Introduction
Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset are phenomena that occur due to the tilt of the Earth’s axis and its revolution around the Sun. The Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees with respect to its orbit around the Sun. This tilt causes the seasons and affects the length of daylight and darkness throughout the year.
Advanced sunrise occurs when the Earth’s tilt causes the Sun to appear to rise earlier than it normally would. This phenomenon is most noticeable during the months leading up to the summer solstice in the northern hemisphere, which occurs around June 21st. During this time, the tilt of the Earth’s axis causes the Sun to appear to rise earlier each day, resulting in earlier sunrises. This effect is most noticeable at higher latitudes, where the difference in daylight hours between summer and winter is more pronounced.
Delayed sunset, on the other hand, occurs when the Earth’s tilt causes the Sun to appear to set later than it normally would. This phenomenon is most noticeable during the months leading up to the winter solstice in the northern hemisphere, which occurs around December 21st. During this time, the tilt of the Earth’s axis causes the Sun to appear to set later each day, resulting in later sunsets. Again, this effect is most noticeable at higher latitudes, where the difference in daylight hours between summer and winter is more pronounced.
Both advanced sunrise and delayed sunset have significant impacts on human behavior and natural systems. For example, in areas where agriculture is a major industry, the timing of sunrise and sunset can affect planting and harvesting schedules.
What Is Refraction?
Refraction is a phenomenon that occurs when a wave, such as light, sound, or water, travels from one medium to another. When the wave encounters the interface between the two mediums, it changes direction, and its speed changes. This change in direction and speed is due to a change in the wave’s wavelength and frequency as it passes through the interface.
In the case of light, refraction occurs when light waves pass through a medium with a different refractive index, such as air to water, or glass to air. The refractive index is a measure of how much a material slows down the speed of light compared to its speed in a vacuum. The larger the refractive index, the slower the speed of light in that medium.
When a beam of light enters a medium with a higher refractive index, it slows down and bends towards the normal, which is an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface of the interface. When a beam of light enters a medium with a lower refractive index, it speeds up and bends away from the normal.
The amount of bending or deviation of the light wave depends on the angle of incidence, which is the angle between the incident ray and the normal, as well as the refractive indices of the two media. The angle of refraction, which is the angle between the refracted ray and the normal, can be calculated using Snell’s law, which states that the The ratio of the two media’s refractive indices is equal to the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction.
What is Atmospheric Refraction?
Atmospheric refraction is a phenomenon that occurs when light travels through the Earth’s atmosphere, causing it to bend or change direction. This bending of light is caused by the variation in the density of the atmosphere, which causes the speed of light to vary. Atmospheric refraction is the reason why the sun and other celestial bodies appear to be higher in the sky than they actually are, particularly during sunrise and sunset.
The amount of bending that occurs depends on the angle at which the light enters the atmosphere, as well as the density of the atmosphere at different altitudes. When the light passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, it slows down and changes direction, causing the object to appear higher than it actually is. This effect is more pronounced at lower altitudes, where the density of the atmosphere is higher.
Atmospheric refraction also affects the appearance of the moon, stars, and planets. The apparent size and position of these celestial objects can be affected by the amount of atmospheric refraction that occurs. In some cases, atmospheric refraction can even cause objects that are below the horizon to be visible, a phenomenon known as a mirage.
Atmospheric refraction also plays an important role in the field of astronomy. Astronomers must take into account the effects of atmospheric refraction when observing celestial objects, particularly those near the horizon. This is because the apparent position of these objects can be significantly different from their true position, making accurate observations difficult.
Advanced Sunrise Explanation
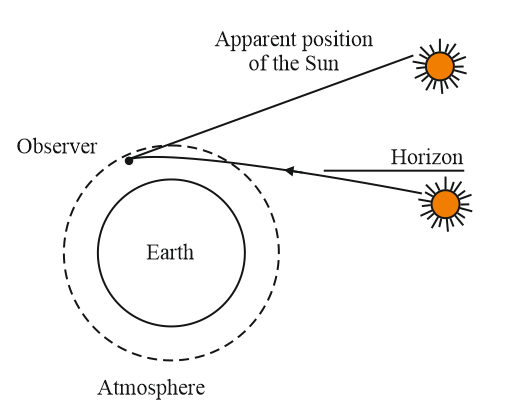
Sunrise is a natural phenomenon that occurs every day when the sun appears on the horizon, marking the beginning of a new day. This beautiful event is a result of the Earth’s rotation on its axis as it orbits around the sun.
