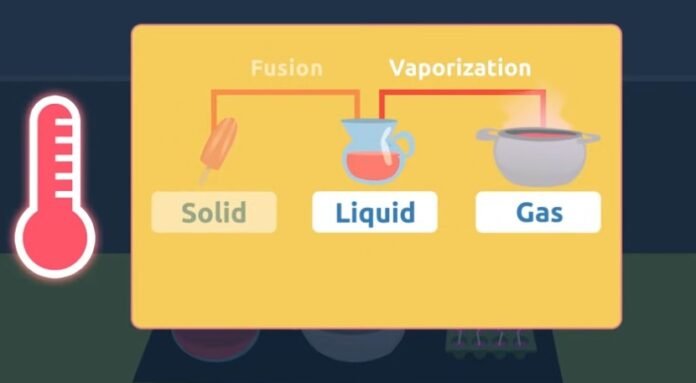
Changing states of matter occur when matter loses or absorbs energy. When a substance absorbs energy; the atoms and molecules move more rapidly and this increased kinetic energy pushes particles far enough that they change form. This energy is usually heat or thermal energy.There are generally three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. In the solid-state, the molecules or particles are closely packed to each other, and hence they have a strong intermolecular force of attraction. In the liquid state, particles are quite separated from each other and hence have less force of attraction between them. However, in gasses, particles are highly apart from each other and thus have an almost negligible force of attraction.
Whenever there is a change in the pressure or temperature of a substance, changing states of matter occur. The effect of temperature on states of matter changing is directly proportional to the increase in interaction between the molecules present in the substance. When the temperature decreases, particles get a chance to relax into a more rigid structure
Change of State: A change of state is a physical change in a matter. They are reversible changes and do not involve any changes in the chemical makeup of the matter. Common changes of the state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization. The change of state is shown in the diagram below:
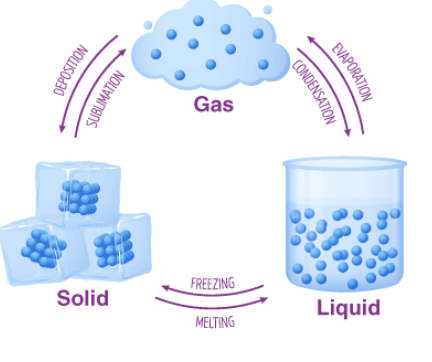
Causes for phase change: When temperature or pressure change of a system occurs, phase changes occur. When the temperature or pressure increases, the interaction between the molecules increases. Similarly, when the temperature decreases, it is easier for molecules and atoms to settle into a more rigid structure.
Five Changes of State are:
- Melting
- Freezing
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- Sublimation
The process by which a substance changes from the solid phase to the liquid phase is known as melting.
The process by which a substance changes from the liquid phase to the solid phase is known as freezing.
The process by which a substance changes from the liquid phase to the gaseous phase is known as evaporation. The process by which a substance changes from the gaseous phase to the liquid phase is known as condensation. The transition of the solid phase to the gaseous phase without passing the intermediate liquid phase is known as sublimation.
FREEZING: Heat transfer occurs between the warmer tray and the colder air in the freezer. The warm water loses heat to the cold air in the freezer. This heat transfer occurs until no energy is available for the particles to slide past each other. This forces them to remain in fixed positions, locked in place by the force of attraction between them. This way liquid water is changed into solid ice. The process of liquid water changing to solid ice is termed as freezing. The temperature at which it occurs is known as the freezing point.
MELTING: If you took out the ice cubes from the freezer and placed them in a warm room, the ice would absorb energy from the warmer air around them. This absorbed energy would facilitate them to overcome the force of attraction holding them together, enabling them to slip out of the fixed position that they held as ice. The process in which a solids change to a liquid is called melting. The melting point is the temperature at which a solids change to a liquid.
Vaporisation: If the water is hot enough, it starts to boil. Bubbles of water vapor are formed in the boiling water. This happens as particles of liquid water gain enough energy to completely overcome the force of attraction between them and change to the gaseous state. The bubbles rise through the water and escape from the pot as steam. The process in which a liquid boils and changes to a gas is called vaporization. The temperature at which a liquid boils is its boiling point.
