Introduction
A thermodynamic system in which the state of matter changes due to differences in pressure, volume, and temperature (P, V, and T) without the thermodynamic system or its environment transmitting heat or mass. This process is called the “adiabatic process“. A change in internal energy (U) represents the process in which there is no heat transmission (or heat neither increases nor decreases) during the process, which is known as an adiabatic process. It is the thermodynamic process by which neither during expansion nor compression does heat transfer from the system to its surroundings. Either the adiabatic process is reversible, or it is irreversible.
What is the Equation for the Adiabatic Process?
The adiabatic process equation is as follows:
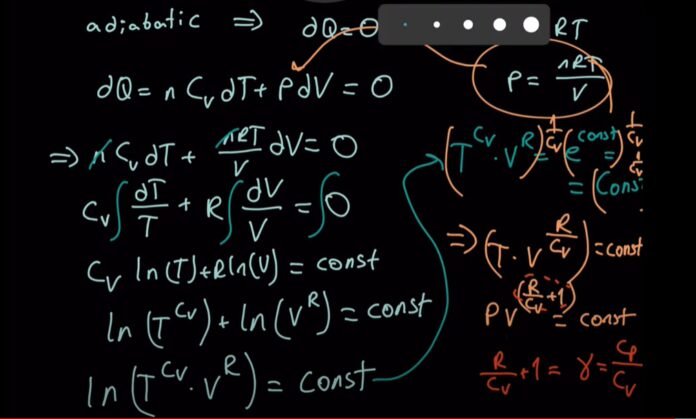
PVγ = constant,
where
P is the pressure,
V is the volume, and
γ is the adiabatic index.
The adiabatic index is calculated as the ratio of the system’s heat capacity at constant pressure (CP) to its heat capacity at constant volume (CV).
The adiabatic process prevents heat transfer. It makes the internal energy change equal to the work done.
Reversible Adiabatic Process
We additionally refer to the reversible adiabatic procedure as an isentropic process. It is a hypothetical example of a thermodynamic process that is adiabatic, has minimal friction, and is devoid of heat or matter transfer. An idealised process like this is helpful in engineering as a reference point and model for actual processes.
As there is no heat transmission in an adiabatic operation, there is also no entropy change. We, thus, consider the process to be isentropic by nature.
As there will be no heat movement,
Entropy S = dQ/dT,
So, dQ = 0, and d (S) = 0.
Q = Heat Transfer
T= Absolute Temperature
Take a Look at a Few Real-Life Instances:
• Steam expansion in steam turbines
• Air compression in compressors
PV remains constant during a reversible adiabatic process.
Irreversible Adiabatic Process
Because of frictional dissipation, there will be a change in entropy during an irreversible adiabatic process of expansion. At equilibrium, we cannot carry irreversible expansion out.
How Does Adiabatic Expansion Work?
We describe adiabatic expansion as the expansion in which there is no thermal interaction of the system with the environment. The component does work at the expenditure of its internal energy. The gas does the work of increasing the volume and lowering the temperature.
How Does Adiabatic Compression Work?
We describe adiabatic compression as the compression of the air in which the air experiences no heat addition or loss. It experiences an increase in internal energy that is similar to the external work applied to the air. As the temperature rises during compression, the air’s pressure exceeds its volume.
Adiabatic Relation Between Pressure and Temperature
We know that for an ideal gas, it gives the equation:
PV = RT (for each mole of gas).
V = RT/P… (1)
Adding equation 1’s value to the equation PVγ= K
P(RT/P)γ = G
= P (1 – γ) Tγ = G (Constant)
Adiabatic Relation Between Volume and Temperature
For each mole of gas, PV = RT.
P = RT/V,
when we put PV γ = G,
we get
RT/V * Vγ = G or T*V(γ – 1) = G/ R
= TV(γ – 1) = G (Constant)
For an ideal gas, the adiabatic relationship between V and T is described by this equation.
Examples of an Adiabatic Process
There are many examples, some of which are listed below.
1. The gas compression process produces heat. The release of air from a rubber tire would be one of the most straightforward instances.
2. Adiabatic efficiency is used to describe components like turbines, compressors, and nozzles. This defines one of the best adiabatic processes used.
3. An illustration of this is a pendulum that oscillates in a vertical plane.
4. Quantum harmonic oscillation is a type of adiabatic system.
5. The ice does not lose or gain heat when we place it in the icebox.
Recommended Articles:
Adiabatic Process – Definition, Examples, and Process
Addition of Vectors and its Concept, Methods, and Examples
Actions of Transistor Based on Construction
Acoustics | Properties, Propagation, & Scale
Principle & Working Of Accelerometer
A thermodynamic process which is adiabatic means that no heat is transferred into or out of the system. An adiabatic process for an ideal gas is a reversible process. It has a constant entropy. The expression represented the adiabatic process ΔQ=0. We define adiabatic expansion as an expansion in which there is no heat exchange between the system and its environment. The system uses its own energy to perform work. We define the process by which air is compressed adiabatically; the air experiences no heat addition or loss. It experiences an increase in internal energy that is equal to the external work applied to the air. As the temperature rises during compression, the air's pressure exceeds its volume. The adiabatic process keeps the system's heat constant. When a high-pressure gas cylinder explodes, the gas experiences an irreversible adiabatic shift. This results in a temperature drop. Adiabatic Process FAQs
What does "adiabatic process" mean?
How does adiabatic expansion work?
How does adiabatic compression work?
What property of an adiabatic process is constant?
How does the gas experience an explosion if a cylinder housing it at high pressure explodes?