The physicist Pierre Curie and his wife Marie Curie made significant contributions to the study of magnetism and the discovery of the phenomena of radioactivity, and as a result, the Curie constant named after them. The Curie constant is a fundamental constant that may be found in Curie’s law, which explains how magnetic materials behave at extreme temperatures. This law helps in studying the nature of magnetic material according to temperature. As our main topic is Curie constant but we will also study Curie Law and Curie Weiss law to differentiate and study the nature of magnetic material according to temperature.
Introduction
Every matter that exists in nature tends to show magnetic properties when placed in an external magnetic field.A magnetic field like the one created by each pole of a bar magnet can affect even materials like copper and aluminum that are not typically regarded to have magnetic properties. Matter is classified as paramagnetic or diamagnetic depending on whether it is attracted to or repelled by the pole of a magnet. A few substances, most notably iron, exhibit a strong attraction to the pole of a permanent bar magnet; these substances are referred to as ferromagnetic substances. To understand the variation of magnetic property of material with varying temperature through Curie constant given by Curie Law, we must have an idea about the magnetic susceptibility of material and how its values classify the type of substances.
Magnetic susceptibility, – It is a dimensionless quantity that measures how a magnetic substance responds to an external magnetic field. It is small and positive for paramagnetic substances. It is small and negative for diamagnetic material.
Curie Law and Curie Constant
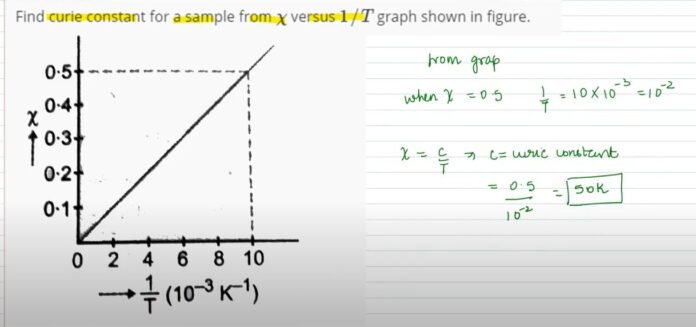
Curie’s law states that the magnetic susceptibility of a material is proportional to the inverse of the absolute temperature, T, and the Curie constant, C, of the material. In other words, the magnetic susceptibility, , is given by-
The Curie constant is a material-specific constant that characterizes the magnetic properties of a material. It is defined as the ratio of the magnetic moment per unit volume or magnetisation, to the magnetic field strength, , therefore magnetic susceptibility is given as , at high temperatures when the material is in a paramagnetic state. The Curie constant is denoted by the symbol C and has units of Joules per Kelvin per Tesla (J/K/T). A modified form of equation given by Curie Law is given by-
,
known as Curie-Weiss Law, which gives transitional properties of ferromagnets to paramagnet at high temperature. The ferromagnetic property depends on temperature. At high enough temperature, a ferromagnet becomes a paramagnet. The domain structure of ferromagnetic material disintegrates with temperature. This disappearance of magnetisation with temperature is gradual.The temperature of transition from ferromagnetic to paramagnetism is called the Curie temperature . The susceptibility above the Curie temperature are in the paramagnetic phase given by,
The Curie constant is an important parameter in the study of magnetism and magnetic materials, as it provides information about the strength of the magnetic interactions in a material. It is also useful in the design of magnetic materials for a variety of applications, including data storage, sensing, and energy conversion.
Recommended Articles:
Convex Mirror: Introduction, Works, Formation, Properties, And Uses
Coriolis Effect: Introduction, Causes, Demonstration, And Characteristics
Coriolis Effect: Introduction, Effect, Derivation, Characteristics, And Significance
Critical Pressure: Introduction, Point, Substances, And Applications
Critical Velocity: Introduction, Formula,Number, And Calculate
The unit of Curie Constant is Joules per Kelvin per Tesla (J/K/T). The relationship between magnetic susceptibility of a material and curie constant at absolute temperature is given by- Curie's law states that the magnetic susceptibility of a material is proportional to the inverse of the absolute temperature, T, and the Curie constant, C, of the material. At high temperature, Curie-Weiss Law gives transitional properties of ferromagnets to paramagnet. The ferromagnetic property depends on temperature. At high enough temperature, a ferromagnet becomes a paramagnet. The domain structure of ferromagnetic material disintegrates with temperature. This disappearance of magnetisation with temperature is gradual.The temperature of transition from ferromagnetic to paramagnetism is called the Curie temperature . The susceptibility above the Curie temperature are in the paramagnetic phase given by, Curie Constant FAQs
What is the unit of Curie Constant?
What is the relationship between magnetic susceptibility of a material and curie constant at absolute temperature?
What is Curie Law?
Explain the relationship between the ferromagnets and paramagnets in terms of temperature.