One of the five necessary elements for life to develop on Earth, the only planet where life exists, is air. Have you ever seen air, though? Although you might not have seen the air, you must have felt it in many other ways.
Have you flown a kite before? What propels the kites through the air? Not air, is it? When you hang your laundry to dry, you must have observed that it flies into the air. The tree’s leaves rattle as the wind passes across them. The book pages start to flutter as soon as you turn on the fan. There are several instances all around you when air is present.
Did you know that there are several gases in the air? What elements make up the chemical composition of air? What characteristics does air have? Do you understand the chemistry of air? What is the composition of air?
You may answer all these air-related puzzles with the help of this article.
What does Air Composition mean?
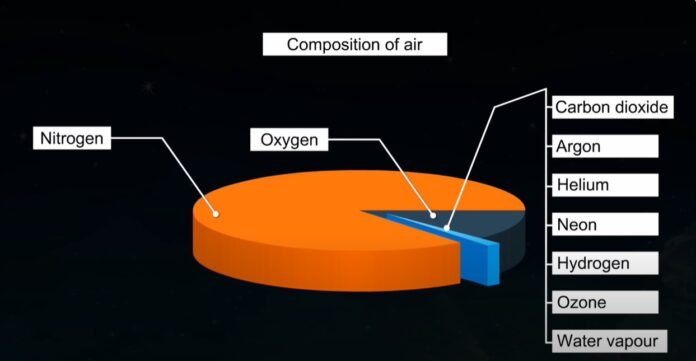
The atmosphere contains several gases that make up the composition of the air. Nitrogen and oxygen are the two significant gases in the air. While oxygen comes in second, nitrogen makes up the majority of air.
Additional minor components of air include water vapor, argon, carbon dioxide, etc. You may breathe pure air, also known as clean air, which is beneficial to you since it comprises gases that contain nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, and water vapor. In addition to the typical components, trace amounts of helium, ozone, hydrogen, and other gases are also present. The air also contains tiny dust particles in addition to these gases.
What Constitutes the Chemical Composition of Air?
The chemistry of air is very straightforward. There are many types of gases that travel from one location to another in the atmosphere referred to as air. the following are the primary gases in the atmosphere:
- Nitrogen (78%) – The atmosphere contains significant levels of nitrogen. Plants need nitrogen, however, unlike mammals, they obtain it via the roots. It is extremely stable and inert. As a result, it offers an environment that is low in reactivity and does not quickly alter chemicals when they contact with air.
- (21%) Oxygen – Each living thing on Earth needs it to survive. They won’t survive without it. Every living thing on Earth depends on plants because they provide oxygen. For living things, it is an essential chemical. Furthermore, it facilitates combustion, which works largely to our advantage.
- Gases (less than 1%), including carbon dioxide – When a living thing exhales, it emits carbon dioxide. Even Nevertheless, as manufacturers upset the natural equilibrium by releasing dangerous gases into the atmosphere, carbon dioxide levels are rising.
You can see the composition of air in the table below –
| Important Gasses | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of the Gas | Chemical Formula | In Percentage | In ppmv |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 78.084 | 780,840 |
| Oxygen | O2 | 20.946 | 209,460 |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | 0.039445〜 0.04 | 394.45 〜 400 |
| Trace Gases (out of 1%) | |||
| Helium | He | 0.00052 | 5.24 |
| Neon | Ne | 0.001818 | 18.18 |
| Argon | Ar | 0.934 | 9,340 |
| Krypton | Kr | 0.00011 | 1.14 |
| Methane | CH4 | 0.000179 | 1.79 |
| Hydrogen | H2 | 0.000055 | 0.55 |
| Xenon | Xe | 0.000009 | 0.09 |
| Ozone | O3 | 0.0-0.000007 | 0.0-0.07 |
| Carbon Monoxide | CO | 0.00001 | 0.1 |
| Nitrogen Dioxide | NO2 | 0.000002 | 0.02 |
Air and its Properties
The characteristics of air are that it is odorless and colorless.
