If you want to learn about the Batteries In Series Parallel, you have come to the right place!
The purpose of this article is to understand the battery’s connections in series and parallel. You will also find much other important information that you need to know. If you do not have time to read all of the information, then read the introduction sections first.
Introduction
A battery is an electrical component that converts chemical energy to electrical energy to provide electric current in the electric circuit. It is an active element in the circuit. We must take a few factors into account when choosing and wiring the batteries. The voltage demand of our load should be one of the first considerations then we have to decide how to wire a battery or which battery to use. Since most batteries only provide 12 volts DC, the amount of power our load requires may determine how many batteries we utilize and how we wire them.
The number of batteries required
Once the voltage and capacity needs has been established, we can then calculate how many batteries to utilize and how the system should be wired. Let’s begin with voltage first. Assume we have a straightforward 12-volt setup. We would just require one 12-volt battery in this scenario. Assume we now have a 24-volt system. In this instance, two 12-volt batteries would be required to generate that 24 volts. This can be done by series connection. Further, we will discuss the series and parallel connection of batteries.
Series connection of batteries
In order to connect batteries in series, we must first connect the negative terminal of battery 1 to the DC negative bus. The negative connection on battery 2 is then connected to the positive terminal on battery 1. Then, we connect our load to the positive terminal of battery 2 by taking it. Thus, remember that while wiring in series, we are merely raising the voltage of our system. But, this has no effect on our system’s capacity or amp power rating.
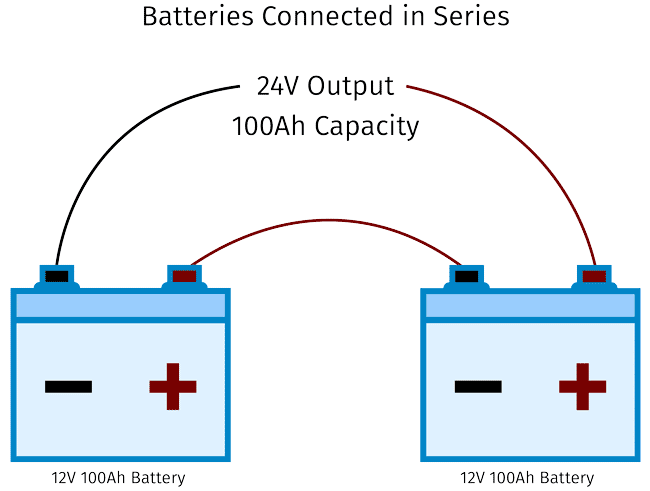
Fig – 1
Advantage and disadvantage of series connection
A higher system voltage is achieved by connecting the batteries in series, which lowers the system’s electric current. Low current suggests thinner wiring and less voltage loss throughout the system. But there are some disadvantages also like, to attain low voltages in a system of series-connected batteries, a converter is required.
So let’s explore a different illustration. If we need to keep the same voltage while increasing our capacity, or amp hour rating. Let’s say we have two 12-volt batteries for this situation. We need to connect these batteries in parallel in order to boost our capacity.
Parallel Connection of batteries
To establish a parallel connection the positive terminal of battery 1 is connected to the positive terminal of battery 2. Similarly, the negative terminal of battery 1 is connected to the negative terminal of battery 2. After that positive and negative terminals of battery 1 or battery 2 can be connected to the load as shown in the figure.
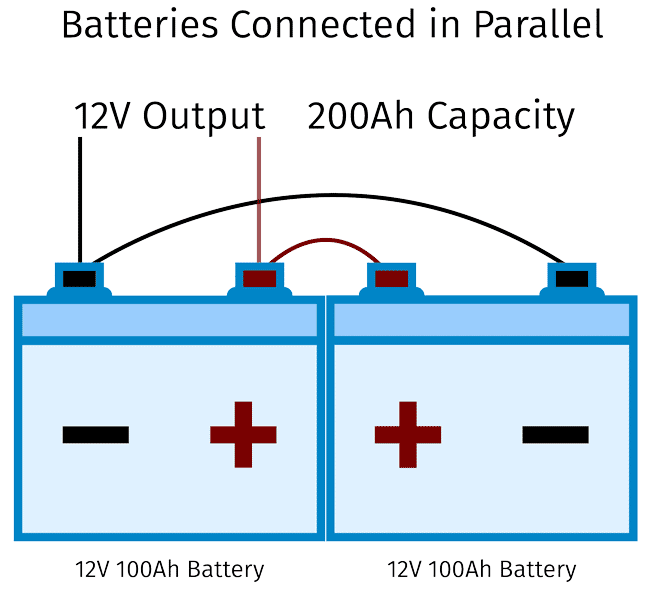
Fig- 2
Positive and negative wires are connected in parallel with each other. This boosts our system’s capacity and power rating, but it has no effect on its voltage rating.
Advantage and disadvantage of parallel connection
One of the most noticeable benefits of parallel battery connections are that power can still be generated even if one of the batteries fails to function. But there are some disadvantages also like, A parallel connection of batteries causes a greater current draw or more voltage drop and thicker wires are indicated by this.
Recommended Articles:
Bar Magnet: Uses, Similarities, Behavior and Derivation
Bar Magnet: Classification, Types, Properties, Lines, and Uses
Barometer: Definition, Working, Pressure, Types and Unit
Basic Laws of Physics: Motion, Conservation of Energy, Mass and Thermodynamics
Basic Properties of Electrical Charge
