Lenses are ubiquitous in our daily lives, from our eyeglasses to the cameras on our smartphones. They are optical devices that bend and refract light to form an image. Lenses have been used for centuries, with the ancient Greeks using glass lenses to start fires and magnify objects. Today, lenses are used in a wide range of applications, from astronomy to medicine.
Introduction:
Types of Lenses:
Lenses are versatile optical devices with a wide range of applications across various fields. They come in various shapes and sizes and are used in everything from cameras to microscopes. The development of new technologies, such as smart lenses that can automatically adjust their focus, promises to push the boundaries of what is possible with lenses even further. Lenses will continue to be essential tools for scientists, engineers, and artists, allowing us to see the world in new and exciting ways.
There are two primary types of lenses: convex and concave. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. They bend light rays towards the center and converge them, forming a real image. Convex lenses are commonly used in cameras, telescopes, and eyeglasses. Concave lenses, on the other hand, are thinner in the middle and thicker at the edges. They bend light rays away from the center and diverge them, forming a virtual image. Concave lenses are often used in correcting vision problems such as nearsightedness and farsightedness.
Convex Lens:
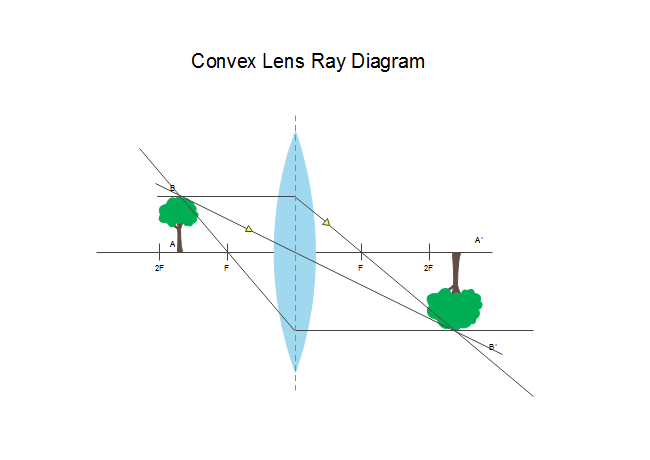
A convex lens, also known as a converging lens, is a type of lens that is thicker in the middle than at the edges. It is a curved piece of glass or other transparent material that is used to bend and focus light.
The working of a convex lens can be explained by the following steps:
- Light rays enter the lens: When a beam of light enters a convex lens, the lens causes the rays to converge or come together at a single point known as the focal point.
- Refraction of light: As light passes through the lens, it is refracted or bent due to the curved surface of the lens. This bending of light causes the rays to converge toward the focal point.
- Focal point: The focal point is the point where all the light rays converge after passing through the lens. The distance between the center of the lens and the focal point is known as the focal length.
- Magnification: The convex lens can also be used to magnify an object. The image formed by the lens will be larger than the object, and the size of the image depends on the distance between the object and the lens.
- Real and virtual images: Depending on the position of the object and the lens, the image formed by the convex lens can be real or virtual. A real image is formed when the light rays actually converge at a point, while a virtual image is formed when the rays appear to converge at a point, but do not actually do so.
Overall, the convex lens is used in a variety of optical devices, such as cameras, telescopes, and eyeglasses, to bend and focus light, and create clear images of objects.
Concave Lens:
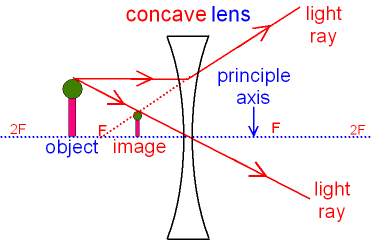
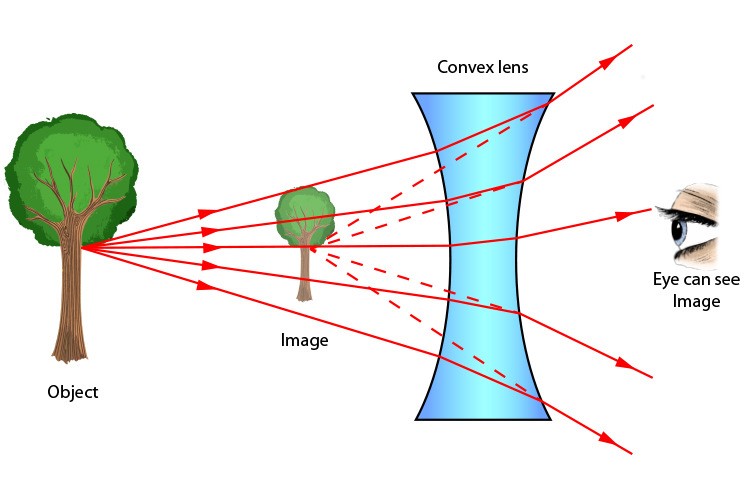
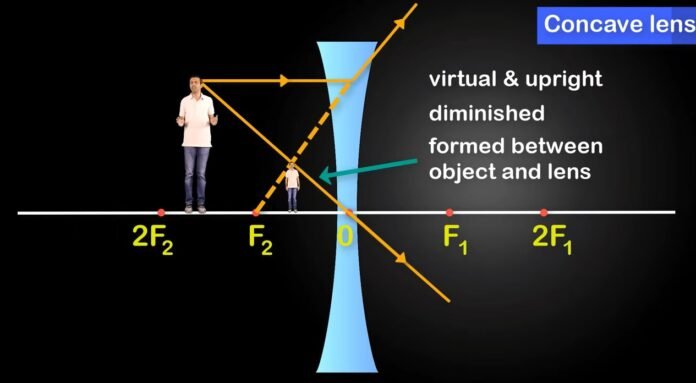
A concave lens, also known as a diverging lens, is a type of lens that is thinner in the middle than at the edges. It is a curved piece of glass or other transparent material that is used to diverge light.
