Introduction
Sound is a fascinating phenomenon we encounter in our daily lives. We listen to music, talk to one another, hear the sounds of nature, and experience many other auditory sensations. But have you ever wondered how sound is produced, how we hear it, or how the pitch and loudness of a sound are determined?
In this article, we will explore the basics of sound and its parameters, such as amplitude, frequency, and period. We will also answer some commonly asked questions to help you understand the sound better. Let’s dive into the world of sound and discover some of its mysteries.
Amplitude: What it is and How it Affects Sound
Amplitude refers to the maximum displacement of a sound wave from its equilibrium position. It measures the loudness of a sound and is measured in decibels (dB).
Amplitude Formula:
x = A sin (ωt + ϕ) or x = A cos (ωt + ϕ) represents the mathematical expression of a simple harmonic motion, which is a type of oscillation that occurs in many physical systems, including sound waves.
x = displacement (metres, m) of the sound wave from its equilibrium position
A = amplitude (metres, m) of the sound wave, which is the maximum displacement of the wave from its equilibrium position
ω = angular frequency (radians per second, rad/s) of the sound wave, which is related to its frequency (f) by the formula ω = 2πf or ω = 2π/t
t = time period (seconds, s)
ϕ = phase angle (radians, rad) of the sound wave, which determines the initial position of the wave at time t = 0
The sin and cos functions represent the oscillatory nature of the sound wave, which is characterised by its period and frequency.
Key Points about Amplitude:
● The greater the amplitude, the louder the sound.
● Amplitude can be measured using a sound level metre.
● The human ear can hear sounds with amplitudes ranging from 0 dB (the threshold of hearing) to 120 dB (the threshold of pain).
● Prolonged exposure to high-amplitude sounds can damage hearing.
Frequency: Understanding the Pitch of Sound
Frequency refers to the number of oscillations per second of a sound wave. It is the measure of the pitch of a sound and is measured in hertz (Hz).
Frequency Formula:
f = v/λ
f = frequency of the sound wave (hertz, Hz)
v = velocity of sound (metres per second, m/s)
λ = wavelength of the sound wave (metres, m)
Key Points about Frequency:
● The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch of the sound.
● Frequency can be measured using a frequency counter.
● The human ear can hear sounds with frequencies ranging from 20 to 20,000 Hz.
● Sounds with frequencies below 20 Hz are called infrasound, and those with frequencies above 20,000 Hz are called ultrasound.
● Some animals can hear frequencies outside of the human range of hearing.
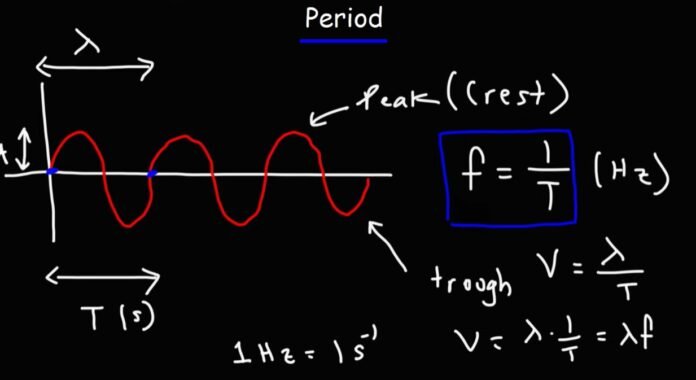
Period: Measuring Time for One Complete Cycle
The period of a sound wave refers to the time it takes for one complete cycle of the wave to occur. It is measured in seconds (s) or milliseconds (ms), depending on the frequency of the wave.
Another important concept related to the period is the wavelength. The wavelength of a sound wave is the distance between two consecutive points on the wave that is in phase (i.e., the same part of the wave cycle).
Wavelength formula: λ = v/f, where λ = wavelength, v = velocity of sound, and f = frequency. If the wavelength of a sound wave is known, we can calculate its period using the following formula: T = λ / v
Key Points about Period:
● The higher the frequency of a sound wave, the shorter its period.
● The period of a sound wave is related to its frequency and is inversely proportional to its frequency.
● T = 2π/ω = 1/f, where T is the period in seconds and f is the frequency in Hz.
Here’s a table summarising the relationships between amplitude, frequency, and period:
| Parameter | Measure | Related to | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude | Decibels | Loudness | x = A sin (ωt + ϕ)
x = A cos (ωt + ϕ) |
| Frequency | Hertz | Pitch | f = v/λ |
| Period | Seconds | Frequency | T = 1/f
T = 2π/ω T = λ / v |
Key Points about Sound Waves:
● Sound waves are characterised by their amplitude, frequency, and period. A waveform can graphically represent them.
● The speed of sound waves depends on the medium through which they travel. In the air, sound travels at a speed of approximately 343 metres per second.
Recommended Articles:
Ampere: The Basics of Electrical Currents
Alpha Particles Mass
Process, Occurrence, Measured of Alpha Decay
Air Composition Properties and Its Properties
Aerofoil: Introduction, Terminology, and Types
Amplitude refers to the maximum displacement of a sound wave from its equilibrium position. Frequency refers to the number of oscillations per second of a sound wave. Amplitude and frequency are essential parameters for producing high-quality sound in music. The amplitude of a sound wave can be used to control the loudness of individual notes in a song. The frequency of a sound wave is used to control the pitch of individual notes in a song. The range of human hearing is typically between 20 and 20,000 Hz. Amplitude can be measured using a sound level metre. The period of a sound wave can be calculated using the formula T = 1/f, where T is the period in seconds and f is the frequency in Hz. Amplitude Frequency Period Sound FAQs
What is the difference between amplitude and frequency?
How are amplitude and frequency related to sound quality?
What is the range of human hearing?
How can amplitude be measured?
What is the formula for calculating the period?