Introduction
Anemometers are devices used to measure wind speed and direction. They are commonly used in weather stations, airports, and other locations where knowledge of wind conditions is important. In this article, we will explore what anemometers are, how they work, the different types of anemometers available, and some of the practical applications of these devices.
What is an anemometer?
An anemometer is a scientific instrument that measures the speed and direction of the wind. The word “anemometer” comes from the Greek word anemos, which means wind, and metre, which means to measure. Anemometers have been used for centuries to measure wind speed. Today, they are commonly used in the fields of weather forecasting, aviation, and sailing.
How does an anemometer work?
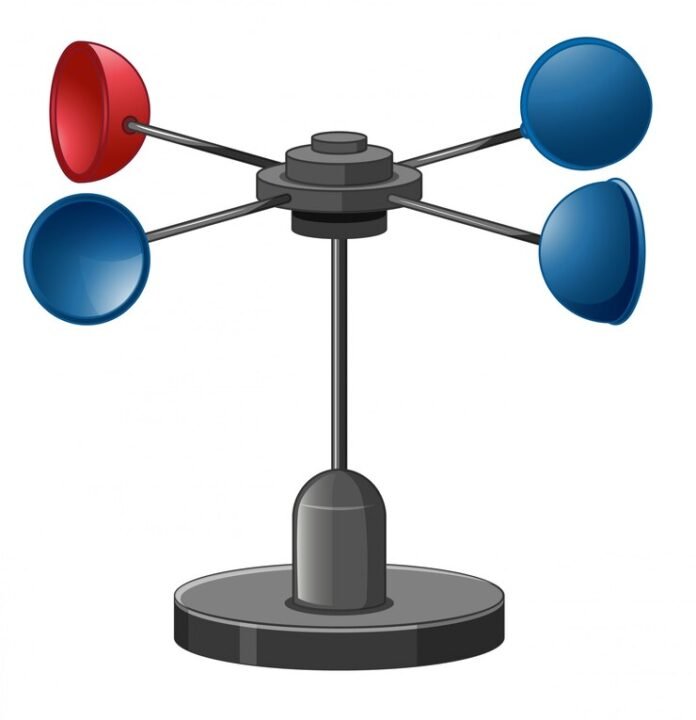
Anemometers work by measuring the pressure or flow of air. There are several types of anemometers available. However, the most common type is the cup anemometer. Cup anemometers consist of three or four cups attached to a vertical axis. When the wind blows, the cups rotate and the speed of rotation is proportional to the speed of the wind.
Another type of anemometer is the vane anemometer. Vane anemometers use a horizontal arm with a small fin or vane at one end. The vane points into the wind, and the wind’s force rotates the arm. The speed of rotation is again proportional to the wind speed.
Ultrasonic anemometers are also used to measure wind speed and direction. These anemometers use ultrasonic waves to detect the speed and direction of the wind. They are particularly useful in situations where other types of anemometers may be difficult to install, such as on tall buildings or offshore wind farms.
Different Types of Anemometers
There are several types of anemometers, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common types of anemometers are mentioned below.
- Cup anemometers: As mentioned earlier, cup anemometers are the most common type of anemometer. They are simple to install and operate and are relatively low cost. Cup anemometers are also highly accurate and can measure wind speeds of up to 200 miles per hour.
- Vane anemometers: Vane anemometers are commonly used in the aviation field. They can measure wind speeds of up to 150 miles per hour. They are also highly accurate and can measure wind direction as well as wind speed.
- Hot-wire anemometers: Hot-wire anemometers use a heated wire to measure the speed and direction of the wind. They are highly sensitive and can measure wind speeds as low as 0.01 miles per hour. However, they are also relatively expensive and require frequent calibration.
- Sonic anemometers: Sonic anemometers use sound waves to measure wind speed and direction. They are highly accurate and can measure wind speeds up to 200 miles per hour. Sonic anemometers are also relatively expensive and require frequent calibration.
Practical Applications of Anemometers
Anemometers are used in a variety of practical applications:
- Weather forecasting: Anemometers are commonly used in weather forecasting to measure wind speed and direction. This information is used to predict weather patterns and to issue weather warnings.
- Aviation: Anemometers are also used in aviation to measure wind speed and direction. This information is used by pilots to calculate takeoff and landing speeds and to plan flight paths.
- Sailing: These are also used in sailing to measure wind speed and direction. Sailors use this information to navigate and adjust sail settings.
- Wind energy: Anemometers are also used in wind energy production to measure wind speed and direction. This information is used to optimise the performance of wind turbines and to ensure that they are operating safely.
- Environmental monitoring: These are also used in environmental monitoring to measure the airflow and to study the effects of wind on the environment. This information is used to study the dispersion of pollutants, model the transport of airborne particles, and assess the risk of airborne hazards.
By providing accurate and reliable measurements of wind conditions, anemometers play a critical role in many aspects of our lives, from ensuring safe air travel to powering our homes with renewable energy.
Recommended Articles:
Anatomy of Human Ear
Amplitude Frequency Period Sound
Ampere’s Law | Definition, Application & Examples
Ampere: The Basics of Electrical Currents
Alpha Particles Mass
An anemometer is a scientific instrument used to measure wind speed and direction. There are four different types of anemometers available. They are vane anemometers, cup anemometers, hot-wire anemometers, and sonic anemometers. Anemometers are used in a variety of practical applications, such as weather forecasting, aviation, sailing, wind energy, and environmental monitoring. Anemometers work by measuring the pressure or flow of air. On the one hand, cup anemometers and vane anemometers measure the speed of rotation. On the other hand, hot-wire and sonic anemometers use more advanced techniques, such as heated wires or ultrasonic waves. Anemometer FAQs
What is an anemometer?
What are the different types of anemometers?
Why do we use anemometers?
How do anemometers work?