We are aware of how the development of electric current transformed daily life. Many equipment, from simple ones like fans to complex ones like boilers and heaters, depend on it as their basic power source. Electrical charge carriers flow is referred to as current.
Current
We are aware of the changes brought about by the development of electric current. It serves as the primary power source for a wide range of equipment, from straightforward devices like fans to more intricate ones like boilers and heaters. Current is the flow of electrical charge carriers. It is denoted by ‘A’. It’s S.I., unit is ampere.Standardaly, the current is symbolized by ‘I’. Conventional current is defined as the flow of electricity from comparatively positive to negative places. Common negatively-charged carriers that move from relatively negative to positive places are known as electrons.
Conversely, if we try to define what the current is so it can be defined as one coulomb of charge ( charge carriers) travels past a certain spot every second with a current of one ampere.
Formula for current is given by,
Where, Current
Charge
and, time in seconds.
Types of Current
There are two types of current and are mentioned below:
i. Direct Current
ii. Alternating Current
Direct Current
It is a type of current which does not change its polarity with time. To get it better it can be understood as while the instantaneous magnitude can vary, direct current always moves in the same direction. The one thing which can be noted here is the frequency of the direct current will always be zero.
Example of D.C. is the current produced by an electrochemical cell.
Alternating Current
It is a type of current which changes its polarity with time.In an alternating current, charge carriers periodically flow in the opposite direction. Frequency, measured in Hertz, is the quantity of AC cycles per second. Frequency of alternating current can vary but it will always be more than zero.
Alternating current is used by the majority of electrical devices, including fans, lamps, air conditioners, and motors (AC).
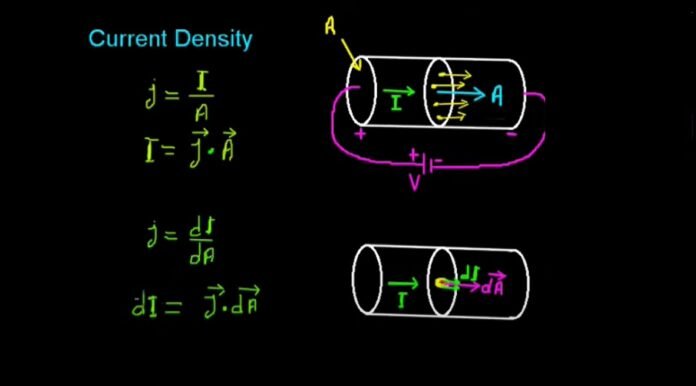
Current Density
Current density, which is measured in amperes per square meter, is the quantity of electric current flowing through a unit of cross-sectional area. The current density will increase as the conductor’s current increases. However, alternating currents at higher frequencies cause the current density to change in various locations of an electrical conductor.
or, The entire amount of current flowing through one unit of a cross-sectional area is referred to as current density. If the current flow is uniform, it will flow through a particular conductor with the same quantity at all of its points, regardless of how the conductor’s area changes.
Magnetic fields are always produced by electric current. The magnetic field is more potent the stronger the current. Signal propagation works on the idea that varying AC or DC generates an electromagnetic field.
A vector quantity with both a direction and a scalar magnitude is current density. The direction perpendicular to the flow of direction is taken into account when calculating the electric current passing through a solid with units of charge per unit time.
Formula for Current Density
Current Density is denoted by ‘J’ and is given by:
where, Current Density
Ampere (Current)
Area (square meter)
Another, form of calculating the current density is there which is given by:
Where, Current Density
Conductivity
Electric Field.
Recommended Articles:
Critical Velocity: Introduction, Formula,Number, And Calculate
Curie Constant: Introduction, Law, And Constant
Curie Weiss Law: Introduction, Limitation, Theory, And FAQ
Curie’s Law: Definition, Formula, Temperature, And Limitations
Current Coil: Introduction, Applications, Specifications, And Difference
Current is the flow of electrical charge carriers. It is denoted by ‘A’. It's S.I., unit is ampere. There are two types of current and are mentioned below: i. Direct Current ii. Alternating Current Current Density is the quantity of electric current flowing through a unit of cross-sectional area. Direct Current. Current Density FAQs
Define current and mention its S.I. unit.
How many types of current are there? Enlist them.
Define Current Density.
What type of current has frequency as zero?