What is Prism?

Prism is a transparent, 3-dimensional wedge-shaped body with two flat polished refracting surfaces inclined to each other at some angle. The two plane surfaces that reflect the rays of light and the angle included between these two surfaces is called the angle of a prism or the refracting angle.
Prisms break the rays of light into their spectral colours with the polarisation of light or to reflect light. The white light that enters into the prism is a combination of various wavelengths and frequencies of colours. After passing through the prism, the frequency of each ray of light bends in a different direction.
Prism Formula
Prism Formula is based on the concept of bending of a light ray when it passes through a prism that relates the relationship between the incident angle and the angle of refraction. The prism formula is derived by using Snell’s Law which relates the refractive index with the angle of the prism and the angle of minimum deviation. It is given as:
where
is a refractive index
is the angle of the Prism
is the minimum angle of deviation
Types of Prism
Prisms are called dispersive prisms that are classified into various types based on their properties and use. Following are the types of prism:
- Dispersive Prisms: They split the light into their different constituent spectrum colours. For example, Triangular prism, Amici roof prism, Compound prism, and Grism.
- Reflective Prisms: They are used to rotate, invert, deviate, or displace the beam of light from the source. This type of prism is used in binoculars or single-lens reflex cameras to get an erect image. For example, Pentaprism, retroreflector or dove prism.
- Polarising Prisms: They are used to break the beam of light into components by variation in polarization. This is made up of materials that are known as birefringent crystalline. For example, the Nicol prism and Glan-Taylor prism.
- Beam-splitting Prisms: This type of prism breaks a beam into two or more two beams. For example, the dichroic prism and Beam splitter cube
- Deflecting Prism: They deflect the ray of white light at a fixed angle. For example, Wedge prisms.
Derivation of Prism Formula
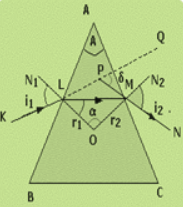
In the above figure, ABC represents the principal section of a glass prism. A ray KL incident on the face AB at the point L where is the angle of incidence. The ray then passes through the ray LM and due to refraction taking place from air to glass, the refracted bends toward the normal such that is the angle of refraction.
The refracted ray LM then incident on the face AC where is the angle of incidences. Now this time the refraction takes place from denser to rarer medium, and so is the angle of emergence.
Recommended Articles:
Derivation of Mirror Formula: Terms, Formula, Assumptions, And Derivation
Derivation of the One-Dimensional Wave Equation
Derivation Of Orbital Velocity: Introduction, Derivation, Escape, Relation And Factor
Derivation of Phase rule
Potential Energy: Introduction, Definition, Types, Unit, And Derivation
Snell's law describes that in the refraction of light between two transparent media, the relationship between the incident angle and refraction angle. The refractive index is determined from Snell's law using the minimum deviation angle through a prism. The formula is . The angle that is made by the two faces or surfaces of the prism that are refracting is known to be the angle of the prism. The angle by which the incident beam of light is refracted by passing from the prism is known to be the refractive index of the prism. It is denoted by The formula for the refractive index is, where the refractive index is the angle of the Prism is the minimum angle of deviation When a ray of white light incident on the surface of the prism and passes parallel to the base of the prism and the angle of refraction formed are equal and the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence. Derivation Of Prism Formula FAQs
What is Snell's law described in prism?
What do you mean by the term angle of the prism?
What do you mean by the term refractive index of the prism?
What is the formula for the refractive index of the prism?
What is the minimum deviation of the prism?