The central force is radially oriented and its strength varies with the distance from the source. The gravitational, electrostatic, and spring forces are a few examples of core forces.
Definition
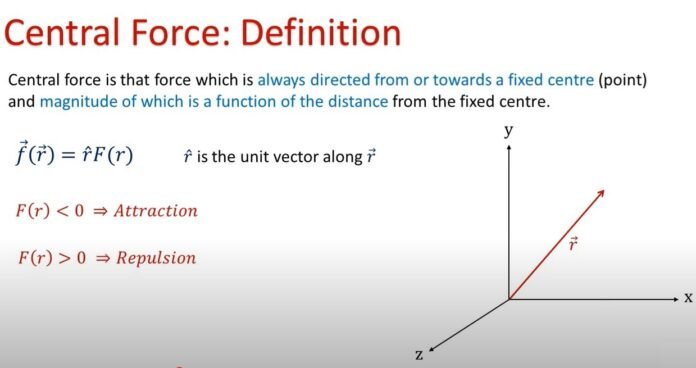
In classical mechanics, the force acting on an object that is directed along the line between the object and the origin is referred to as the central force. Only the distance between the object and the center determines the size of the central force.
The following theorems describe how central force and angular momentum are related:
Theorem 1: An object must only be subjected to the central force in order for its angular momentum to be conserved.
Theorem 2 : The second theorem states that an object must only be affected by the central force in order for it to move on a plane.
Mathematical Equation
where F stands for the conservative core force.
Vector magnitude, r,
is the separation from the force’s center.
A conservative force known as the central force is written as follows:
Where,
is a central force’s strength.
and, is the potential energy independent of time.
A particle moving uniformly in a circle under a central force should have the following centripetal force:
Where,
is the starting radius.
and, is the speed that fulfills the centripetal force equation.
Field of Central Force
The following is how fields are derived using Lagrangian:
The Central Force Motion’s Significance
Relevance of a particle’s central force motion:
The fundamental force in physics is defined by numerous natural phenomena. A few of these have been noticed in:
- The planets that orbit the sun
- Satellites orbiting the earth naturally
- When two charged particles move in opposition to one another
Properties
The following equation can be used to understand that the particle’s overall motion can follow a flat curve :
where ‘’ is the acceleration and ‘’ is the mass.
and,
is a constant vector
where remains perpendicular to the same plane for all values of are located in the same plane. As a result, the path maintains a plane.
The conserved particle’s angular momentum can be calculated using the equation above as follows:
’is constant, and so is the angular momentum.
With regard to the central force, the position vector has a constant areal velocity since it travels across the same amount of ground in the same amount of time. The radius r in the graph below covers an area of in a brief period of time. As a result, the covered area is comparable to one-half of a parallelogram with sides .
Variations in a Central Force
In a central force field, there are essentially two separate motion types present which are as follows:
Bounded Motion: In this scenario, the separation between two bodies or objects maintains a constant value and never increases beyond the predetermined limits. The planets’ orbits around the sun serve as examples of this type of motion.
Unbounded Motion: In this scenario, the initial and end distances between the two bodies or objects are infinite. The dispersion of alpha particles in the Rutherford experiment is an illustration of such a movement.
Recommended Articles:
Cbse Class 11 Physics Practical Syllabus
CBSE Physics Important Questions
Read All About Celestial Bodies
Cell Electromotive Force and Internal Resistance
Celsius And Fahrenheit Difference
What drives everything forward? The central force is the force acting on an object that is directed along the axis connecting the object to the origin. Examples of central forces are : Force of Gravitation Spring Force Electrostatic force Only the object's distance from the center affects the central force's magnitude. True. Central Force FAQs
Define central force
List a few examples of central forces.
What factor determines the central force's magnitude?
State whether it is true or incorrect that a core force causes natural satellites to orbit the Earth.