Introduction
There are different theories given by scientists to explain the structure of the atom. One of the first to suggest the name “atoms” was Democritus. He proposed that all matter in the universe is made up of atomos, or atomon, which are tiny, indivisible, solid objects. Dalton put up a brand-new atomic theory (1803). Later, this was called Dalton’s atomic theory. He believes that atoms, which are incredibly minuscule particles, make up all matter. A given element’s atoms are all the same size, mass, and other characteristics. Atoms are eternal and cannot be created, generated, or destroyed. In 1911 Rutherford explain his model which is based on nucleolus. After that Niels Bohr, a Danish scientist, proposed the Bohr model in 1913 as a description of atomic structure, particularly that of hydrogen.
Bohr’s Model
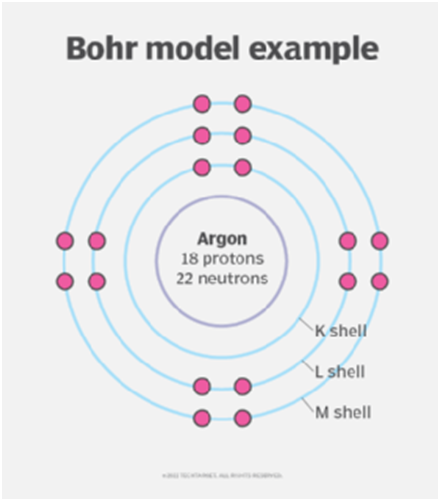
Bohr’s hypothesis modified the atomic structure model by explaining that electrons move in fixed orbitals (shells) and not anyplace else in between. He also demonstrated the fixed energy of each orbit (shell). Bohr added electrons and their many energy levels to Rutherford’s revised concept of the atom’s nucleus.
He explained that in an atom, negatively charged electrons follow a predetermined circular path known as orbits or shells as they move around the positively charged nucleus. Because each of these circular orbits has a specific energy, they are known as orbital shells. He designates the atomic orbits n=1, 2, 3, 4… as K, L, M, N… shells, and when an electron reaches the ground state, it has attained the lowest energy level. The electrons of an atom move from a lower energy level to a higher energy level by receiving the required energy, and from a higher energy level to a lower energy level by losing some amount of energy.
What is Bohr radius?
The distance between a hydrogen atom’s electron and nucleus in its ground state is represented by the Bohr radius, a physical constant (lowest energy level). The value of the constant, denoted by a0, is around 5.29177210903(80) x 10-11 meters (m).
Since it was first proposed in 1913 by Danish physicist and philosopher Niels Bohr, the Bohr radius has undergone a small adjustment. The Committee on Data of the International Science Council (CODATA), which aims to facilitate global collaboration to advance open science and enhance the accessibility and usability of data, issued the most recent official number for the Bohr radius in 2018.
CODATA value for the Bohr radius is determined by the following relation.
Where represents Bohr’s radius. The reduced Planck constant is h. The fine-structure constant’s symbol is α, the mass of an electron is me and the velocity of light in a vacuum is c.
Bohr’s radius derives from Bohr’s model
The Bohr model of the atom, which Niels Bohr proposed in 1913 to explain how an atom’s electrons behave, is where the Bohr radius originates. Bohr believed that atoms were made up of tiny, dense positive electric nuclei, around which negatively charged electrons traveled in a ringlike pattern, much like planets orbit the sun. In order to prevent an electron from striking the nucleus, the Bohr model described how it is “quantized” to its orbit.
Today, physicists believe that the Bohr model oversimplifies the atomic structure; they now believe that the electrons actually surround the nucleus in spherical probability zones known as shells. The Bohr radius is still a helpful constant, though, because it essentially reflects the smallest mean radius that a neutral atom can typically achieve.
Recommended Articles:
Black Hole: Formation, Types, and Capacity
Blind Visually Impaired Braille
Blind Visually Impaired Non Optical Low Aids Vision
Blind Visually Impaired Optical Low Vision Aids
Bohr Model of Hydrogen Atom
Bohr’s model of an atom failed to explain the effect of magnetic (Zeeman effect) and electric field (Stark effect) on the spectra of atoms. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle is also invalidated in this model. According to Rutherford's model theory, an atom has a tiny, compact, positively charged center called a nucleus, where almost all of the mass is concentrated, while light and negatively charged particles revolve around it in different orbits like planets orbit the Sun called electrons. Bohr’s atomic model describes the energy levels of orbits. The Committee on Data of the International Science Council (CODATA), aims to facilitate global collaboration to advance open science and enhance the accessibility and usability of data. 5.29177210903 x 10-11 m is the latest value of Bohr’s radius according to CODATA.What are the limitations of Bohr’s Model?
What does Rutherford's model explain about atomic structure?
Which model describes the energy levels of orbits?
Which Committee facilitates global collaboration to advance open science and enhance the accessibility and usability of data?
What is the latest value of Bohr’s radius according to CODATA?