The weight of the air molecules above the atmosphere is what generates atmospheric pressure. The air layer presses down on the earth’s surface. Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted by the atmosphere per unit area on the surface of any object on Earth, whereas gauge pressure refers to the atmosphere surrounding the sensor. A reference point is needed to pinpoint the exact pressure being measured because the sensing device deflects when there is a change in pressure.
In this article, we will see about atmospheric pressure and gauge pressure in detail. Let’s have a look
Pressure
The force applied perpendicularly to an object’s surface divided by the surface area over which it is applied. Since the pressure is a function of the area that the force is acting on, it can rise and fall without affecting the force. If the force applied remains constant, the pressure will rise as the surface gets smaller and vice versa. In other words, as the surface shrinks, so does the pressure. This explains why our knives and nails are so razor-sharp. The force is dispersed over the full cutting edge of a knife. A sharp knife makes cutting easier since a sharp edge exerts more pressure.The force in a blunt knife is dispersed over a larger surface area of its blunt surface. Hence, in order to cut, we must exert more effort. A knife is therefore best when it is most sharp.
Different Types of Pressure
Pressure can be referred to in a number of different ways. In order to recognise and relay pressure measurements accurately, the application must be taken into account. References for pressure sensors must include:
- Gauge Pressure makes use of the atmosphere close to the sensor as a reference. A reference point is needed to pinpoint the exact pressure being measured because the sensing device deflects when there is a change in pressure.
- Absolute Pressure is used as a benchmark for the ideal vacuum. This kind of pressure reference combines the pressure of the atmosphere with the media pressure gauge.
- Comparable to the gauge or the absolute pressure, differential pressure essentially measures the difference between the two sources.
- Even though Sealed Pressure is less well-known than the first three, it nevertheless has a place in the world of pressure. Not merely a vacuum is used as the default reference point for sealed pressure.
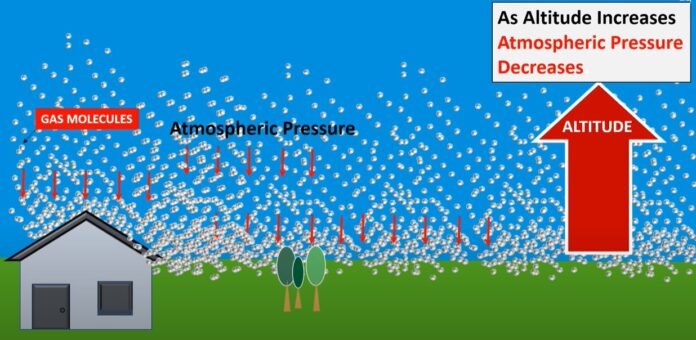
- The pressure within Earth’s atmosphere is referred to as atmospheric pressure or barometric pressure . The Earth’s mean sea-level atmospheric pressure is roughly equivalent to one atm, or one atmosphere, and is measured in the atm unit.
In this article we will be seeing atmospheric and gauge pressure in detail as we will move further in this article.
Atmospheric Pressure
The pressure within Earth’s atmosphere is referred to as atmospheric pressure or barometric pressure . The definition of the standard atmosphere is
The Earth’s mean sea-level atmospheric pressure is roughly equivalent to one atm, or one atmosphere, and is measured in the atm unit.
The planet’s gravitational pull on the gasses above its surface produces atmospheric pressure, which depends on the planet’s mass, the radius of its surface, the quantity, composition, and vertical distribution of the gasses in the atmosphere. It is altered by the planetary rotation as well as regional factors including wind speed, temperature-related changes in density, and composition changes.
Gauge Pressure
The pressure measured in relation to the outside atmospheric pressure is known as the gauge pressure. A diaphragm sensor can be used to measure gauge pressure, with one side of the diaphragm exposed to the measurement fluid and the other to atmospheric pressure at ambient temperatures.It should be noted that while measuring gauge pressure, unless the measurement point is directly exposed to ambient air pressure, the measured gauge pressure will change with changes in barometric pressure caused by changes in weather patterns. calculating pressure gauge sensor To appropriately ventilate the vacuum chamber to ambient pressure in vacuum systems and prevent contamination of the particles while opening up to the atmosphere, the pressure gauge may be measured and monitored.Moreover, semiconductor load lock applications employ this technique.
Recommended Articles:
Aristotle Fallacy : Law Of Motion
Artificial Transmutation: History, Types, Works and Applications
Asteroid and Comet Difference
Astigmatism Eye Defects: Causes, Types And Correction
Atmosphere: Definition, Layers and Significance
Pressure is defined as force applied perpendicularly to an object's surface divided by the surface area over which it is applied. Gauge, absolute and atmospheric pressures are the three types of the pressure. The pressure measured in relation to the outside atmospheric pressure is known as the gauge pressure. The pressure within Earth's atmosphere is referred to as atmospheric pressure or barometric pressure Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure FAQs
Define pressure
Enlist any three types of pressure.
Define gauge pressure
What do you mean by atmospheric pressure?