Resistance is the measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current through a material. It is an essential concept in understanding electrical circuits and plays a crucial role in many everyday electronic devices. The resistance of a material is determined by several factors, including the material’s physical properties, the length of the conductor, and the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Resistance
Resistance is the measure of how much a material or object opposes the flow of electrical current through it. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and is represented by the letter R. The resistance of a conductor depends on its material, dimensions, and temperature. The unit of resistance, ohms, is named after Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist who discovered Ohm’s Law, which states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied to it, provided its temperature and other physical conditions remain constant.
Potential Difference
Potential difference is the difference in electric potential between two points in an electrical circuit. It is measured in volts (V) and is represented by the letter. Potential difference is also known as voltage, electric pressure, or electric tension. Potential difference is the driving force that causes electrical current to flow through a conductor.
Current
Current is the flow of electrical charge through a conductor. It is measured in amperes and is represented by the letter. Current is the rate at which electric charge flows through a conductor, and it is defined as the amount of charge flowing per unit time.
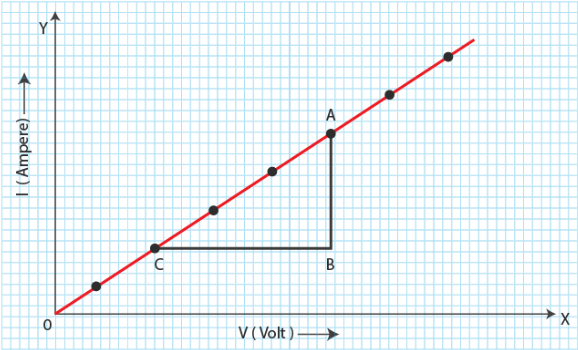
Resistance Plotting Graph of Potential Difference versus Current
To determine the resistance of a conductor, a graph is plotted with the potential difference along the y-axis and the current along the x-axis. The graph is then analyzed to determine the resistance of the conductor. The graph is a straight line passing through the origin.
The equation for the straight line passing through the origin is given by:
where is the potential difference,is the current, and is the resistance.
The slope of the straight line passing through the origin is equal to the resistance of the conductor. This can be seen by rearranging the equation for the straight line passing through the origin to give:
where is the resistance, is the potential difference, and is the current.
The resistance of the conductor can also be determined by measuring the potential difference and the current flowing through it and then using the equation
The potential difference across the conductor is measured using a voltmeter, which is connected in parallel across the conductor. The current flowing through the conductor is measured using an ammeter, which is connected in series with the conductor.
The resistance of a conductor is dependent on its dimensions and material. The resistance of a conductor increases with its length and decreases with its cross-sectional area. The resistance of a conductor also depends on its material, with some materials being better conductors than others.
To plot a resistance graph, follow the following steps:
Step 1: Set up a simple circuit that includes the material whose resistance you want to measure, a voltage source, and a resistor. Use a digital multimeter to measure the potential difference across the material and the current flowing through it. Make sure the circuit is properly connected and there are no loose connections.
Step 2: Measure the potential difference across the material for different values of current flowing through it. Record the readings in a table.
Step 3:
Plot the potential difference on the y-axis and the current on the x-axis. Use a ruler to draw a straight line through the plotted points. The slope of the line represents the resistance of the material.
Step 4: Calculate the resistance of the material using the slope of the graph. The resistance is equal to the ratio of the potential difference to the current.
Factors Affecting Resistance Plotting Graph of Potential Difference versus Current
Several factors can affect the resistance of a conductor, and hence the potential difference versus current graph. These factors include the length and cross-sectional area of the conductor, the temperature of the conductor, and the material of the conductor.
- Length and Cross-Sectional Area of the Conductor
The resistance of a conductor increases with its length and decreases with its cross-sectional area. This is because the longer the conductor, the more resistance it offers to the flow of electric current. Similarly, the smaller the cross-sectional area of the conductor, the more resistance it offers to the flow of electric current.
- Temperature of the Conductor
The temperature of the conductor also affects its resistance. As the temperature of the conductor increases, its resistance also increases. This is due to the fact that as the temperature of the conductor increases, the atoms and molecules within the conductor vibrate more rapidly, which leads to an increase in the number of collisions between them. These collisions impede the flow of electrical current through the conductor, resulting in an increase in its resistance.
- Material of the Conductor
The material of the conductor also plays a significant role in determining its resistance. Some materials are better conductors than others, meaning they offer less resistance to the flow of electrical current. For example, copper and aluminum are excellent conductors of electricity, while materials like rubber and glass are poor conductors.
Recommended Articles:
Destruction caused cyclones
Destructive Interference: Introduction, Properties, And Application
Detergents And Surface Tension: Introduction, Solution, Affecting, And Uses
Determination Of Focal Length Of Concave Mirror And Convex Lens
Determine Mass Of Two Different Objects By Using A Beam Balance
Current is the flow of electrical charge through a conductor. Temperature, Material and length of the conductor are the few factors which can affect resistance plotting graphs of potential difference versus current. Potential difference is the difference in electric potential between two points in an electrical circuit. Circuit Analysis, Electrical Safety and Electronic Component Design are the few applications. Resistance Plotting FAQs
Define current.
What are the factors affecting resistance plotting graphs of potential difference versus current?
Define potential difference.
Enlist some applications of resistance plotting graphs of potential difference versus current.