The working of a concave lens can be explained by the following steps:
- Light rays enter the lens: When a beam of light enters a concave lens, the lens causes the rays to diverge or spread out.
- Refraction of light: As light passes through the lens, it is refracted or bent away from the central axis of the lens due to the curved surface of the lens. This bending of light causes the rays to diverge away from each other.
- Focal point: Unlike a convex lens, a concave lens does not have a focal point where the light rays converge. Instead, the lens causes the rays to appear to originate from a point behind the lens, known as the virtual focal point.
- Magnification: The concave lens can also be used to reduce the size of an object. The image formed by the lens will be smaller than the object, and the size of the image depends on the distance between the object and the lens.
- Virtual images: Depending on the position of the object and the lens, the image formed by the concave lens will always be virtual, meaning the rays do not actually converge, but appear to diverge away from the virtual focal point.
Overall, the concave lens is used in a variety of optical devices, such as binoculars and projectors, to diverge light and create clear images of objects.
Differences between convex and concave lenses:
| Convex Lenses | Concave Lenses |
|---|---|
| Thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges | Thinner in the middle and thicker at the edges |
| Refracts or bends light inward | Refracts or bends light outward |
| Has a focal point where the light rays converge | Does not have a focal point, but creates a virtual focal point where the rays appear to diverge from |
| Produces real and inverted images of objects that are farther away than the focal point | Produces virtual and upright images of objects |
| Magnifies objects when they are closer than the focal point | Always produces smaller images than the original object |
| Used in cameras, telescopes, and magnifying glasses to focus light and produce clear images | Used in devices like binoculars and projectors to spread out light and create wider fields of view |
| used in eyeglasses for correcting farsightedness | Used in eyeglasses for correcting nearsightedness |
Applications of Lenses:
Lenses have a wide range of applications in various fields. Here are some of the most common applications of lenses:
- Photography: Lenses are a critical component of cameras, and different types of lenses can produce different effects. Wide-angle lenses are used to capture panoramic landscapes, while telephoto lenses are used to zoom in on distant objects.
- Telescopes: Telescopes use lenses to gather and focus light from distant objects in space, allowing astronomers to study the stars and planets.
- Microscopes: Microscopes use lenses to magnify objects that are too small to see with the naked eye. The lenses in a microscope are often stacked together to create a more significant magnification.
- Eyeglasses: Eyeglasses use lenses to correct vision problems, such as nearsightedness and farsightedness.
- Medical Imaging: Lenses are used in medical imaging equipment, such as X-ray machines and MRI scanners, to focus and direct beams of radiation or magnetic fields onto the patient’s body.
- Projectors: Projectors use lenses to magnify and project images onto a screen or wall.
Recommended Articles:
Communication Systems: Introduction, Types, Examples And Elements
Compound Lenses Thin Lenses in Contact
Compressive Stress: Introduction, Unit, formula, Dimension And Strength
Compton Wavelength: Introduction, Equation, Importance, And Effect
Concave And Convex Mirrors Spherical Mirrors
A convex lens is used to focus light and create clear images of objects. It is commonly used in cameras, telescopes, and eyeglasses. A concave lens diverges light and creates clear images of objects. It is commonly used in devices such as binoculars and projectors. A convex lens works by bending light rays inward as they pass through the curved surface of the lens. This causes the rays to converge or come together at a single point known as the focal point. A concave lens works by bending light rays outward as they pass through the curved surface of the lens. This causes the rays to diverge or spread out, and the lens appears to originate from a point behind the lens, known as the virtual focal point. The main difference between a convex and a concave lens is their shape and the way they bend light. A convex lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges and bends light inward, while a concave lens is thinner in the middle than at the edges and bends light outward. Yes, convex and concave lenses can be used together in combination to produce different optical effects, such as correcting vision problems or creating a wider field of view. Convex lenses are used to correct farsightedness, while concave lenses are used to correct nearsightedness. By adjusting the way light is refracted through the lens, the lenses can help the eye focus on objects at different distances. Concave Convex Lenses FAQs
What is a convex lens used for?
What is a concave lens used for?
How does a convex lens work?
How does a concave lens work?
What is the difference between a convex and a concave lens?
Can convex and concave lenses be used together?
How do convex and concave lenses correct vision problems?