The sun is a massive, hot, and luminous star located at the center of the solar system. It emits energy in the form of light and heat, which is vital for the existence of life on Earth. At sunrise, the sun’s light is refracted by the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the sun to appear larger and reddish in color.
As the Earth rotates, different parts of the planet are exposed to the sun’s light, creating the day and night cycle. At sunrise, the part of the Earth facing the sun begins to receive its rays of light, while the part facing away from it enters darkness.
The exact moment of sunrise depends on the geographical location and time of year. In equatorial regions, the sunrise occurs at around the same time every day, while in regions closer to the poles, the time of sunrise varies greatly between seasons.
Sunrise is not only a breathtaking sight but also has important cultural and spiritual significance in many societies. It symbolizes new beginnings, hope, and renewal, making it a powerful symbol of optimism and positivity.
Delayed Sunset Explanation
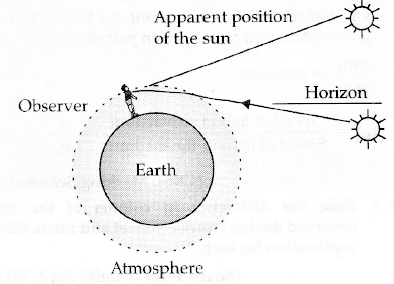
A delayed sunset refers to a situation where the sun appears to set later than expected based on its regular pattern of movement across the sky. This phenomenon is often observed in certain locations during specific times of the year.
The primary reason for a delayed sunset is the angle of the Earth’s tilt in relation to its orbit around the sun. During the summer months in the northern hemisphere, the North Pole is tilted towards the sun, resulting in longer daylight hours and shorter nights. This causes the sun to appear to move more slowly across the sky, leading to a delayed sunset.
Another factor that contributes to a delayed sunset is the Earth’s atmosphere. The atmosphere acts like a prism, refracting and scattering the sun’s light. This causes the sun to appear higher in the sky than it actually is, resulting in an apparent delay in its setting time.
Finally, the position of an observer can also affect the timing of a sunset. For example, someone standing on top of a mountain will observe the sun setting later than someone standing at sea level due to the difference in altitude and angle of the horizon.
A delayed sunset is caused by a combination of factors including the Earth’s tilt, the atmosphere, and the position of the observer. While it may seem strange or unexpected, it is a natural phenomenon that can be observed and explained through the laws of physics and astronomy.
Recommended Articles:
Adiabatic Process: Definition, Process, Work, and Temperature
Adiabatic Process – Definition, Examples, and Process
Addition of Vectors and its Concept, Methods, and Examples
Actions of Transistor Based on Construction
Acoustics | Properties, Propagation, & Scale
An advanced sunrise and delayed sunset refer to the phenomenon of the sun appearing to rise earlier and set later than expected based on the time of year and the location of an observer. This phenomenon is most commonly associated with the summer months. The Earth's tilt and its orbit around the sun cause the length of daylight to change throughout the year. During the summer months, the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, resulting in longer days and shorter nights. This tilt causes the sun to appear to rise earlier and set later than expected. Longer daylight hours can provide more time for outdoor activities, which can be beneficial for physical health and mental well-being. Additionally, increased exposure to sunlight can help regulate sleep patterns and improve mood. Some people may find it difficult to adjust to changes in their sleep patterns, particularly if they are sensitive to changes in daylight. Additionally, increased exposure to sunlight can increase the risk of skin damage and heat-related illnesses if proper precautions are not taken. No, the timing and duration of advanced sunrise and delayed sunset vary depending on an observer's location on the Earth's surface. The effect is most pronounced at higher latitudes, particularly in polar regions. Advanced Sunrise And Delayed Sunset FAQs
What is an advanced sunrise and delayed sunset?
What causes advanced sunrise and delayed sunset?
What are the benefits of advanced sunrise and delayed sunset?
Are there any negative effects of advanced sunrise and delayed sunset?
Is advanced sunrise and delayed sunset a global phenomenon?