Both color and smell are absent from the air. For all living things to breathe, air is necessary. The wind is the term used to describe air movement. Air is transparent.
Taking Up Space
A matter is also air. Consequently, it has weight and mass like other stuff (or gases). When we put an empty bottle into a water bucket, bubbles indicate that the bottle is not empty and is instead filled with air. When you tilt the bottle, water and air begin to enter the bottle. The bottle’s space gets filled with air.
Air applies pressure in all directions.
Air pressure is the pressure that air applies because of its weight. As the height rises, the air pressure falls. The balloon begins to expand as we fill it with air, which is due to air pressure.
Air Expansion
Air can expand. When heated, air begins to expand and take up space. The air gets thinner as a result of the expansion. A cold breeze, therefore, exerts more pressure than a warm wind.
Air can get compressed
When the cap of the cold beverage gets opened, the pressure of the carbon dioxide (CO2) inside the bottle gets released. This demonstrates the air compressed inside the bottle.
Temperature
The air is also impacted by temperature. Air molecules move more quickly when the temperature of the atmosphere rises.
Height’s Impact on Air
Height has an impact on the air. The air pressure decreases as altitude or height rises. Because oxygen is thinner at higher elevations or mountains, Everest climbers bring oxygen cylinders with them. They can breathe easier thanks to oxygen tanks.
These are the Properties of Air described in the table below –
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.229 kg/m⁻³ |
| Pressure | 1.013 kN/m² |
| Specific Volume | 0.814 m³/kg |
| Temperature | 15⁰C / 288 K |
| Specific heat ratio | 1.4 |
| Gas Constant | 0.286 J/g/K |
| Viscosity | 1.73 x 10⁻⁵N – s/mc |
| Molecular Weight | 28.97 grams per mole |
| Thermal Conductivity at 0 ⁰C | 24.35 W/mK |
| Thermal Conductivity at 20 ⁰C | 0.026 W/m/K |
| Gravity Acceleration | 9.8 ms⁻² |
| Specific heat capacity (CP) | 1.006 kJ/kg K |
| Specific heat capacity (CV) | 0.7171 kJ/kg K |
| Enthalpy at 0 ⁰C | 11.57 kJ/mol or 399.4 kJ/kg |
| Entropy at 0 ⁰C | 0.1100 kJ/mol K or 3.796 kJ/kg K |
| Triple Point Temperature | 59.75 K or – 213.40 ⁰C or – 352.12°F |
| Triple Point Pressure | 0.05196 atm
0.05265 bar 5265 Pa 0.7636 psi |
Things to Keep in Mind
- The atmosphere, a thin layer of air, shields the world.
- The atmosphere contains excessive levels of nitrogen and oxygen.
- Around 1% of the content of the air comprises trace gases.
- Air lacks both color and smell.
- Air molecules move more quickly as the temperature rises.
- Air pressure and height are negatively correlated with one another.
Recommended Articles:
Aerofoil: Introduction, Terminology, and Types
Advanced Sunrise And Delayed Sunset
Adiabatic Process: Definition, Process, Work, and Temperature
Adiabatic Process – Definition, Examples, and Process
Addition of Vectors and its Concept, Methods, and Examples
Meteorologists identify air masses according to where they form over Earth. There are four categories for air masses: arctic, tropical, polar, and equatorial. The answer is that anything with mass will take up space. As a result, the air takes up space. The atmosphere shelters all life on the Earth, a layer of gases that regulates temperatures over a narrow range and deflects dangerous solar radiation. The exosphere, Thermosphere, Mesosphere, Stratosphere, and Troposphere comprise the layers of the Atmosphere. Water vapor is also carried by air. How much water can exist in the air as vapor depends on the amount of water it carries and the air’s temperature? As additional vapor gets added, the air becomes unable to retain any more water, which causes rain to start falling. Air Composition Properties FAQs
What are the types of air?
Does air take up any room?
What exactly is the atmosphere?
Which of the atmosphere's several layers are they called?
What part does air plays in precipitation?