Do you know that respiration and breathing are not the same and combustion occurs in our body too? Ever heard that respiration occurs without oxygen in some organisms? Breathing generally refers to exchanging gases (intake of Oxygen and exhaling Carbon dioxide), but respiration is a whole different thing; it is the energy production from the absorbed food. After digestion and absorption, the food goes to every cell of the body, producing energy. You already know that when organic compounds are burnt in the air, it gives energy in heat. Just like that, combustion also occurs in our body; glucose acts as fuel and combustion takes place without any flame producing lots of energy in return. We will know everything about it in detail through this article and clear all of the confusion that we generally have by mistaking the actual meaning of some of the terms.
Introduction:
Cellular respiration involves the actual oxidation (breakdown) of food material inside the cell. Due to this breakdown, energy is produced. In the form of ATP, energy is stored. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is also called the cell’s energy currency. Cellular respiration usually occurs in the presence of oxygen, but in a few organisms, it occurs even without oxygen.
Definition:
Cellular respiration is a catabolic process in which food particles are oxidised within the cell to release energy.
Glucose (food)+Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP).
Steps in Respiration:
- Breathing and gaseous exchange
- Gaseous transport through the blood
- Oxidation of food inside the cell.
The first and second steps together are known as external respiration. External respiration differs in different organisms, but cellular or internal respiration is the same in all organisms. So, we shall discuss it first in this article.
In the process of oxygen, cellular respiration usually occurs. Still, in a few organisms, it occurs even in the absence of oxygen hence based on this, cellular respiration is divided into two parts, i.e. Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration.
Glycolysis:
- This is the first step in cellular respiration in all organisms.
- Inside the cytoplasm of the cell, the process of glycolysis occurs.
- In this process, one glucose (a 6-carbon sugar)molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid or pyruvate(a 3-carbon molecule ).
- Oxygen is not necessary for the procedure. The production of CO2 is also zero.
- A small amount of ATP is generated as energy during this process.
Now pyruvate molecules will undergo Aerobic or Anaerobic respiration depending on oxygen availability.
Aerobic Respiration: 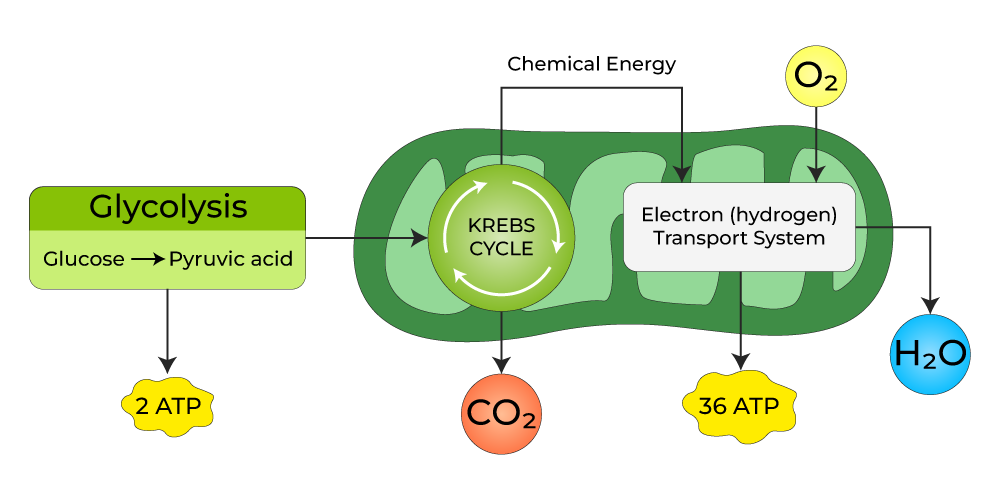
The respiration in which oxygen is used is called aerobic respiration. Higher organisms have sufficient oxygen available in their cells. The pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria in these oxygen-rich circumstances and proceed with aerobic respiration. This respiration involves Krebs’ cycle ETC.
Krebs’ cycle:
- The Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid or Tricarboxylic acid cycle.
- This step occurs mainly in mitochondria.
- Each pyruvate molecule from glycolysis is completely oxidised to produce 3 molecules of Carbon dioxide.
- In this way, 6 molecules of CO2 are produced from 2 molecules of pyruvate.
- Reduced Coenzymes are produced from this process which contains a lot of energy.
Electron Transfer Chain (ETC)
- It is the final step in producing ATP.
- This also occurs inside the mitochondria.
- In this process, the reduced coenzymes produced during Krebs’ cycle are oxidised with the oxygen’s help.
- At last, the water molecules are produced.
- During this, a lot of energy is released and stored as ATP.
Anaerobic Respiration
The respiration which occurs without oxygen is called anaerobic respiration. In organisms like yeast and some bacteria, energy is released from the food, even without oxygen. The whole anaerobic process occurs in the cytoplasm without going to mitochondria.
Fermentation:
When the pyruvate molecules formed in glycolysis are not completely oxidised. Instead, ethanol is produced as an end product, then the process is known as fermentation which is anaerobic respiration. This respiration process is less efficient, and ATP production in this is very small.
Note: Anaerobic respiration also occurs in our muscles when oxygen deficiency hits our muscles (heavy exercises).
Under these conditions, the oxygen demand becomes very high in our muscles, and to cope with that deficiency, our muscles follow anaerobic respiration until the proper oxygen supply is maintained. Energy is produced during this whole respiration. Also, Lactic acid is the end product, without any CO2 production.
Cellular Respiration: Anaerobic Respiration and Aerobic Respiration FAQs
Que 1. State two differences between aerobic and Anaerobic respiration.
Ans 1. The two main differences between them are as follows:
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen on the other hand, anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence or lack of oxygen
The end product of anaerobic respiration is ethanol or lactic acid while in the case of aerobic no such end products are produced
Que 2. How has Aerobic and anaerobic respiration evolved?
Ans 2. The evolution of anaerobic respiration occurs earlier than aerobic respiration because Earth had a much lower oxygen level when the first unicellular organisms developed, almost entirely lacking in oxygen. On the other hand, anaerobic respiration produces only 2 ATP molecules per cycle, enough for unicellular needs but inadequate for multicellular organisms.
Que 3. What is the efficiency of Aerobic respiration approximately?
Ans 3. One glucose stores 686 kcal,
One ATP stores 8.1 kcal
One glucose yields 38 ATP
Efficiency =38×8.1×100/686= 45%
Que 4. Which event is crucial in Aerobic Respiration?
Ans 4. The complete oxidation of pyruvate and the passing of the electrons removed as a part of the hydrogen atoms to molecular oxygen with the simultaneous synthesis of ATP is one of the crucial events of Aerobic respiration.
Que 5. Who discovered the Tricarboxylic acid cycle?
Ans 5. Tricarboxylic acid cycle, more commonly known as Krebs cycle, was discovered by Hans Krebs, who first discovered it in the flight muscles of pigeons.