Introduction
Thermal expansion is called the increase in length, area, and volume due to the increase in temperature. If we focus on the expansion in one dimension only and take expansion in other dimensions as negligible or zero is called linear expansion. Thermal expansion in the material can be seen in the materials due to the molecular fast movement and thermal vibration. The thermal coefficient is a property of the material which shows the behavior of the material toward heating. Thermal expansion can be seen in all three states of material i.e. solid, liquid, and gas. All of these show different behavior toward heating and cooling.
Linear expansion
Linear expansion affected the length of any object. While an object is heating the length of the object will be increased or decreased.
Consider an iron rod of length Lo at NTP. Now the rod is heated by some external medium by δQ heat. There will change in length (ΔL) can be observed due to the supply of heat.
Now, if we heat wood or stone with the same heat then expansion cant be observed with the naked eye in this case. So we can say different materials show different behavior with an increase or decrease in temperature. On this basis thermal coefficient come into the picture. Linear thermal expansion depends on the cohesive forces of the materials. More cohesive forces mean low linear thermal expansion.
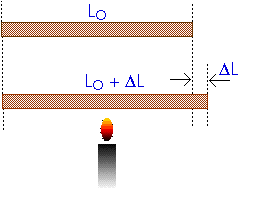
Fig-1
The change in length of the rod depends on the initial length and the rise in temperature. Let the rise in temperature by supplying δQ heat is.
So,
To remove the proportionality sign we have to use some constant.
Here is known as linear expansion coefficient which is the property of the material.
If the one-meter rod is heated which causes the unit change in temperature to be observed then the change in length will be the linear expansion coefficient.
The unit of thermal expansion coefficient is oC-1 or K-1
Linear expansion of different materials
As we already learned that linear expansion is the property of the material. Thus, different materials have different values of linear expansion. For example, metal has higher linear expansion than nonmetals. Lead is the metal having the highest linear thermal expansion coefficient i.e. 29 x 10-6 K-1. Lead is a soft material and it contract and expands easily due to temperature differences.
The decreasing order of thermal expansion of some important metals is given below:
Lead > Al > Brass > Cu > gold > Iron
Negative thermal expansion coefficient can also be seen in some materials like wood. These are contracts due to heating.
Linear thermal coefficients for some important materials are given below.
| Metals | Coefficient of linear expansion ( K-1) |
|---|---|
| Lead | 29 x10-6 |
| Aluminum | 23 x 10-6 |
| Brass | 19 x 10-6 |
| Copper | 17 x 10-6 |
| Gold | 14 x 10-6 |
| Iron or steel | 12 x 10-6 |
Real-life examples of linear thermal expansion
There are many examples of linear thermal expansion can be seen around. Some of them are given below.
- There is a gap provided between two subsequent rails of the railway track. Because in the summer due to heating rails need some space to expand.
- Electric cables installed between two electric poles are provided some slake. This is to avoid cable becoming too tight due to the contraction during winter.
- Air in the moving car’s tyre get warm during summer and sometimes explodes due to thermal expansion.
Recommended Articles:
Classification Of Polymerization: Introduction, Classification, And FAQs
Clausius Statement: Introduction, law, Statement, And Application
Clinical Laboratory Thermometers: Introduction, Principles, Types And Applications
Clothes: Introduction, Types, Synthetic, Summer And Winter
Cloud Formation: Introduction, Formed, Experiment And Important
Linear thermal expansion is the ratio of the rate of change in length (with respect to temperature) to the original length. It is very useful in machine design. When we design a machine that has to work in different atmospheric conditions it is important to consider the elongation and contraction in length due to temperature variation. The unit of thermal expansion coefficient is oC-1 or K-1. Linear thermal expansion, Areal thermal expansion, and Volume thermal expansion. Span of bridge = 1200 m Temperature difference = 40-(-20) = 60oC Linear thermal expansion coefficient for steel = 12 x 10-6 So the change in the length of the span can be calculated using the following formula. Coefficient of Linear Expansion FAQs
Explain linear thermal expansion and how it is important in machine design.
What is the unit of linear thermal expansion coefficient?
Name different types of thermal expansion coefficients.
The span of a bridge is 1200 m long. The bridge is exposed to temperatures ranging from−20oC to 40oC. What is its change in length between these temperatures? Assume that the bridge is made entirely of steel.
