Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot a French physicist, engineer, and mathematician, gave the first successful account of heat engines, the Carnot cycle, and laid the foundations of the second law of thermodynamics and developed the Carnot theorem which is also known as the Carnot’s rule in 1824.
What is Carnot’s Theorem
Carnot’s theorem was developed by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot a French physicist, engineer, and mathematician, and specifies the limit on the maximum efficiency that can be obtained by a heat engine.
This theorem states that all heat engines operating between the same two heat or thermal reservoirs can’t have efficiencies greater than a reversible heat engine that is operating between the same reservoirs. In other words, we can say that heat engines that are working between two heat reservoirs are less efficient than the Carnot heat engine that is operating between the same reservoirs.
Maximum efficiency
Maximum efficiency is given by:
ηmax= ηcarnot=1−TC/TH
Where, : the ratio of work done by the engine to the heat drawn out of the hot reservoir
TC: absolute temperature of the cold reservoir, and
TH: absolute temperature of the hot reservoir.
Proof of Carnot’s Theorem
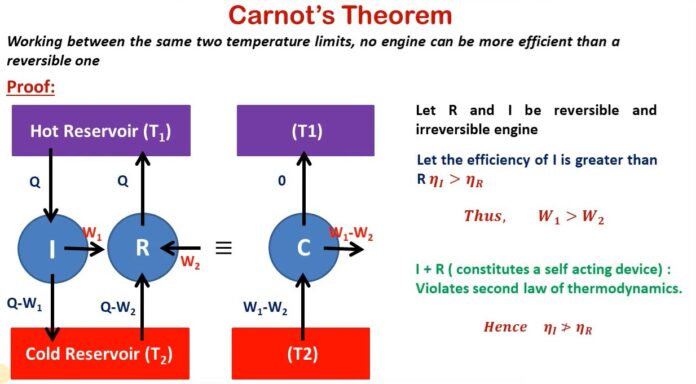
Consider two heat reservoirs at fixed temperatures i.e., at t1 and t2 (t1 > t2). A reversible engine R and irreversible engine (I) are operating between the same two thermal reservoirs as shown in the figure below
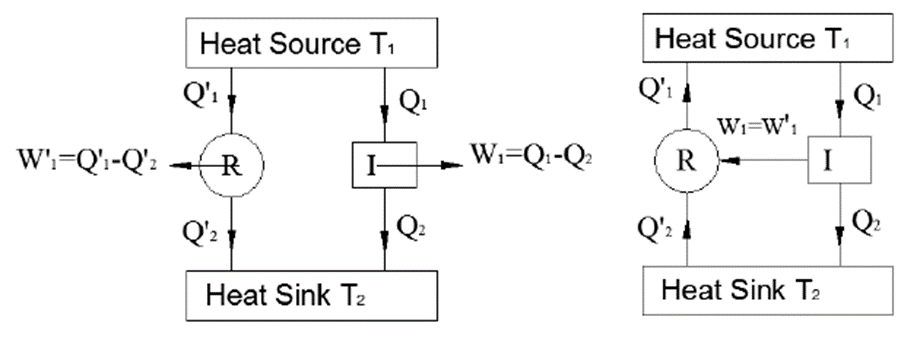
The engine ‘I’ i.e., the reversible engine takes in heat Q1 rejects heat Q2, and does the work W1,
W1 = Q1 − Q2
While the reversible engine takes in heat Q1’ rejects heat Q2’ and does the work W1’
W1’ = Q1’ − Q2’
Both the engines are so adjusted that they produce an equal amount of work i.e. W1 = W1’ Q1 − Q2= Q1’ − Q2’
Let this be the first equation
Now Assume that the efficiency of an irreversible engine I is greater than the efficiency of the reversible engine i.e., R.
ηI > ηR
W1/ Q1 > W1’/ Q1’
Q1’> Q1
Let this be the second equation
since W1 = W1’
from the first and second equations
Q2’> Q2
Let this be equation third.
It follows from equations second and third that a more efficient reversible engine will abstract less amount of heat from the source and rejects less amount of heat to the sink compared to a less efficient reversible engine provided that both the engines produce an equal amount of work.
Reversible and Irreversible Engines
Thermodynamics involves many processes and these can be carried out in two ways:
Reversible engine:
The efficiency of all reversible engines remains the same which works between two heat reservoirs that are the same.
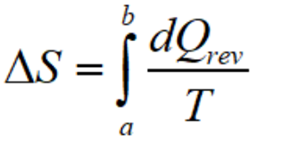
Where, T= temperature,
ΔS is a change in entropy, and

Irreversible Engine:
Irreversible engines are those engines that undergo loss of energy in due course of the operation and due to the losses in case of irreversible engines are present so naturally, their efficiency will be less as compared to reversible engines.
No irreversible engine is more efficient when compared to the Carnot engine working between the two reservoirs.
Examples:
Friction, Spontaneous Chemical reactions, and Plastic deformation.
Limitations of the Carnot’s Theorem
The Carnot rule does not apply to all sorts of devices and is applicable to examine heat engines only.
The Carnot Cycle is a theoretical concept and an ideal cycle, meaning it does not exist and cannot be created.
Applications of the Carnot’s Theorem
Refrigeration: Refrigeration is a reversible process and it is a method of removal of heat from a low temperature and dissipating it to a higher temperature.
Carnot’s theorem has applications in engines that convert thermal or heat energy to work.
Carnot Theorem also finds application in our day-to-day life like the heart pumps to produce heating, the steam turbines used in ships, refrigerators to produce cooling, combustion engines of combustion vehicles, and the reaction turbines of aircraft, etc.
Recommended Articles:
Capacitor And Capacitance: Introduction, Work, Value and Units
CAPACITOR TYPES: Classification, Types, Application, Factor, Common and Value
Capacitors in Parallel: Introduction, Applications, and Combination
Carbon Resistors: Introduction, Components, Symbol, Working and Applications
Carnot Engine: Introduction, Theorem, Cycle and Steps
The Carnot rule does not apply to all sorts of devices and is applicable to examine heat engines only. The Carnot Cycle is a theoretical concept and an ideal cycle, meaning it does not exist and cannot be created. Carnot’s rule states that all heat engines operating between the same two heat or thermal reservoirs can't have efficiencies greater than a reversible heat engine that is operating between the same reservoirs. In other words, we can say that heat engines working between two heat reservoirs are less efficient than the Carnot heat engine operating between the same reservoirs. Irreversible engines are those engines that undergo loss of energy in due course of the operation and due to the losses in case of irreversible engines are present so naturally, their efficiency will be less as compared to reversible engines. Refrigeration: Refrigeration is a reversible process and it is a method of removal of heat from a low temperature and dissipating it to a higher temperature. Carnot’s theorem finds the application in engines that alter thermal or heat energy to work. Carnot Theorem also finds application in our day-to-day life like the heart pumps to produce heating, the steam turbines used in ships, refrigerators to produce cooling, combustion engines of combustion vehicles, and the reaction turbines of aircraft, etc. Carnot’s Theorem FAQs
Enlist the limitations of Carnot’s Theorem.
State Carnot’s rule.
What is an irreversible engine?
Enlist the application of Carnot’s theorem.