If you want to learn about Barometers, you have come to the right place!
In this article, we will discuss the barometer and its applications. We will know how a barometer is a useful apparatus.
The purpose of this article is to understand the basic principles of barometers. You will also find much other important information that you might need to know.
Introduction
Evangelista Torricelli, an Italian physicist was the scientist who discovered the barometer in 1643. The barometer is a device that is used to measure the pressure of the atmosphere or say atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure is a variable quantity and it varies above and below the sea level. To understand the principle of the barometer we should go through with the Torricelli experiment.
Torricelli experiment
Evangelista Torricelli took a tub that is full of mercury. He also filled a glass tube with mercury and marked the cm scale on that. Then he inverted the tube into the tub which was initially filled with mercury. By doing this some quantity of the mercury drained out from the glass tube into the tub but some quantity of mercury was still inside the tube. Because of the mercury drain, there was some space (vacuum) created on the upper side of the glass tube which is known as the Torricelli vacuum. This happened because the equilibrium condition of forces by the glass tube’s mercury and the tub’s mercury was reached. Because the surface of the tub is opened to the atmosphere so atmospheric pressure is present on that. Simply we can say that in steady fluid the pressure on any point of the surface is the same
so,
This is how he measured atmospheric pressure.
Here the pressure of mercury can find out in the terms of height by the following relation.
Where,
h = height
ρ = density of the mercury (i.e. 13600 kg/m3)
g = acceleration due to gravity
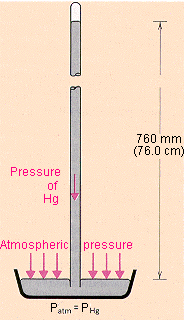
Fig-1
Working of the barometer
The mercury weight inside the glass tube needs to be balanced in relation to the atmospheric pressure for a barometer to work. If the weight of the mercury is less than the air pressure, the mercury level will rise. If the weight of the mercury is greater than the air pressure, the mercury level will also fall. The rise and fall of the mercury is measured using the inch scale inscribed onto the glass tube.
Standard atmospheric pressure
The height of the mercury column is used to gauge the atmospheric pressure. The standard mercury height obtained at sea level is 76 cm (or 0.76 m) of Hg. From this data, we can calculate the atmospheric pressure at sea level as follows.
Since 1 bar =
So
Thus we can say the value of atmospheric pressure at the sea level is
Types of Barometer
There are mainly two types of the barometer.
- Mercury barometer
- Aneroid barometer
Mercury barometer has been discussed in detail in previous headings.
Aneroid barometer is a type of mechanical barometer in which atmospheric pressure is measured with the help of the movement of mechanical parts. It measures more accurately than mercury barometers.
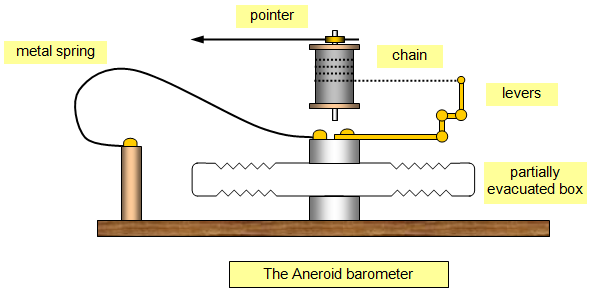
Fig-2
Its construction includes a thin sealed chamber having a partial vacuum inside. This chamber is fitted with certain levers and spring mechanisms to which a needle is connected. A graduated circular card shows the barometer reading in millibars. The whole assembly is enclosed in a metal casing. The thin metal chamber has elastic properties. When atmospheric pressure increases this chamber gets compressed. When atmospheric pressure decreases, the chamber gets expands. This inward and outward movement of the chamber acts on the needle mechanically and the needle gets the reading on the scale fitted on the top.
The accuracy of the measurement depends on the size of the sealed chamber. If the chamber is large the efficiency is higher.
Unit of barometers
- Mercury barometer shows the reading in mm of Hg which is further converted into bar as discussed earlier. It can be further converted into the british unit i.e. psi (pound per square inch) as, 1 bar = 14.5038 psi
- Aneroid Barometer shows the reading in millibars scale which can be converted into bar as, 1 bar = 1000 millibars
Recommended Articles:
Balloon Experiments in Physics
Band Theory Of Solids: Definition, levels, Structures, and Applications
Understanding the Crucial Role Banking Of Roads for Safer Highways
Bar Magnet: Uses, Similarities, Behavior and Derivation
Bar Magnet: Classification, Types, Properties, Lines, and Uses
Atmospheric pressure is very significant for the forecasting of weather. When atmospheric pressure is low it indicates wind, cloudiness, and precipitation whereas higher atmospheric pressure indicates calm weather. There is mainly two types of barometer Mercury barometer and aneroid barometer. The working of an aneroid barometer depends on a sealed chamber. When atmospheric pressure decreases, the chamber gets expanded. This inward and outward movement of the chamber acts on the needle mechanically and the needle gets the reading on the scale fitted on the top. Barometer's working principle is based on the balancing of atmospheric pressure and the pressure exerted by the mercury filled in the inverted glass tube. Barometer FAQs
What is the significance of atmospheric pressure
How many types of barometers are there?
Explain the working of an aneroid barometer in brief.
What is the working principle of a barometer?