Condensation: When you take a hot shower in a closed bathroom, the mirror is likely to fog up. Some hot water from the shower evaporates and when it comes in contact with cooler surfaces such as the mirror, it cools and loses energy. The cooler water particles no longer have the energy to overcome the forces of attraction between them. They come together and form droplets of liquid water. This process in which a gas changes to liquid is known as condensation.
Sublimation: The process in which solids directly change to gasses is known as sublimation. This occurs when solids absorb enough energy to completely overcome the forces of attraction between them. Dry ice is an example of solids that undergo sublimation.
LATENT HEAT: Latent heat is defined as the heat or energy that is absorbed or released during a phase change of a substance. It could either be from a gas to a liquid or liquid to solid and vice versa. Latent heat is related to a heat property called enthalpy.
However, an important point that we should consider regarding latent heat is that the temperature of the substance remains constant. As far as the mechanism is concerned, latent heat is the work that is needed to overcome the attractive forces that hold molecules and atoms together in a substance.
Types of Latent Heat Transfer:
Latent Heat of Fusion
Latent heat of fusion is the heat consumed or discharged when matter melts, changing stage from solid to fluid-structure at a consistent temperature.The ‘enthalpy’ of fusion is a latent heat, in light of the fact that during softening the heat energy expected to change the substance from solid to fluid at air pressure is the latent heat of fusion, as the temperature stays steady during the procedure. The latent heat of fusion is the enthalpy change of any measure of substance when it dissolves.At the point when the heat of fusion is referenced to a unit of mass, it is typically called the specific heat of fusion, while the molar heat of fusion alludes to the enthalpy change per measure of substance in moles.
The fluid state has higher inward energy than the solid-state. This implies energy must be provided to the solid so as to dissolve it and energy is discharged from a fluid when it solidifies, on the grounds that the particles in the fluid experience more fragile intermolecular force thus have higher potential energy (a sort of bond-separation energy for intermolecular powers).
At the point when fluid water is cooled, its temperature falls relentlessly until it drops just underneath the line of the point of solidification at 0 °C. The temperature at that point stays consistent at the point of solidification while the water takes shape. When the water is totally solidified, its temperature keeps on falling.
Latent Heat of Vaporization
Latent heat of vaporization is the heat consumed or discharged when matter disintegrates, changing state from fluid to gas state at a consistent temperature.The heat of vaporization of water is the most elevated known. The heat of vaporization is characterized as the measure of heat expected to transform 1 g of a fluid into a fume, without a change in the temperature of the fluid.
he enthalpy of vaporization, ΔHv, is additionally named the “latent heat of vaporization.” And ΔHv is the distinction between the enthalpy of the soaked fume and that of the immersed fluid at a similar temperature. The enthalpy of vaporization information is utilized in process estimations, for example, the plan of alleviation frameworks including unpredictable mixes. In refining, the heat of vaporization esteems are expected to discover the heat loads for the reboiler and condenser, and information on the enthalpy of vaporization is required in the structure of heat exchangers for disintegrating fluids.
Recommended Articles:
Celsius And Fahrenheit Difference
Central Force: Definition, Equation, Field, Significance, Properties and Variations
Centripetal Acceleration: Definition, Derivation, Understanding, Applications
Centripetal And Centrifugal Force and Its Component
Change State Solid Liquid Melting Point
Solids transform into liquid when they reach their melting point. Boiling point is defined as a temperature at which a pure liquid changes into a gas. The melting point is defined as the temperature at which the solid starts to melt. Sublimation is defined as the process in which the solid-state changes to a gaseous state without changing into a liquid state. When the liquid gets converted to gas at all the temperatures, it is known as evaporation. Changing States Of Matter FAQs
When solids reach their melting point, what do they become?
What is the boiling point?
What is the melting point?
What is the process in which solids directly transform into a gas?
What is evaporation?