The purpose of this article is to understand Cell Electromotive Force and Internal Resistance. You will also find much other important information that you need to know. For a better understanding of the cell’s electromotive force, it is important to go through the internal resistance of cells because these two terms are related to each other.
Introduction
A device that transforms chemical energy into electrical energy is called an electric cell. It has two terminals, one of which is positive and the other which is negative. It is a portable device which used to supply power to an electric circuit. Electromotive force is the entity that is required to maintain the potential difference. A general question is asked when we connect an electric cell to the electric circuit why is the value of the potential difference obtained less than the value of EMF? These types of general questions can be answered by you at the end of reading this article.
Battery or Cell
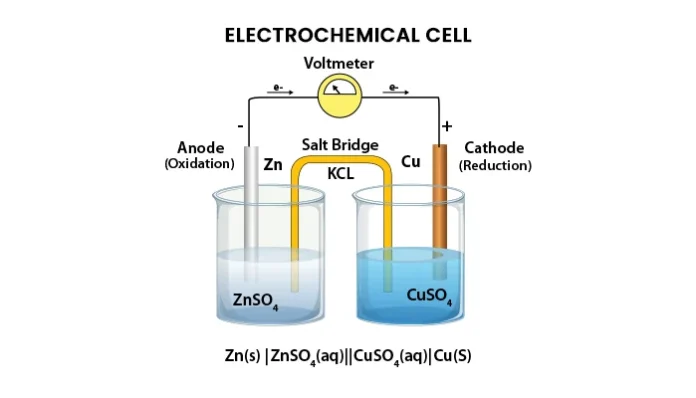
Electric cell or battery is one of the components of an electric circuit that provides electrical energy to other elements of the circuit. As we know the electric current in the circuit is flow because of the flow of electric charge or electron. The cell provides electric energy to the electric charge by virtue of which it flows in the electric circuit. Electrochemical cells are widely used cells in the electric circuit. It converts chemical energy to electrical energy. It consists of two electrodes an anode and a cathode. Which are immersed inside an electrolyte conducting solution.
Fig -1
The anode and cathode are connected with an electric circuit on which electric energy is supplied. There is an exothermic reduction and oxidation reaction inside the cell.
Electromotive Force of the cell
The electromotive force of a cell, or EMF of a cell, is the highest potential difference that exists between two electrodes of a cell when there is no current flow in the circuit (open circuit). It is sometimes referred to as the difference in net voltage between the oxidation and reduction half-reactions. it is the force that motivates to transfer of electrons. For example, in a galvanic cell, electrons move from the anode to the cathode under the influence of an external force known as the EMF. The unit of EMF is a volt. EMF of the electrochemical cell is given by
Here, the +ve sign represents the cathode, and the -ve sign represents the anode.
The internal resistance of the cell
When an electric cell is connected to the electric circuit and current is drawn from it then the value of the potential difference of the cell is less than the value of the electromotive force of the cell. This is due to the internal resistance of the cell. The current flows in the electric circuit due to the flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode and then into the electrolyte. When electrons flow from the positive to the negative terminal inside the electrolyte it offers some resistance which is called internal resistance. So, Internal resistance is the barrier that the cell’s electrolyte material presents in the way of the current’s flow.. The symbol of internal resistance is r.
Representation in the electric circuit
Internal resistance of the cell is represented in the front of the electric cell as shown in the figure.
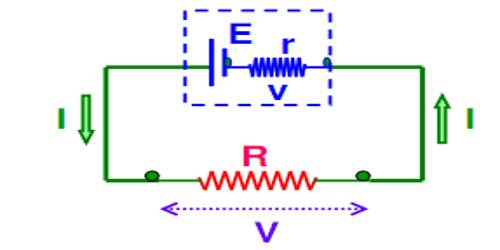
Fig- 2
Terminal voltage
The terminal voltage of the electric cell is less than the value of EMF due to the internal resistance. Terminal voltage can be expressed in the terms of internal resistance as follows.
Where E is the EMF of the cell
I is the current flowing in the circuit
r is the internal resistance of the cell
We can calculate the value of current i in the circuit shown in fig 2 as follows.
From Ohm’s law, the terminal voltage is
Where R is the external resistance of the circuit.
Thus,
Factors affecting internal resistance
The internal resistance of the cell is affected by the following factors.
- It increases with increasing the distance between electrodes.
- It decreases by increasing the area of electrodes
- The material and the concentration of the electrolyte affects internal resistance. It increases with the concentration of electrolytes.
- Internal resistance of the cell is increased with the increase of the temperature of the electrolyte.
Recommended Articles:
Casimir Effect: Observation, Practice, Applications, Space and Time
CBSE Class 11th Physics Exam Preparation Tips
Cbse Class 11 Physics Practical Syllabus
CBSE Physics Important Questions
Read All About Celestial Bodies
EMF is the maximum cell voltage whereas voltage is the actual value of potential difference which is less than the value of EMF. Internal resistance is the barrier that the cell's electrolyte material presents in the way of the current's flow. Internal resistance of the cell is affected by the positions and area of the electrode, electrolyte material, and concentration, and by the temperature of the electrolyte. Terminal voltage of the circuit is calculated by considering the internal resistance of the cell by the following formula. Cell Electromotive Force and Internal Resistance FAQs
What is the basic difference between EMF and voltage?
What is the internal resistance of the cell?
On which factors internal resistance of the cell is affected?
How terminal voltage of the circuit consisting of a cell and resistance is calculated?