The purpose of this article is to understand the difference between electric and magnetic fields. You will also find many other important information that you might need to know. If you do not have time to read all of the information, then I would suggest reading the introduction sections first.
Introduction
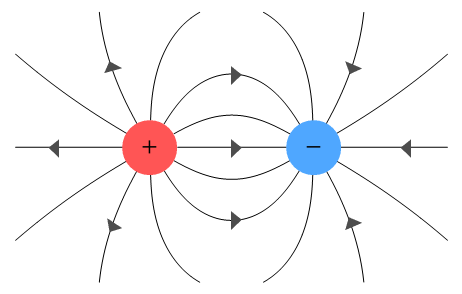
Any charged object produces an effect that can be measured as an electric field. Can we predict how other electric charges will behave when they pass close to an object with a certain amount of net charge? Michael Faraday, a British scientist, created an approach to accomplish this. According to his theory, every charged object creates an electric field that penetrates the entire universe and exerts a force on every other charged particle it comes into contact with. By applying electric forces, a field transmits energy to other charged materials. We will introduce a small positive test charge, q, and measure the force acting on it in order to investigate the impact that charge Q has on other charges. Now, when we express it as an equation, the electric field created by a charged object is the electric force between the objects and the test charge divided by the magnitude of that test charge. To find electric force F, we just have to use Coulomb’s Law.
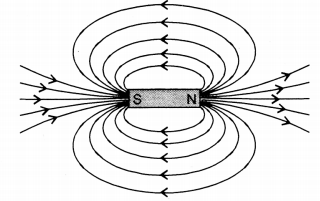
An electric charge, an electric current, and magnetic materials are all affected magnetically by a magnetic field, which is a vector field.. A magnetic field can be depicted using field lines just like an electric field, and though they will appear to begin at the north pole of the magnet and end at the South Pole, they have no true ends. They are closed loops that continue through the magnet itself.
In this article, we will discuss the Difference between electric and magnetic fields. Magnetic field can be generated from the electric current so a general question arise that how electric field is different from magnetic field?
We will know how the electric and magnetic field is important and how these parameters are different from each other. After learning this we will learn the basic formula used to calculate the electric and magnetic field.
Electric field formula
Electric field can be calculated using the electric force between two charged objects and the magnitude of charge.
i.e
From Coulomb’s Law
Where
Q and q = value of charge in Coulomb.
r = Distance between two charged particles.
= absolute permittivity
Volts per metre (V/m) is the electric field’s SI unit.
Magnetic field formula
Magnetic fields can be generated in different ways. For example, the static magnetic field can be generated using solid magnets. Whereas a current-carrying conductor can generate a magnetic field. SI unit of the magnetic field can be termed as Tesla.
The amount of magnetic field generated by a current-carrying conductor is given by the following formula:
Or,
Here,
B amount of magnetic field is generated by a wire that carries ‘I’ current at ‘r’ distance.
Where,
Now the difference between electric and magnetic fields is summarized in the following table.
Difference between electric and magnetic field
| Sl. No. | Electric Field | Magnetic Field |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Around the electric charge, an electric field is formed. | The magnetic field is generated around the magnets and moving electric charge. |
| 2 | The magnitude of the electric charge determines the force of the electric field. | The force of the Magnetic field depends on the amount of electric charge as well as its speed. |
| 3 | The movement of the electric field is normal to the magnetic field in an electromagnetic field | The movement of the magnetic field is normal to the electric field in an electromagnetic field |
| 4 | The lines of the electric field due to a charge distribution start from a point and ends at another point | Magnetic fields lines start and end at the same point. It forms a closed loop. |
| 5 | The positive charge produces electric field lines that finish at the negative charge.
|
Magnetic field lines are from the north pole to the south pole outside the magnet and south to a north pole inside the magnet.
|
| 6 | The electric field is measured in volts per metre (V/m), a SI unit. | Tesla is the magnetic field’s SI unit. |
| 7 | Electric field can influence an electric charge | Electric field cannot influence a magnetic charge |
| 8 | Electric fields is measured using the electrometer. | The magnetic field is measured using the magnetometer. Sometimes it also measures the direction of magnetic fields. |
Recommended Articles:
Difference Between Diode And Rectifier
Difference Between Discovery And Invention
Difference Between Distance And Displacement
Difference Between Earth And Neutral
Difference Between Earthing And Grounding
Magnetic field is measured by the magnetometer. Sometimes it also measures the direction of magnetic fields. The magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials is described by a magnetic field, which is a vector field. The unit of the magnetic field is Tesla. Ferromagnetism is the physical phenomenon in which certain materials are strongly attracted under a magnetic field. Difference Between Electric Field And Magnetic Field FAQs
What instrument is used to measure magnetic field?
How magnetic field can be defined?
What is the unit of the magnetic field?
What is ferromagnetism?