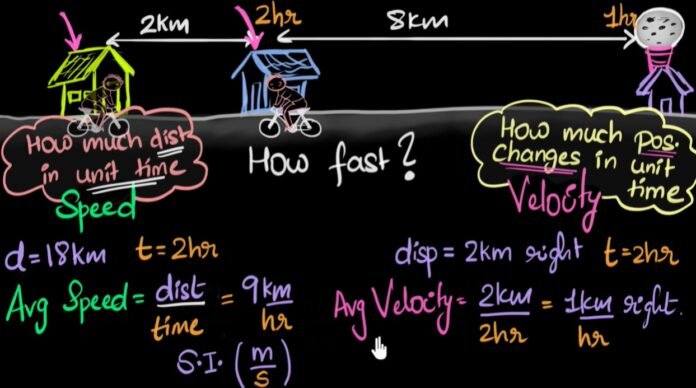
Average speed and velocity cannot be understood without knowing Speed and Velocity. In everyday life, we use the words speed and velocity interchangeably to refer to how fast a body moves, but they have different meanings in physics. Speed is the total distance traveled by a body in unit time, whereas velocity is the total displacement traveled by the body in unit time.
Speed and Velocity
Speed is the total distance traveled by a body in unit time i.e., the rate at which it covers distance, whereas velocity is the total displacement traveled by the object in unit time i.e., the rate at which a body covers displacement. Speed is a scalar quantity i.e., it has only magnitude whereas velocity is a vector quantity i.e., it has both magnitude and direction.
Speed = distance/ time and its unit are m/s and velocity = displacement/ time and its unit are the same as that of speed i.e., m/s.
Average speed and its Formula
Average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by a body by the time interval. The average speed of a moving object tells us at how much average pace a body is going to cover a certain distance. Throughout a journey, the speed of the object may vary from time to time and In that case, finding the average speed of the object becomes important to have an estimate of the rate at which the journey is completed.
For example, Radha takes 20 minutes to drive 20 miles north and then 20 miles south (to end up at the same place), and has an average speed of 40 miles divided by 20 minutes, or 2 miles per minute (120 mph).
The formula for Average speed
We can use the following formula to find the average speed of a body
S = d/t
where,
S= average speed
d= total distance traveled by the body and
t= total time taken
So, we can say that the unit of average speed is m/s.
Average Velocity and its Formula
Average velocity is defined as the change in position or displacement (∆x) of a body divided by the time intervals (∆t) in which the displacement occurs.
The formula for Average Velocity
We can use the following formula to find the average velocity of a body:
V = x/t,
Where,
x = displacement and
t= time taken.
Or
V= Xf – Xi/ tf – ti
where Xi = initial displacement,
Xf = final displacement
ti = initial time, tf = final time
As the unit of displacement is the meter and the unit of time is seconds, thus the SI unit of average velocity is m/s.
For example, the average velocity of Shyam who moves 6 m in 6 seconds and 20 m in 8 seconds along the x-axis is 7m/s.
Sol) Initial distance traveled by Shyam, xi = 7 m,
Final distance traveled by Shaym, xf = 20 m,
Initial time interval i.e., ti = 6 sec,
Final time interval i.e., tf = 8 sec
Using the formula, V= Xf – Xi/ tf – ti
Average velocity= 20-6/ 8- 6 = 14/2 = 7m/s
Here the average velocity is 7m/s.
Similarities between Average Speed and Average Velocity
The SI unit of both average speed and average velocity is the same i.e., m/s.
The formula is used to calculate the average speed and average velocity are almost the same. In average velocity, we have to mention the direction so there has to be a specific sign with respect to the displacement because both displacement and velocity are vector quantities i.e., they have magnitude as well as direction.
Differences between Average Speed and Average Velocity
The major difference is that the Average speed is a scalar quantity while the average velocity is a vector quantity. Being a scalar quantity, the final average speed is not affected by the object’s direction; contrary to that, average velocity is a vector quantity and its final outcome will depend on the direction of displacement.
While calculating average speed, the distance traveled by an object is taken into consideration, while in the case of average velocity, we have to deal with the displacement of the object.
Recommended Articles:
Atmosphere: Definition, Layers and Significance
Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure
Read all about Atomic Number Mass Number
Atomic Radii: Introduction, States and Variation
Atomic Spectra – Absorption, States, Structures, and Applications
No, Speed is a scalar quantity since it does not specify the direction of the object while velocity is a vector quantity since it takes into consideration both magnitude and direction. Distance travelled= speed * time Thus, we can say that Distance = 70×20 = 1400 kilometers. Now we have to find the time taken to travel from Goa to Punjab Time taken= Distance / speed = 1400/70 = 20 hours. So, Average Speed = Total distance /Total Time 1400 + 1400 / 20 + 20 = 2800/40 = 70 km/hr. The displacement would be zero since her initial and final position is the same. Initial distance traveled by Mohan, xi = 8 m, Final distance traveled by Mohan, xf = 18 m, Initial time interval i.e., ti = 6 sec, Final time interval i.e., tf = 8 sec Using the formula, V= Xf – Xi/ tf – ti Average velocity= 18-8/ 8- 6 = 10/2 = 5m/s Here the average velocity is 5m/s. Average Speed and Average Velocity FAQs
Are both Speed and Velocity a scalar quantity?
A bus goes from Delhi to Goa with an average speed of 70 km/hr. The journey takes 20 hours. It returns from Goa to Punjab on the same road with an average speed of 70 km/hr. What was the average speed of the bus during the roundtrip? Answer
If Radha is moving in a circular path and completes one revolution, the distance traveled will be the perimeter of the circle. What would be the displacement in this case?
Find Mohan’s average velocity, who moves 8 m in 6 seconds and 18 m in 8 seconds along the x-axis.