involves varying the amplitude of a high-frequency carrier wave in proportion to the signal that needs to be transmitted. The resulting modulated wave carries the information being transmitted and is then transmitted through the air to a receiving antenna.
The process of AM modulation can be described mathematically as the product of two signals: the carrier wave and the modulating signal. The carrier wave is a high-frequency sinusoidal wave with a fixed amplitude and frequency. The modulating signal, on the other hand, is a low-frequency signal that contains the information to be transmitted.
The equation for a carrier wave can be written as:
where Ac is the amplitude of the carrier wave, FC is the frequency of the carrier wave, and t is time.
The equation for the modulating signal can be written as:
where Am is the amplitude of the modulating signal, fm is the frequency of the modulating signal, and t is time.
To produce the modulated wave, the carrier wave is multiplied by the modulating signal:
This equation shows that the amplitude of the carrier wave varies in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. This variation in amplitude produces sidebands that contain the information being transmitted.
The frequency of the modulated wave is given by:
where k is a constant called the modulation index. The modulation index determines the amount of frequency deviation that occurs in the modulated wave. The greater the modulation index, the greater the frequency deviation.
- At the receiving end, the demodulation process involves separating the modulating signal from the modulated wave. This is achieved by using a circuit called a detector or demodulator. The most common types of detectors used in AM demodulation are envelope detectors and synchronous detectors.
In an envelope detector, a diode and a capacitor are used to extract the envelope of the modulated wave. The resulting signal is then passed through a low-pass filter to remove any high-frequency components that may be present.
What are the advantages of AM?
One advantage of AM is that it is relatively simple and inexpensive to implement. AM receivers are widely available and can be purchased at affordable prices. AM is also better suited for long-range communication than FM. This is because AM signals can travel farther and penetrate obstacles such as buildings and mountains more easily than FM signals.
What are the disadvantages of AM?
One significant disadvantage of AM is that it is susceptible to interference. This is because AM signals are affected by changes in the amplitude of the signal, such as noise, static, and other interference. AM signals are also more prone to fading, where the strength of the signal fluctuates due to changes in the ionosphere, which can lead to a loss of signal.
What is Frequency Modulation (FM)?
Frequency modulation is another technique used to transmit information over radio waves. Unlike AM, FM involves varying the frequency of the carrier wave in proportion to the signal being transmitted. In FM, the amplitude of the carrier wave remains constant, while its frequency changes. FM is often used in VHF and UHF radio broadcasts.
How does FM work?
Frequency modulation (FM) is a technique used to transmit information over radio waves. It involves varying the frequency of a high-frequency carrier wave in proportion to the signal that needs to be transmitted. The resulting modulated wave carries the information being transmitted and is then transmitted through the air to a receiving antenna.
- At the receiving end, the modulated wave is captured by the antenna and amplified by the receiver. The receiver then separates the modulated wave from the carrier wave and amplifies the modulating signal. The demodulated signal is then passed through an audio amplifier to produce the sound that corresponds to the original signal.
The process of FM modulation can be described mathematically as the addition of two signals: the carrier wave and the modulating signal. The carrier wave is a high-frequency sinusoidal wave with a fixed amplitude and frequency. The modulating signal, on the other hand, is a low-frequency signal that contains the information to be transmitted.
The equation for a carrier wave can be written as:
where Ac is the amplitude of the carrier wave, fc is the frequency of the carrier wave, and t is time.
The equation for the modulating signal can be written as:
where Am is the amplitude of the modulating signal, fm is the frequency of the modulating signal, and t is time.
To produce the modulated wave, the frequency of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. This variation in frequency produces sidebands that contain the information being transmitted.
The equation for the modulated wave can be written as:
where k is a constant called the modulation index, and ∫m(τ)dτ is the integral of the modulating signal. This equation shows that the frequency of the carrier wave varies in proportion to the integral of the modulating signal.
- The modulation index determines the amount of frequency deviation that occurs in the modulated wave. The greater the modulation index, the greater the frequency deviation. The frequency deviation is the maximum amount by which the frequency of the carrier wave is allowed to vary.
- At the receiving end, the demodulation process involves separating the modulating signal from the modulated wave. This is achieved by using a circuit called a demodulator or detector. The most common types of detectors used in FM demodulation are frequency discriminators and phase-locked loops.
In a frequency discriminator, the modulated wave is fed into a resonant circuit that has a frequency response that is sensitive to changes in frequency. The resonant circuit produces an output voltage that is proportional to the frequency deviation of the modulated wave.
In a phase-locked loop, a local oscillator generates a waveform that is synchronized with the carrier wave.
What are the advantages of FM?
One advantage of FM is that it is less susceptible to interference than AM. This is because FM signals are affected by changes in frequency rather than amplitude. FM signals are also less prone to fading than AM signals, which makes them more reliable for short-range communication. FM also provides better sound quality than AM because it has a wider frequency range.
What are the disadvantages of FM?
One disadvantage of FM is that it requires a larger bandwidth than AM. This means that fewer FM stations can fit into a given frequency range compared to AM stations. FM receivers are also more complex and expensive than AM receivers, which makes them less accessible to some users.
Another disadvantage of FM is that it has a shorter range than AM. This is because FM signals do not travel as far as AM signals and are more easily blocked by obstacles such as buildings and mountains. FM signals also require a clear line of sight to the transmitter, which can limit their range.
Recommended Articles:
Dielectric Properties: Introduction, Constant, Strength, And Applications
Difference Between Ac And Dc Generator
Differences between Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
Difference Between Alcohol And Phenol
Difference between Alternator and Generator
It depends on the application. AM is better suited for long-range communication, while FM is better for short-range communication and provides better sound quality. Yes, AM and FM signals can be transmitted simultaneously, but they require different frequencies and bandwidths. AM signals travel farther than FM signals because they have a longer wavelength and are less affected by obstacles such as buildings and mountains. FM is better for music than AM because it has a wider frequency range and can transmit higher-fidelity sound. Difference Between Am And Fm FAQs
Which is better, AM or FM?
Can AM and FM signals be transmitted simultaneously?
Why do AM signals travel farther than FM signals?
Why is FM better for music than AM?