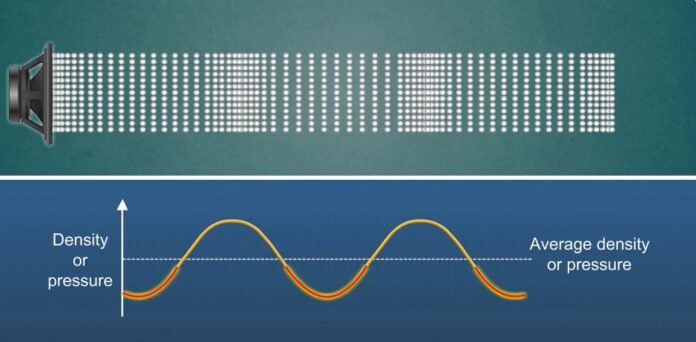
Sound is a form of energy, produced in the form of a pressure wave, and created by a vibrating object. To and fro motion of an object is known as vibration. Sound wave can be characterized into three types:
Infrasonic Sound Waves: This sound waves have the frequency below than and is inaudible to hear for humans.
Audible Sound Waves: The sound waves having the frequency ranged between and . This is the range which is audible to Humans.
Ultrasonic Sound Waves: This sound waves have the frequency more than frequency of and is inaudible to hear.
Sound waves are a form of mechanical waves i.e., it requires a medium to propagate. The mechanism of movement of sound waves is it moves by the compression and expansion of the particles of the medium it travels through. Since sound waves always require a medium to propagate thus, it can not travel in vacuum.
Sound: A Wave
Waves are of two types i.e., electromagnetic and mechanical. Electromagnetic Waves are those waves which do not require any medium to propagate, for e.g., Light
whereas, Mechanical waves are those waves which require a medium to propagate, for e.g., Sound.
Some basic properties can be noticed, when sound waves are represented as waveforms. This waveform representation of sound is nothing but a presentation of variation of pressure in the air, which propagates as sound. There are regions of high pressure and low pressure alternatively.
Characteristics of Sound Waves
Since sound always requires a medium to travel thus it can not propagate through vacuum. Compared to the light waves, which do not require a medium to travel or propagate,sound waves are typically longitudinal waves and light waves are transverse waves is another distinction that goes outside the scope of the syllabus. But they don’t differ all that much either.
There are few characteristics which we will see are : amplitude, wavelength, frequency and timbre. Let’s see these characteristics one by one.
Amplitude
It is the amount of energy carried by a wave, to get it better, it can be understood that the wave which is having a higher amplitude, it will be having more energy, what it actually means is, the highest vertical distance up to where the wave is displaced from its mean position can be termed as amplitude.
Wavelength
As discussed above, the area covered by the sound waves is alternatively having high and low pressure, whereas high area curves are known as the peak of the graph and low area curves
are known as troughs of the graph. The distance between two consecutive crests and troughs is known as wavelength.
Frequency
It is the rate of vibration of the sound wave while propagating through the medium, to get it better, it can be understood that, the number of completed cycles in one time period. It is also known as the pitch.
Time period of a wave is known as the time taken by the wave to complete its one cycle.
The mathematical formula for the frequency is ,
Wavelength , frequency and velocity of the wave is connected by the formula:
Where,
velocity of the wave,
frequency of the wave
wavelength of the wave
Timbre
It is defined as the quality of sound through which two sounds of same frequency and amplitudes are differentiated. Thus, it can be concluded that if two sound waves generated by two different instruments, having the same frequency and amplitudes, then by definition of timbre, they will be different in terms of timbre.
Reflection of the Sound Wave
Reflection is the process of bouncing back of sound waves and this characteristic of the sound wave produces the echo. Additionally, the repeated reflections from the clouds and ground surfaces have a significant role in how thunder rolls. It follows the same principle as the light waves i.e., angle of incidence equals angle of reflection. To get the better reflected sound, the surface through which it is being reflected, it should have a larger surface area. This characteristic of the Sound is used in SONAR (Sound Navigation and Ranging), whereas the sound waves are used for navigation and ranging of the objects, mainly underwater.
Refraction of the Sound Wave
It is the process of the changing of the path of propagation of the sound wave, when the medium through which it propagates, changes. The amount of deviation from its normal path depends on the density of the changed medium. Since, in our atmosphere, there are layers of different densities, thus refraction occurs in the atmosphere. With the increase in temperature, density decreases, thus difference in temperature affects the refraction of the sound wave.
Diffraction of the Sound Wave
It is the characteristic of the sound waves by which sound waves can bend from their path if any obstacle interferes with their propagation.Light too goes under diffraction but in a very smaller magnitude. Our perception of the environment is significantly influenced by the diffraction of sound waves. While lightning strikes that are close to you sound like a sharp crack and those that are farther away sound like thunder, respectively. This is so that you only hear the deep rumbling since the deeper tones of sound waves can bend past barriers better than the acute noises. Even light waves experience diffraction, albeit to a far smaller extent.
Recommended Articles:
Change State Solid Liquid Melting Point
Changing States Of Matter And Its Types
Changing the Period Of A Pendulum
Configuration and Characteristics of a Transistor
Characteristics of EM Waves
The waves which require a medium to propagate are known as mechanical waves. One very common example of the mechanical wave is Sound Waves. Reflection of the Sound Waves Characteristics of Sound Waves FAQs
Define mechanical waves with one example.
Which characteristic of the sound is responsible for the echo of the sound?