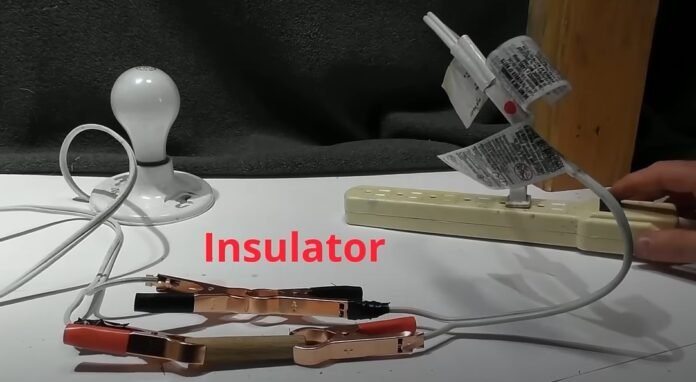
In the world of electricity, two types of materials play a vital role in the transmission of electrical energy: conductors and insulators. Conductors are materials that allow electricity to pass through them, while insulators are materials that resist the flow of electricity. Understanding the properties and differences between conductors and insulators is crucial for anyone interested in electrical engineering, physics, or related fields. Conductors and insulators are two important types of materials in the world of electricity.
Conductors are typically metals, such as copper, silver, aluminum, and gold. These materials are efficient conductors of electricity and are often used in electrical wiring, as well as in other applications where electrical current needs to be transmitted over long distances.
Insulators, on the other hand, are materials that resist the flow of electric current. They have high resistance to electricity, meaning that very little current can pass through them. Semiconductors are a third category of materials that have properties that are somewhere between those of conductors and insulators. They can conduct electricity under certain conditions but not as well as conductors, and they can also act as insulators under certain conditions as well.
Conductors
A conductor is any material that allows an electric current to flow through it. This happens because conductors have free electrons that can move easily between atoms. When a voltage is applied to a conductor, the electric field pushes these free electrons, causing them to move towards the positive end of the voltage source. This movement of electrons is what constitutes an electric current.
Characteristics of Conductors
Conductors have several properties that make them useful in electrical applications.
- Firstly, they have a low resistance to the flow of electricity, meaning that the electric current can pass through them with minimal impedance. This property makes conductors ideal for transmitting electrical power over long distances, as less energy is lost as heat due to the low resistance.
- Secondly, conductors are typically good thermal conductors as well, meaning that they can easily dissipate heat. This property is important for applications where the conductor is carrying a lot of electrical energy, as it can help prevent the conductor from overheating and becoming damaged.
Examples of Conductors
Some common examples of conductors include copper, silver, aluminum, and gold. These metals are often used in electrical wiring, as they are efficient conductors of electricity and relatively inexpensive. Other materials, such as carbon and some types of plasma, can also act as conductors under certain conditions.
Insulators
An insulator is any material that resists the flow of electric current. Unlike conductors, insulators do not have free electrons that can move through the material. Instead, they have tightly bound electrons that do not move easily.
Characteristics of Insulators
Insulators have several properties that make them useful in electrical applications as well.
- Firstly, they have a high resistance to the flow of electricity, meaning that very little current can pass through them. This property is important for applications where electrical current needs to be controlled or prevented from flowing, such as in electrical switches or circuit breakers.
- Secondly, insulators are typically good thermal insulators, meaning that they do not conduct heat well. This property is useful for applications where the material needs to insulate against heat, such as in the insulation around electrical wires or in building materials.
Examples of Insulators
Common examples of insulators include rubber, glass, plastic, and air. These materials are used in a variety of electrical applications, such as in the insulation around electrical wires, as the casing for electrical devices, or as the dielectric material in capacitors.
Semiconductors : A Third Category
In addition to conductors and insulators, there is a third category of materials known as semiconductors. Semiconductors have properties that are somewhere between those of conductors and insulators. They have a moderate resistance to the flow of electric current, meaning that they can conduct some electricity under certain conditions but not as well as conductors. At the same time, they have fewer free electrons than conductors, meaning that they can act as insulators under certain conditions as well.
Recommended Articles:
Concave lens: Introduction, Terminology, Image, And Application
Concentration of Ore: Introduction, Types and Properties of Ore
Conduction of Electricity in liquids
Conduction Of Electricity: Introduction, Liquids, Substances, And Compounds
Conductivity of Water: Electric, Thermal, Variation, And Conductance
A conductor is any material that allows an electric current to flow through it. An insulator is any material that resists the flow of electric current. Common examples of insulators include rubber, glass, plastic, and air. Yes Conductors Insulators FAQs
Explain conductors in brief.
Explain insulators in brief.
Give some examples of insulators.
Do semiconductors have the properties of both conductors and insulators?