Curie’s Law is a fundamental principle in the study of magnetism that describes the relationship between temperature and magnetic susceptibility in certain types of materials. It is named after the famous French physicist Pierre Curie, who first discovered the law in 1895. Curie’s Law has since become a keystone of the study of magnetism and is widely used in a variety of applications, including the design of magnetic materials and devices.
Definition of Curie’s Law
Curie’s Law states that as the temperature of a material increases, its magnetic susceptibility decreases, meaning that its magnetic strength becomes weaker. Curie’s Law is particularly relevant for ferromagnetic and paramagnetic materials, which exhibit the strong magnetic properties that make them useful for various technological applications.
Curie’s Law Formula
According to the law, the magnetization of a paramagnetic substance is inversely proportional to temperature and directly proportional to the applied magnetic field. The relationship between magnetization, magnetic field, and temperature in paramagnetic materials is described by a significant magnetism principle.
The formula for Curie’s Law is given as:
Where:
M is the magnetization of the paramagnetic material
B is the magnetic field applied to the material
T is the temperature of the material
C is the Curie constant, a material-specific constant representing the magnetic susceptibility of the material at low temperatures
What Is Meant By Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic is a term used to describe materials that are weakly attracted to a magnetic field. These materials have a small magnetic moment, meaning that the individual magnetic dipoles within the material are aligned only slightly in the presence of a magnetic field. This weak magnetic alignment results in a small magnetic susceptibility, meaning that the material is only weakly magnetized in response to an applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials include elements like aluminum, platinum, and titanium, as well as certain compounds and alloys. In contrast, diamagnetic materials are weakly repelled by a magnetic field, and ferromagnetic materials exhibit strong magnetic interactions and can be strongly magnetized.
What is Magnetic Susceptibility?
Magnetic susceptibility is a measure of the magnetic properties of a material, and it describes the material’s ability to be magnetized in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic susceptibility is an important parameter in the study of magnetism, as it helps to understand how different materials interact with magnetic fields.
Magnetic susceptibility can be positive, negative, or zero. Positive magnetic susceptibility means that the material is attracted to a magnetic field and will become magnetized in response. Negative magnetic susceptibility means that the material is weakly repelled by a magnetic field. And zero magnetic susceptibility means that the material is not affected by a magnetic field and remains unmagnetized.
In summary, magnetic susceptibility is a crucial factor in determining the magnetic properties of a material and is important for understanding the behavior of magnetic materials in different conditions.
The Curie Temperature
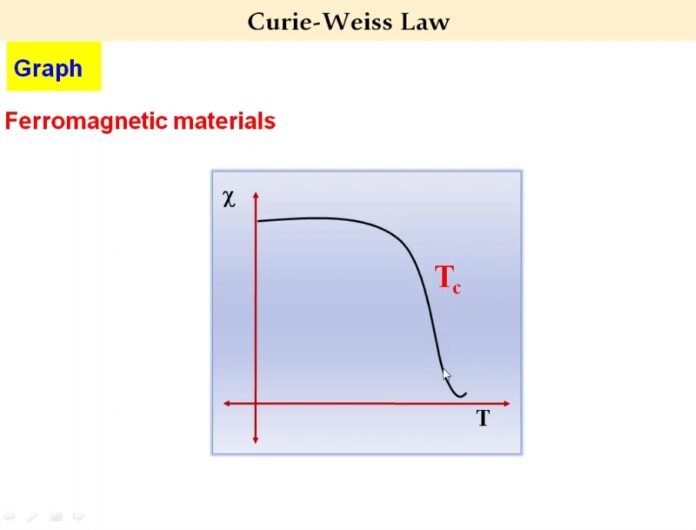
The Curie temperature () is an important parameter in the study of magnetism and is closely related to Curie’s Law. It is the temperature above which the magnetic susceptibility of a material decreases rapidly and approaches zero.This is due to the thermal energy breaking apart the magnetic interactions between the constituent particles of the material.
Also, it is the temperature at which a material transitions from a ferromagnetic or paramagnetic state to a diamagnetic state, and its magnetic properties change dramatically. It is dependent on the magnetic interactions between the individual magnetic dipoles within the material. Above the Curie temperature, the thermal energy is sufficient to overcome these interactions, causing the magnetic susceptibility to decrease.
Overall, the Curie temperature is a critical point in the study of magnetism and is used to understand the magnetic properties of a material at different temperatures. It is an important parameter for the design of magnetic materials and devices, as it helps to determine the conditions under which a material will exhibit magnetic behavior.
Limitations of Curie’s Law
- Curie’s Law is only applicable for certain types of materials, like ferromagnetic and paramagnetic materials. It does not describe the behavior of diamagnetic materials, which are weakly repelled by a magnetic field.
- Curie’s Law is only valid up to the Curie temperature (Tc), which is the temperature above which the magnetic susceptibility decreases rapidly. At temperatures below Tc, the magnetic interactions between the magnetic dipoles within the material become more complex, and Curie’s Law may not accurately describe the magnetic behavior.
- Curie’s Law assumes that the magnetic interactions between the magnetic dipoles within the material are well described by a single constant. In reality, the magnetic interactions can be more complex, and Curie’s Law may not accurately describe the magnetic behavior in all cases.
- Magnetic properties are not isolated from other properties of a material, and the magnetic behavior can be influenced by other factors such as mechanical strain, chemical composition, and microstructure. Curie’s Law does not take into account these additional factors, and its applicability may be limited in some cases.
Recommended Articles:
Coriolis Effect: Introduction, Effect, Derivation, Characteristics, And Significance
Critical Pressure: Introduction, Point, Substances, And Applications
Critical Velocity: Introduction, Formula, Number, And Calculate
Curie Constant: Introduction, Law, And Constant
Curie Weiss Law: Introduction, Limitation, Theory, And FAQ
Curie's Law is applicable to ferromagnetic and paramagnetic materials. The components of Curie's Law are magnetic susceptibility (χ), temperature (T), and the Curie constant (C). Curie's Law is useful because it helps scientists understand how temperature affects the magnetic properties of materials. This information is important in the design of magnetic devices and materials. Curie's Law states that the magnetic susceptibility of a material decreases as the temperature increases, meaning that the magnetic strength of the material becomes weaker as the temperature goes up. Curie's Law helps us understand how temperature affects the magnetic properties of materials, which is important in many applications, such as the design of magnetic devices and materials. Curie's Law FAQs
What materials does Curie's Law apply to?
What are the components of Curie's Law?
How is Curie's Law useful?
How does Curie's Law relate to temperature?
What is the significance of Curie's Law?