The problem of local reality or the entanglement of particles is addressed by Bell’s theorem which is an essential concept in quantum physics. This is named after physicist John Stewart Bell. In simple words, we can say that Bell’s Theorem is a significant mathematical concept that can help in our understanding of the unusual world of quantum mechanics.
What does Bell’s Theorem mean?
According to Bell’s Theorem,
“There will be no physical theory that can be reproduced to the quantum mechanical predictions for the local hidden variables.”
The theorem is named after John Stewart Bell. Also, John Stewart Bell was a renowned physicist who made significant contributions to the study of subatomic particles and quantum mechanics. The microscopic characteristics of particles that are challenging to observe with the available microscope are known as hidden variables. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that these variables don’t exist apart from the context of observation.
Despite the conflict among well-known scientists, the normally accepted view is that hidden variables are not essential for a complete theory of quantum mechanics; John Bell was the first who disproved the need for local hidden variables in the year 1964.
Bell’s Theorem Formula
The formula. Known as Bell’s inequality, is expressed as
Where are Photon measurement variables, and is the probability of which is mathematically relevant.
What is Bell’s Inequality?
Bell’s inequality can be understood and described with the help of quantum mechanics. It’s interesting to see how electrons behave when they’re in the magnetic field. Quantum mechanics can be used to study them.
According to this theory, half of the electrons that are sent across the magnetic field are deflected to the right and the other half to the left. The right half of the electrons are once more sent across a magnetic field that is perpendicular to the first one, and after splitting into half, some of them travel upward direction and the other few go in a downward direction. This is regarded as the electron’s randomness, and Bell’s theorem is used to study it.
What is Local Realism?
To prove and explain Bell’s theorem; a concept is used known as Local realism with Alice and Bob(the consequence of random specimens) two distant observers who observed the values with detector settings as and b is respectively.
So, the expression that states local realism is like
where represents a local property of the system, is the probability distribution of the properties, and the integral is taken over all possible values of
However, some Physicists discovered the existence of quantum hypergraph states. The perfect association exists in the quantum hypergraph states. According to scientists, the hypergraph state strongly disrupts local realism. According to the research, when there are more particles in a quantum hypergraph state, local realism can be badly violated. It starts an exponential increase in strength with the number of particles.
These states have highly entangled that can only be explained by non-local correlations between the particles. According to local realism, some types of singularities that do not exist in quantum mechanics are required. The requirement is known as Bell’s inequality.
Example of Bell’s Theorem
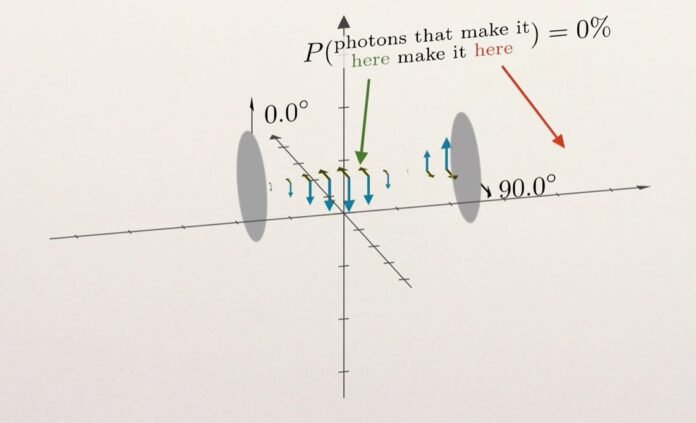
Photon Polarization is the best example of Bell’s theorem or Bell’s inequality that can be explained with the help of the polarization of light. This is the polarization of entangled photons. This consists of the study of the particles.
When two photons are entangled, and their polarizations are measured at different angles, the results will be correlated in a way that cannot be explained using classical physics.
Recommended Articles:
Basic Properties of Electrical Charge
Batteries In Series Parallel
Definition of Beats: Occur, Frequency, Formula, Effect and Applications
Beer-Lambert Law: History, Expression, Derivation and Conditions
Read All About Behaviour Of Gas Molecules
There is no physical theory that can reproduce the predictions of the quantum mechanics for the local hidden variables. Bell's theorem is important because it proved that no local hidden variables theory could explain the predictions of quantum mechanics, which are in contradiction with those of classical physics. Hence, there must be some non-local correlations among the particles. Entanglement occurs when a pair of particles, such as photons, interact physically. A Bell test, also referred to as the Bell inequality test or Bell experiment, is a practical physics experiment designed to test the relationship between Albert Einstein's theory of local realism and quantum mechanical theory. In order to state and prove Bell's theorem, the concept of local realism is formalized. Bell's Theorem FAQs
Define the Bells Theorem.
Why is Bell's theorem important?
What causes quantum entanglement?
What is Bell Experiment?
What is Local Realism?