The purpose of this article is to understand the Characteristics of EM Waves. You will also find much other important information that you need to know. For a better understanding of the Characteristics of EM Waves, it is important to discuss what are electromagnetic waves exactly.
Introduction
Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of electromagnetic (EM) field waves that move over space while carrying electromagnetic radiant energy. It is made up of radio waves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet light, microwaves, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each of these waves belongs to the electromagnetic spectrum. James Clerk Maxwell discovered the symmetry and wave-like properties of the electric and magnetic fields by deriving a waveform of the equations. Maxwell came to the conclusion that light is an EM wave because the speed of EM waves is predicted by the wave equation.
Electromagnetic wave
The electromagnetic wave is generated by altered Electric and magnetic fields, which also carry energy and momentum through space. The basic equations of electrodynamics, known as Maxwell’s equations, have solutions that are electromagnetic waves. The absence of a medium allows EM waves to pass into empty space. Electromagnetic waves include sinusoidal plane waves. Although not all electromagnetic waves (EM) are sinusoidal plane waves, all EM waves can be considered as a linear superposition of sinusoidal plane waves moving in any direction.
Characteristics of electromagnetic waves
There are the following characteristics of EM waves.
Velocity
The velocity of electromagnetic waves is equal to the velocity of light in the air and vacuum. But in any medium, the velocity is less than the velocity of light.
Mathematically,
Velocity in the air and vacuum =
Velocity in any medium <
The variation in the speed depends on the density of the medium. A high-density medium has less velocity.
Produced by
Electromagnetic waves are produced by accelerated, oscillated charge and atomic excitation methods. In the atomic excitation method, EM waves are generated by giving some energy to the atoms. It leads to exciting the state of atoms by the virtue of which electrons go to the upper orbit and when they return back to the lower orbit they release some amount of energy in the form of an EM wave.
Effect of electric and magnetic field
EM waves do not have any kind of charge. It is only a form of energy that can transmit from one place to another. Thus it can not be affected by the electric and magnetic field.
Transverse nature
EM waves are of transverse nature. It means the variation of the electric and magnetic field in the EM waves are perpendicular to the direction in which it travels as shown in fig. Here the electric field is shown in the y-direction and the magnetic field is in the z-direction. Thus the direction of travel of the EM wave is along the x-direction.
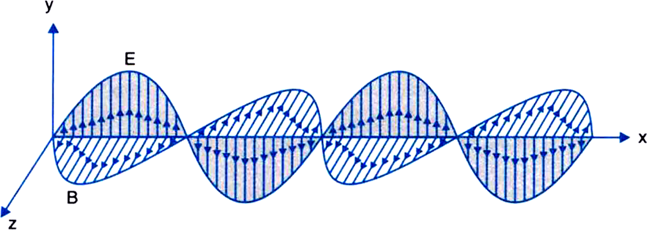
Fig – 1
The ratio of the electric and magnetic field
The ratio of the electric and magnetic field in an EM wave is always constant and is equal to the speed of light.
Representation
Electric field and magnetic field in the EM waves are changed as sign function. So EM waves are the sinusoidal wave.
Representation of electric field:
Representation of magnetic field
The value of sine is same for the electric and magnetic field because the value of frequency, wavelength and time period is same for the electric and magnetic field.
The direction of propagation
The direction of EM wave is found out by the direction of the cross product of electric and magnetic field.
Thus, the direction of the EM wave = the direction of
Energy density
Total energy density of the EM wave is equal to the energy density of the electric field and energy density of the magnetic field.
Thus, the total energy density of the EM wave, and the value of is equal to .
So, the total energy density of the EM wave, U = 2 =
Recommended Articles:
Centripetal And Centrifugal Force and Its Component
Change State Solid Liquid Melting Point
Changing States Of Matter And Its Types
Changing the Period Of A Pendulum
Configuration and Characteristics of a Transistor
EM waves are the type of which is created by the vibration of the electric and magnetic field. The direction of the EM wave is perpendicular to the direction of the electric and magnetic field direction. The energy density of an EM wave is the summation of the energy density of the electric and magnetic fields. The energy density of the electric and magnetic fields is equal thus the value of energy density for an EM wave is equal to twice the energy density of the electric or magnetic field. EM waves are of transverse nature. It means the variation of the electric and magnetic field in the EM waves is perpendicular to the direction in which it travels Characteristics of EM Waves FAQs
What are electromagnetic waves?
What is the direction of propagation of EM wave?
What is the value of the energy density of an EM wave?
Explain the transverse nature of EM waves.
