If you want to learn about the Average Velocity, you have come to the right place!
The purpose of this article is to understand the Average Velocity. You will also find much other important information that you need to know. Before learning the average velocity we will learn the displacement for better understanding. At the end of this article, we will go through some examples which will help us to a better understanding of this topic.
If you do not have time to read all of the information, then read the introduction sections first.
Introduction
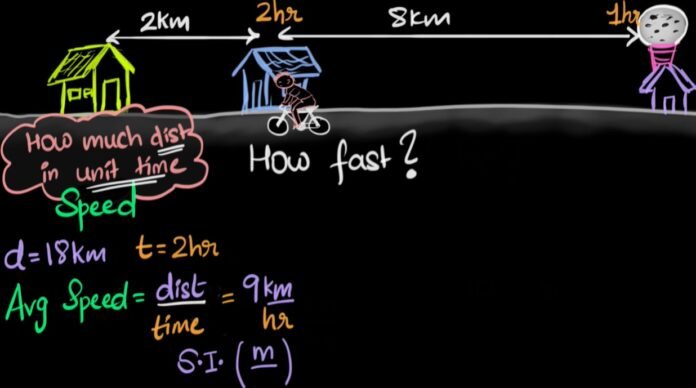
If we observe an object moving in a straight line at 10 km/hr for 2 hours then it moves with the speed of 5 km/hr for 2 hours. We can not understand the motion and final position of the object with this. Because the object can move in any direction. Let’s say it can move forward and then forward again. It can move forward and then backward. Here the speed of an object indicates how fast is object moving. The direction is not considered in the analysis. So velocity is the term that indicates the speed and direction both. Now, if we want to calculate the net speed of the object in its whole journey, we have to take an average of its velocity which is called the average velocity of the object.
Distance and displacement
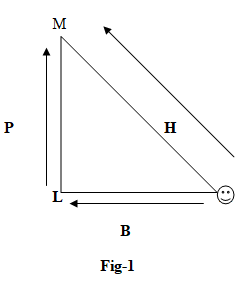
Distance is the length of the traveled path by any object and displacement is the shortest distance traveled by any object.
For example, in figure 1 if the object wants to reach from point K to M then it has two paths first one is K-L-M and the second one is K-M. If the object follows path K-L-M then the length of the total path traveled by the object is distance. But if it follows the path K-M then it is called displacement. Because path K-M is the shortest path to reach point M from K.
Definition of average velocity
Average velocity is defined as the ratio of an object’s overall displacement and its total time of motion.
- The SI unit of average velocity is m/s.
- The dimension of average velocity is .
Example
A car started its journey from Dehradun to Delhi at the velocity of 40 km/hr for one hour. After that driver increased the velocity of the car to 60 km/hr for two hours and then 80 km/hr for 1 hour and reach the destination. During this whole journey car traveled 250 km distance. Here we can observe that at different time intervals, there are different velocities. But if we talk about the average velocity we have to take the ratio of the total displacement of the car to the total time taken by it.
So, the average velocity of the car is 62.5 km/hr in this whole journey.
Here, these different velocities i.e. 40, 60, and 80 km/hr are the velocities in certain time intervals. These are called instantaneous velocities.
Recommended Articles:
Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure
Read all about Atomic Number Mass Number
Atomic Radii: Introduction, States and Variation
Atomic Spectra – Absorption, States, Structures, and Applications
Average Speed and Average Velocity
Velocity and speed are looks quite similar because both terms tell us how fast anything is moving. But the main difference between these is direction. Speed does not show direction but velocity shows the direction of the movement. Distance is the length of the traveled path by any object and displacement is the shortest distance traveled by any object. The displacement of the car is zero so the average velocity of the car should be zero in this case. Whereas the average speed should be 20/2 = 10 km/hr. S = 2 m/s t= 10 minutes= 1060 = 600 sec Speed, So, he can cover the distance of 1200 m if he walks at the average speed of 2 m/s. B 4 km A 3 km In this question Mohan started to walk from point A towards the west and covered the distance of 3 km. then walk towards the north and cover a 4 km distance and reached point B. To find average velocity first of all we have to find out the displacement (i.e. shortest distance to reach point B from point A) = = 5 km Average velocity = 2.5 So the average velocity of Mohan will be 2.5 km/hr. Average Velocity FAQs
State the difference between speed and velocity.
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
If a car is moving in a circular path having a circumference of 20 km. it starts its journey from any point A and finishes at the same point after 2 hours. What should be its average speed and average velocity?
A man can walk at a speed of 2 m/s. How much distance can he cover in 10 minutes?
Mohan walks 3 km west in 1 hour and then moves 4 km north in 1 hour. Find the total average velocity of Mohan.