We are aware that the total energy of the system is preserved in accordance with the rule of conservation of energy in a closed system, or a system that is separated from its surroundings. The law of energy conservation is observed by conservative forces.
Conservative force is a force that only affects an object’s beginning and ending positions and has no bearing on the path a body has taken.
A nonconservative force is one that considers the path taken along with the object’s initial and ultimate positions when performing its work.
With illustrative examples, we shall explore the differences between conservative and nonconservative forces in this article. Let’s have a look.
Conservative and Non Conservative Forces
In the first physics chapters in class 11, students are introduced to the ideas of displacement, force, energy, and work. There are two categories of forces in the chapter on forces: “conservative” forces and “non-conservative” forces. These two categories of forces will be discussed in this section. We already know that when an object is forced to move from one position to another, work is being done. Its movement may take a straight line or a non-straight path. So, the amount of labor done when an object follows a curved path depends on how much it covers overall. The force used for such operations is referred to as non-conservative force.
Friction, air resistance, viscosity, non-elastic material stress, water drag on a moving boat, and other such instances are a few examples of non-conservative forces.
Yet, in some other circumstances, the work completed is independent of the object’s path. It simply depends on the object’s starting and ending positions. The force used in this instance is referred to as the conservative force. The gravitational force, elastic spring restoring force, buoyancy force, and electrostatic force are a few examples of conservative forces. The mechanical energy utilized in work carried out by the employment of non-conservative forces is converted into other kinds of energy, such as heat or sound, or any other form. Because of this, dissipative forces are another name for non-conservative forces. The energy that results is less usable for carrying out tasks.
When work is done using conservative force, on the other hand, energy is stored. The potential energy of the thing is another name for this stored energy.
Work Done by a Conservative Forces
Think about the following example
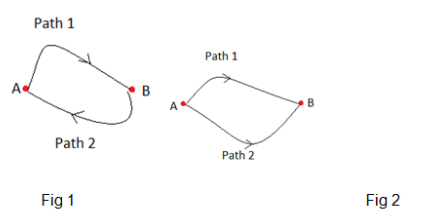
In a closed loop, the conservative force produces no work.
We also have,
Using the above two equations we get,
Figure 1 illustrates that the conservative force’s work in a closed path is zero.
According to the aforementioned equation, the amount of labor required to drive a particle along paths 1 and 2 in figure 2 will be the same. However non-conservative forces do not fall under this definition.
Difference Between Conservative and Non Conservative Forces
| Conservative Forces | Non Conservative Forces |
|---|---|
| In a closed path, | In a closed path, |
| The path has no effect on the force. | The force is affected by the path. |
| Examples of conservative forces are the gravitational force, the spring force, and the electrostatic force between two electric charges. | Non-conservative forces include friction, air resistance, and tension in the cable. |
Formula for Conservative Forces
A conservative force is one that solely depends on the initial and final positions and does not depend on the path taken to complete the task. The law of energy conservation is implemented with conservative force. The fundamental principles of energy conservation apply equally to the conservation of kinetic energy and are as follows:
Recommended Articles:
To Find The Surface Tension Of Water By Capillary Rise Method
To Find v Value For Different u Values Of Concave Mirror Find Focal Length
To study characteristics of common emitters of NPN or PNP transistors.
Relationship between the force of limiting friction and normal reaction.
Physics – To Verify The Laws Of Parallel Combination Of Resistances Using A Metre Bridge Experiment
Conservative force is a force that only affects an object's beginning and ending positions and has no bearing on the path a body has taken. Friction, air resistance, viscosity and non-elastic material stress are some examples of non-conservative forces. Gravitational Force and Electrostatic Force Conservative Forces Conservative Force FAQs
What do you mean by conservative forces?
Give some examples of non-conservative forces.
Give two examples of conservative forces.
In what type of force, work done in a closed loop equals zero?